Chronic HMGCR/HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor treatment contributes to dysglycemia by upregulating hepatic gluconeogenesis through autophagy induction
- PMID: 26389569
- PMCID: PMC4824590
- DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1091139
Chronic HMGCR/HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor treatment contributes to dysglycemia by upregulating hepatic gluconeogenesis through autophagy induction
Abstract
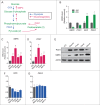
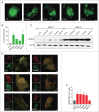
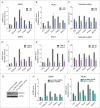
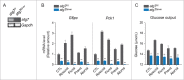
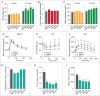
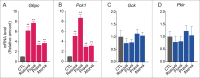
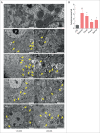
Statins (HMGCR/HMG-CoA reductase [3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase] inhibitors) are widely used to lower blood cholesterol levels but have been shown to increase the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus. However, the molecular mechanism underlying diabetogenic effects remains to be elucidated. Here we show that statins significantly increase the expression of key gluconeogenic enzymes (such as G6PC [glucose-6-phosphatase] and PCK1 (phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 1 [soluble]) in vitro and in vivo and promote hepatic glucose output. Statin treatment activates autophagic flux in HepG2 cells. Acute suppression of autophagy with lysosome inhibitors in statin treated HepG2 cells reduced gluconeogenic enzymes expression and glucose output. Importantly, the ability of statins to increase gluconeogenesis was impaired when ATG7 was deficient and BECN1 was absent, suggesting that autophagy plays a critical role in the diabetogenic effects of statins. Moreover autophagic vacuoles and gluconeogenic genes expression in the liver of diet-induced obese mice were increased by statins, ultimately leading to elevated hepatic glucose production, hyperglycemia, and insulin resistance. Together, these data demonstrate that chronic statin therapy results in insulin resistance through the activation of hepatic gluconeogenesis, which is tightly coupled to hepatic autophagy. These data further contribute to a better understanding of the diabetogenic effects of stains in the context of insulin resistance.
Keywords: HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor; autophagy; diabetes; gluconeogenesis; statin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Statin-associated incident diabetes: a literature review.Consult Pharm. 2014;29(5):317-34. doi: 10.4140/TCP.n.2014.317. Consult Pharm. 2014. PMID: 24849689 Review.
-
Berberine Attenuates Development of the Hepatic Gluconeogenesis and Lipid Metabolism Disorder in Type 2 Diabetic Mice and in Palmitate-Incubated HepG2 Cells through Suppression of the HNF-4α miR122 Pathway.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 24;11(3):e0152097. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152097. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27011261 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of propionate on mRNA expression of key genes for gluconeogenesis in liver of dairy cattle.J Dairy Sci. 2015 Dec;98(12):8698-709. doi: 10.3168/jds.2015-9590. Epub 2015 Sep 26. J Dairy Sci. 2015. PMID: 26409969
-
Fructose induces gluconeogenesis and lipogenesis through a SIRT1-dependent mechanism.J Endocrinol. 2011 Mar;208(3):273-83. doi: 10.1530/JOE-10-0190. Epub 2011 Jan 6. J Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21212096
-
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Similarities and differences.Clin Pharmacokinet. 1997 May;32(5):403-25. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199732050-00005. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1997. PMID: 9160173 Review.
Cited by
-
The Intestinal Effect of Atorvastatin: Akkermansia muciniphila and Barrier Function.Front Microbiol. 2022 Feb 2;12:797062. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.797062. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35185821 Free PMC article.
-
Undertreatment or Overtreatment With Statins: Where Are We?Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Apr 29;9:808712. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.808712. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35571155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Insights Into the Role of Autophagy in Liver Surgery in the Setting of Metabolic Syndrome and Related Diseases.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 1;9:670273. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.670273. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34141709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cholesterol and bile acid-mediated regulation of autophagy in fatty liver diseases and atherosclerosis.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2018 Jul;1863(7):726-733. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2018.04.005. Epub 2018 Apr 10. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2018. PMID: 29653253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic regulation of autophagy in hepatic metabolism.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022 Jan;12(1):33-49. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.07.021. Epub 2021 Jul 28. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022. PMID: 35127371 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sabatine MS WS, Morrow DA, McCabe CH, Canon CP High-dose atorvastatin associated with worsening glycemic control: A PROVE-IT TIMI 22 substudy. Circulation 2004; 110(Suppl III):S834.
-
- Collins R, Armitage J, Parish S, Sleigh P, Peto R, Heart Protection Study Collaborative G . MRC/BHF Heart Protection Study of cholesterol-lowering with simvastatin in 5963 people with diabetes: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2003; 361:2005-16; PMID:12814710; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12475-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sever PS, Poulter NR, Dahlof B, Wedel H, Collins R, Beevers G, Caulfield M, Kjeldsen SE, Kristinsson A, McInnes GT, et al. . Reduction in cardiovascular events with atorvastatin in 2,532 patients with type 2 diabetes: Anglo-Scandinavian Cardiac Outcomes Trial–lipid-lowering arm (ASCOT-LLA). Diabetes Care 2005; 28:1151-7; PMID:15855581; http://dx.doi.org/10.2337/diacare.28.5.1151 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kjekshus J, Apetrei E, Barrios V, Bohm M, Cleland JG, Cornel JH, Dunselman P, Fonseca C, Goudev A, Grande P, et al. . Rosuvastatin in older patients with systolic heart failure. N Engl J Med 2007; 357:2248-61; PMID:17984166; http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0706201 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ridker PM, Danielson E, Fonseca FA, Genest J, Gotto AM Jr., Kastelein JJ, Koenig W, Libby P, Lorenzatti AJ, MacFadyen JG, et al. . Rosuvastatin to prevent vascular events in men and women with elevated C-reactive protein. N Engl J Med 2008; 359:2195-207; PMID:18997196; http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0807646 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
