Activation of Relaxin Family Receptor 1 from Different Mammalian Species by Relaxin Peptide and Small-Molecule Agonist ML290
- PMID: 26347712
- PMCID: PMC4538381
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2015.00128
Activation of Relaxin Family Receptor 1 from Different Mammalian Species by Relaxin Peptide and Small-Molecule Agonist ML290
Abstract
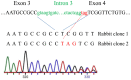
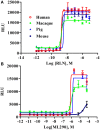
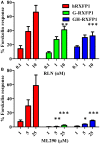
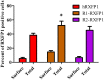
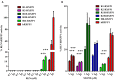
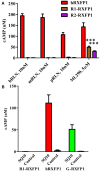
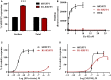
Relaxin peptide (RLN), which signals through the relaxin family peptide 1 (RXFP1) GPCR receptor, has shown therapeutic effects in an acute heart failure clinical trial. We have identified a small-molecule agonist of human RXFP1, ML290; however, it does not activate the mouse receptor. To find a suitable animal model for ML290 testing and to gain mechanistic insights into the interaction of various ligands with RXFP1, we have cloned rhesus macaque, pig, rabbit, and guinea pig RXFP1s and analyzed their activation by RLN and ML290. HEK293T cells expressing macaque or pig RXFP1 responded to relaxin and ML290 treatment as measured by an increase of cAMP production. Guinea pig RXFP1 responded to relaxin but had very low response to ML290 treatment only at highest concentrations used. The rabbit RXFP1 amino acid sequence was the most divergent, with a number of unique substitutions within the ectodomain and the seven-transmembrane domain (7TM). Two splice variants of rabbit RXFP1 derived through alternative splicing of the fourth exon were identified. In contrast to the other species, rabbit RXFP1s were activated by ML290, but not with human, pig, mouse, or rabbit RLNs. Using FLAG-tagged constructs, we have shown that both rabbit RXFP1 variants are expressed on the cell surface. No binding of human Eu-labeled RLN to rabbit RXFP1 was detected, suggesting that in this species, RXFP1 might be non-functional. We used chimeric rabbit-human and guinea pig-human constructs to identify regions important for RLN or ML290 receptor activation. Chimeras with the human ectodomain and rabbit 7TM domain were activated by RLN, whereas substitution of part of the guinea pig 7TM domain with the human sequence only partially restored ML290 activation, confirming the allosteric mode of action for the two ligands. Our data demonstrate that macaque and pig models can be used for ML290 testing.
Keywords: G protein-coupled receptor; RXFP1; receptor structure–function; relaxin; small-molecule allosteric agonist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structural Insights into the Activation of Human Relaxin Family Peptide Receptor 1 by Small-Molecule Agonists.Biochemistry. 2016 Mar 29;55(12):1772-83. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5b01195. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Biochemistry. 2016. PMID: 26866459 Free PMC article.
-
ML290 is a biased allosteric agonist at the relaxin receptor RXFP1.Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 7;7(1):2968. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-02916-5. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28592882 Free PMC article.
-
Human Relaxin Receptor Is Fully Functional in Humanized Mice and Is Activated by Small Molecule Agonist ML290.J Endocr Soc. 2017 Jun;1(6):712-725. doi: 10.1210/js.2017-00112. Epub 2017 May 8. J Endocr Soc. 2017. PMID: 28825052 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery, optimization, and biological activity of the first potent and selective small-molecule agonist series of human relaxin receptor 1 (RXFP1).2012 Mar 10 [updated 2013 May 8]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010–. 2012 Mar 10 [updated 2013 May 8]. In: Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2010–. PMID: 23905199 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Synthetic non-peptide low molecular weight agonists of the relaxin receptor 1.Br J Pharmacol. 2017 May;174(10):977-989. doi: 10.1111/bph.13656. Epub 2016 Nov 30. Br J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27771940 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural Insights into the Activation of Human Relaxin Family Peptide Receptor 1 by Small-Molecule Agonists.Biochemistry. 2016 Mar 29;55(12):1772-83. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5b01195. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Biochemistry. 2016. PMID: 26866459 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-apoptotic and Matrix Remodeling Actions of a Small Molecule Agonist of the Human Relaxin Receptor, ML290 in Mice With Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction.Front Physiol. 2021 Jul 7;12:650769. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.650769. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34305630 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing relaxin receptor expression and exploring relaxin's effect on tissue remodeling/fibrosis in the human bladder.BMC Urol. 2020 Apr 22;20(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12894-020-00607-4. BMC Urol. 2020. PMID: 32321501 Free PMC article.
-
Relaxin-like peptides in male reproduction - a human perspective.Br J Pharmacol. 2017 May;174(10):990-1001. doi: 10.1111/bph.13689. Epub 2017 Feb 27. Br J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27933606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-Component Mechanism of H2 Relaxin Binding to RXFP1 through NanoBRET Kinetic Analysis.iScience. 2019 Jan 25;11:93-113. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2018.12.004. Epub 2018 Dec 10. iScience. 2019. PMID: 30594862 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Halls ML, Bathgate RA, Sutton SW, Dschietzig TB, Summers RJ. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. XCV. Recent advances in the understanding of the pharmacology and biological roles of relaxin family peptide receptors 1-4, the receptors for relaxin family peptides. Pharmacol Rev (2015) 67:389–440.10.1124/pr.114.009472 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

