A novel IL-17 signaling pathway controlling keratinocyte proliferation and tumorigenesis via the TRAF4-ERK5 axis
- PMID: 26347473
- PMCID: PMC4577838
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20150204
A novel IL-17 signaling pathway controlling keratinocyte proliferation and tumorigenesis via the TRAF4-ERK5 axis
Abstract
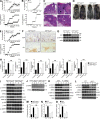
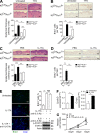
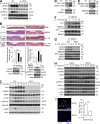
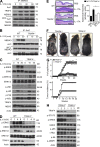
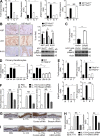
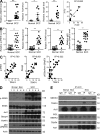
Although IL-17 is emerging as an important cytokine in cancer promotion and progression, the underlining molecular mechanism remains unclear. Previous studies suggest that IL-17 (IL-17A) sustains a chronic inflammatory microenvironment that favors tumor formation. Here we report a novel IL-17-mediated cascade via the IL-17R-Act1-TRAF4-MEKK3-ERK5 positive circuit that directly stimulates keratinocyte proliferation and tumor formation. Although this axis dictates the expression of target genes Steap4 (a metalloreductase for cell metabolism and proliferation) and p63 (a transcription factor for epidermal stem cell proliferation), Steap4 is required for the IL-17-induced sustained expansion of p63(+) basal cells in the epidermis. P63 (a positive transcription factor for the Traf4 promoter) induces TRAF4 expression in keratinocytes. Thus, IL-17-induced Steap4-p63 expression forms a positive feedback loop through p63-mediated TRAF4 expression, driving IL-17-dependent sustained activation of the TRAF4-ERK5 axis for keratinocyte proliferation and tumor formation.
© 2015 Wu et al.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Overexpression of TRAF4 promotes lung cancer growth and EGFR-dependent phosphorylation of ERK5.FEBS Open Bio. 2022 Oct;12(10):1747-1760. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13458. Epub 2022 Aug 17. FEBS Open Bio. 2022. PMID: 35748027 Free PMC article.
-
IL-17R-EGFR axis links wound healing to tumorigenesis in Lrig1+ stem cells.J Exp Med. 2019 Jan 7;216(1):195-214. doi: 10.1084/jem.20171849. Epub 2018 Dec 21. J Exp Med. 2019. PMID: 30578323 Free PMC article.
-
YAP promotes myogenic differentiation via the MEK5-ERK5 pathway.FASEB J. 2017 Jul;31(7):2963-2972. doi: 10.1096/fj.201601090R. Epub 2017 Mar 29. FASEB J. 2017. PMID: 28356344
-
Dynamic life of a skin keratinocyte: an intimate tryst with the master regulator p63.Indian J Exp Biol. 2011 Oct;49(10):721-31. Indian J Exp Biol. 2011. PMID: 22013738 Review.
-
The Emerging Role of the IL-17B/IL-17RB Pathway in Cancer.Front Immunol. 2020 Apr 21;11:718. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00718. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32373132 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association study indicates combined effect of interleukin-10 and angiotensin-converting enzyme in basal cell carcinoma development.Arch Dermatol Res. 2021 Jul;313(5):373-380. doi: 10.1007/s00403-020-02113-x. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Arch Dermatol Res. 2021. PMID: 32772162
-
Biology of Interleukin-17 and Its Pathophysiological Significance in Sepsis.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 28;11:1558. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01558. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32849528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loss of the Epigenetic Mark 5-hmC in Psoriasis: Implications for Epidermal Stem Cell Dysregulation.J Invest Dermatol. 2020 Jun;140(6):1266-1275.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2019.10.016. Epub 2019 Dec 11. J Invest Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 31837302 Free PMC article.
-
A novel immune-related prognostic signature based on Chemoradiotherapy sensitivity predicts long-term survival in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.PeerJ. 2023 Aug 18;11:e15839. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15839. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37609436 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stromal cell-secreted CCL2 promotes antibacterial defense mechanisms through increased antimicrobial peptide expression in keratinocytes.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2021 Dec;10(12):1666-1679. doi: 10.1002/sctm.21-0058. Epub 2021 Sep 16. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34528765 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bulek K., Liu C., Swaidani S., Wang L., Page R.C., Gulen M.F., Herjan T., Abbadi A., Qian W., Sun D., et al. . 2011. The inducible kinase IKKi is required for IL-17-dependent signaling associated with neutrophilia and pulmonary inflammation. Nat. Immunol. 12:844–852. 10.1038/ni.2080 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS071996/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01NS071996/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI089474/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- SC1 GM111172/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI 89474-1/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 10-0134/AICR_/Worldwide Cancer Research/United Kingdom
- T32GM007250/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL103453/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA062220/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007250/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 1P01 HL103453/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01CA062220-16A1/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

