Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Exosomes Suppress Hepatocellular Carcinoma Growth in a Rat Model: Apparent Diffusion Coefficient, Natural Killer T-Cell Responses, and Histopathological Features
- PMID: 26345219
- PMCID: PMC4545422
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/853506
Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Exosomes Suppress Hepatocellular Carcinoma Growth in a Rat Model: Apparent Diffusion Coefficient, Natural Killer T-Cell Responses, and Histopathological Features
Abstract
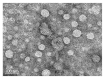
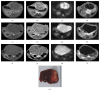
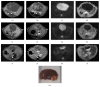
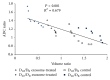
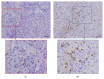
We sought to evaluate the effects of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADMSCs) exosomes on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in rats using apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), natural killer T-cell (NKT-cell) responses, and histopathological features. ADMSC-derived exosomes appeared as nanoparticles (30-90 nm) on electron microscopy and were positive for CD63, tumor susceptibility gene-101, and β-catenin on western blotting. The control (n = 8) and exosome-treated (n = 8) rats with N1S1-induced HCC underwent baseline and posttreatment day 10 and day 20 magnetic resonance imaging and measurement of ADC. Magnetic resonance imaging showed rapidly enlarged HCCs with low ADCs in the controls. The exosome-treated rats showed partial but nonsignificant tumor reduction, and significant ADC and ADC ratio increases on day 10. On day 20, the exosome-treated rats harbored significantly smaller tumors and volume ratios, higher ADC and ADC ratios, more circulating and intratumoral NKT-cells, and low-grade HCC (P < 0.05 for all comparisons) compared to the controls. The ADC and volume ratios exhibited significant inverse correlations (P < 0.001, R (2) = 0.679). ADMSC-derived exosomes promoted NKT-cell antitumor responses in rats, thereby facilitating HCC suppression, early ADC increase, and low-grade tumor differentiation. ADC may be an early biomarker of treatment response.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Apparent Diffusion Coefficient is a Useful Biomarker for Monitoring Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy of Renal Ischemic-Reperfusion Injury.Mol Imaging Biol. 2018 Oct;20(5):750-760. doi: 10.1007/s11307-018-1184-0. Mol Imaging Biol. 2018. PMID: 29549575
-
Apparent diffusion coefficient of hepatocellular carcinoma on diffusion-weighted imaging: Histopathologic tumor grade versus arterial vascularity during dynamic magnetic resonance imaging.PLoS One. 2018 May 11;13(5):e0197070. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0197070. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29750794 Free PMC article.
-
Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for predicting histological grade of hepatocellular carcinoma: Comparison with conventional diffusion-weighted imaging.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Feb 28;24(8):929-940. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i8.929. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29491686 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous administration of xenogenic adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADMSC) and ADMSC-derived exosomes markedly reduced brain infarct volume and preserved neurological function in rat after acute ischemic stroke.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 15;7(46):74537-74556. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12902. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27793019 Free PMC article.
-
The role of extracellular vesicles in mediating progression, metastasis and potential treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 10;8(2):3683-3695. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12465. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27713136 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dual impacts of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on cancer cells: unravelling complex interactions.J Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Dec;17(4):1229-1247. doi: 10.1007/s12079-023-00794-3. Epub 2023 Nov 16. J Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37973719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Hepatobiliary Malignancies.Front Immunol. 2018 Oct 12;9:2270. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02270. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30369925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes alleviate overwhelming systemic inflammatory reaction and organ damage and improve outcome in rat sepsis syndrome.Am J Transl Res. 2018 Apr 15;10(4):1053-1070. eCollection 2018. Am J Transl Res. 2018. PMID: 29736200 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: From Bench to Bedside.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 20;20(6):1406. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061406. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30897788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunomodulatory Mechanisms of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Potential Clinical Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 2;23(17):10023. doi: 10.3390/ijms231710023. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077421 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

