Improved retroviral vectors for gene transfer and expression
- PMID: 2631796
- PMCID: PMC1360503
Improved retroviral vectors for gene transfer and expression
Abstract
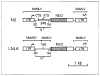
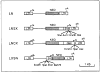
We describe a set of murine retrovirus-based vectors that include unique cloning sites for insertion of cDNAs such that the cDNA can be driven by either the retroviral long terminal repeat, the immediate early promoter of human cytomegalovirus, or the simian virus 40 early promoter. The vectors carry the neomycin phosphotransferase gene expressed from an alternate promoter as a selectable marker. These vectors have been constructed to prevent viral protein synthesis from the remaining viral sequences, to yield high-titer virus stocks after introduction into retrovirus packaging cells, and to eliminate homologous overlap with viral DNAs present in retrovirus packaging cells in order to prevent helper virus production. Methods for generating high-titer virus are described.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Production of retroviral vectors.Curr Protoc Hum Genet. 2001 May;Chapter 12:Unit 12.5. doi: 10.1002/0471142905.hg1205s11. Curr Protoc Hum Genet. 2001. PMID: 18428250
-
A convenient method for positive selection of retroviral producing cells generating vectors devoid of selectable markers.J Virol Methods. 2004 Jun 1;118(1):61-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2004.01.024. J Virol Methods. 2004. PMID: 15158069
-
An improved method for generating retroviral producer clones for vectors lacking a selectable marker gene.Blood Cells Mol Dis. 1998 Jun;24(2):167-82. doi: 10.1006/bcmd.1998.0184. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 1998. PMID: 9642098
-
Retrovirus packaging cells.Hum Gene Ther. 1990 Spring;1(1):5-14. doi: 10.1089/hum.1990.1.1-5. Hum Gene Ther. 1990. PMID: 2081186 Review.
-
Recent advances in retrovirus vector technology.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Feb;3(1):102-9. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80349-1. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993. PMID: 8453267 Review.
Cited by
-
RNase P-associated external guide sequence effectively reduces the expression of human CC-chemokine receptor 5 and inhibits the infection of human immunodeficiency virus 1.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:509714. doi: 10.1155/2013/509714. Epub 2012 Dec 27. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23509733 Free PMC article.
-
The immune response induced by DNA vaccine expressing nfa1 gene against Naegleria fowleri.Parasitol Res. 2012 Dec;111(6):2377-84. doi: 10.1007/s00436-012-3093-5. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Parasitol Res. 2012. PMID: 22955499
-
Herpesvirus saimiri oncogene STP-C488 encodes a phosphoprotein.J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1777-80. doi: 10.1128/JVI.66.3.1777-1780.1992. J Virol. 1992. PMID: 1310780 Free PMC article.
-
The SH2 and SH3 domain-containing Nck protein is oncogenic and a common target for phosphorylation by different surface receptors.Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5824-33. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5824-5833.1992. Mol Cell Biol. 1992. PMID: 1333047 Free PMC article.
-
The requirements for viral entry differ from those for virally induced syncytium formation in NIH 3T3/DTras cells exposed to Moloney murine leukemia virus.J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7262-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.66.12.7262-7269.1992. J Virol. 1992. PMID: 1433518 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beck E, Ludwig G, Auerswald EA, Reiss B, Schaller H. Nucleotide sequence and exact localization of the neomycin phosphotransferase gene from transposon Tn5. Gene. 1982;19:327–336. - PubMed
-
- Boshart M, Weber F, Jahn G, Dorsch-Hsler K, Fleckenstein B, Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985;41:521–530. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
