Systematic tracking of dysregulated modules identifies disrupted pathways in narcolepsy
- PMID: 26309600
- PMCID: PMC4538164
Systematic tracking of dysregulated modules identifies disrupted pathways in narcolepsy
Abstract
Objective: The objective of this work is to identify disrupted pathways in narcolepsy according to systematically tracking the dysregulated modules of reweighted Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI) networks. Here, we performed systematic identification and comparison of modules across normal and narcolepsy conditions by integrating PPI and gene-expression data.
Methods: Firstly, normal and narcolepsy PPI network were inferred and reweighted based on Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC). Then, modules in PPI network were explored by clique-merging algorithm and we identified altered modules using a maximum weight bipartite matching and in non-increasing order. Finally, pathways enrichment analyses of genes in altered modules were carried out based on Expression Analysis Systematic Explored (EASE) test to illuminate the biological pathways in narcolepsy.
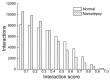
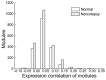
Results: Our analyses revealed that 235 altered modules were identified by comparing modules in normal and narcolepsy PPI network. Pathway functional enrichment analysis of disrupted module genes showed 59 disrupted pathways within threshold P < 0.001. The most significant five disrupted pathways were: oxidative phosphorylation, T cell receptor signaling pathway, cell cycle, Alzheimer's disease and focal adhesion.
Conclusions: We successfully identified disrupted pathways and these pathways might be potential biological processes for treatment and etiology mechanism in narcolepsy.
Keywords: Narcolepsy; disrupted pathways; dysregulated modules; protein-protein interaction network.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systematic Tracking of Disrupted Modules Identifies Altered Pathways Associated with Congenital Heart Defects in Down Syndrome.Med Sci Monit. 2015 Nov 2;21:3334-42. doi: 10.12659/msm.896001. Med Sci Monit. 2015. PMID: 26524729 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic tracking of altered modules identifies disrupted pathways in teratozoospermia.Genet Mol Res. 2016 Apr 25;15(2). doi: 10.4238/gmr.15027514. Genet Mol Res. 2016. PMID: 27173237
-
Temporal Identification of Dysregulated Genes and Pathways in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Based on Systematic Tracking of Disrupted Modules.Comput Math Methods Med. 2015;2015:313740. doi: 10.1155/2015/313740. Epub 2015 Oct 12. Comput Math Methods Med. 2015. PMID: 26543493 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying disrupted pathways by tracking altered modules in type 2 DM-related heart failure.Herz. 2017 Feb;42(1):98-106. doi: 10.1007/s00059-016-4445-1. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Herz. 2017. PMID: 27363418 English.
-
Systematic tracking of disrupted modules identifies significant genes and pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2016 Nov;12(5):3285-3295. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.5039. Epub 2016 Aug 23. Oncol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27899995 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identification of breast cancer risk modules via an integrated strategy.Aging (Albany NY). 2019 Dec 20;11(24):12131-12146. doi: 10.18632/aging.102546. Epub 2019 Dec 20. Aging (Albany NY). 2019. PMID: 31860871 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Black J, Reaven NL, Funk SE, McGaughey K, Ohayon M, Guilleminault C, Ruoff C. High Rates of Medical Comorbidity in Narcolepsy: Findings from the Burden of Narcolepsy Disease (BOND) Study of 9,312 Patients in the United States. 2013 - PubMed
-
- Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM. Principles of neural science. McGraw-Hill New York. 2000
-
- Silber MH, Krahn LE, Olson EJ, Pankratz VS. The epidemiology of narcolepsy in Olmsted County, Minnesota: a population-based study. Sleep-New York. 2002;25:197–204. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Dong X, Yan H, Liu Y, An P, Zhao L, Li Q, Zhang X, Gao Z, Han F. [Positivity analysis of human leukocyte histocompatibility antigen-DQB1* 0602 allele in Chinese patients with narcolepsy] . Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2014;94:763–765. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources