Point mutations of the mTOR-RHEB pathway in renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 26255626
- PMCID: PMC4627224
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.4963
Point mutations of the mTOR-RHEB pathway in renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
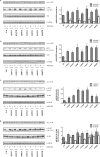
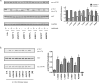
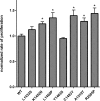
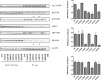
Aberrations in the mTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin) axis are frequently reported in cancer. Using publicly available tumor genome sequencing data, we identified several point mutations in MTOR and its upstream regulator RHEB (Ras homolog enriched in brain) in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), the most common histology of kidney cancer. Interestingly, we found a prominent cluster of hyperactivating mutations in the FAT (FRAP-ATM-TTRAP) domain of mTOR in renal cell carcinoma that led to an increase in both mTORC1 and mTORC2 activities and led to an increased proliferation of cells. Several of the FAT domain mutants demonstrated a decreased binding of DEPTOR (DEP domain containing mTOR-interacting protein), while a subset of these mutations showed altered binding of the negative regulator PRAS40 (proline rich AKT substrate 40). We also identified a recurrent mutation in RHEB in ccRCC patients that leads to an increase in mTORC1 activity. In vitro characterization of this RHEB mutation revealed that this mutant showed considerable resistance to TSC2 (Tuberous Sclerosis 2) GAP (GTPase activating protein) activity, though its interaction with TSC2 remained unaltered. Mutations in the FAT domain of MTOR and in RHEB remained sensitive to rapamycin, though several of these mutations demonstrated residual mTOR kinase activity after treatment with rapamycin at clinically relevant doses. Overall, our data suggests that point mutations in the mTOR pathway may lead to downstream mTOR hyperactivation through multiple different mechanisms to confer a proliferative advantage to a tumor cell.
Keywords: RHEB; mTOR; mutations; rapamycin; renal cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing financial interests in relation to the work described.
Figures


Similar articles
-
RhoA modulates signaling through the mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) in mammalian cells.Cell Signal. 2014 Mar;26(3):461-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.11.035. Epub 2013 Dec 3. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24316235 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistically distinct cancer-associated mTOR activation clusters predict sensitivity to rapamycin.J Clin Invest. 2016 Sep 1;126(9):3526-40. doi: 10.1172/JCI86120. Epub 2016 Aug 2. J Clin Invest. 2016. PMID: 27482884 Free PMC article.
-
p53 Deletion or Hotspot Mutations Enhance mTORC1 Activity by Altering Lysosomal Dynamics of TSC2 and Rheb.Mol Cancer Res. 2016 Jan;14(1):66-77. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-15-0159. Epub 2015 Sep 18. Mol Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26385560 Free PMC article.
-
Non-canonical functions of the tuberous sclerosis complex-Rheb signalling axis.EMBO Mol Med. 2011 Apr;3(4):189-200. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201100131. Epub 2011 Mar 16. EMBO Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21412983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of mTORC1 by PI3K signaling.Trends Cell Biol. 2015 Sep;25(9):545-55. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2015.06.002. Epub 2015 Jul 6. Trends Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26159692 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A phase II study of sapanisertib (TAK-228) a mTORC1/2 inhibitor in rapalog-resistant advanced pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNET): ECOG-ACRIN EA2161.Invest New Drugs. 2022 Dec;40(6):1306-1314. doi: 10.1007/s10637-022-01311-w. Epub 2022 Oct 20. Invest New Drugs. 2022. PMID: 36264382 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
DEPTOR at the Nexus of Cancer, Metabolism, and Immunity.Physiol Rev. 2018 Jul 1;98(3):1765-1803. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00064.2017. Physiol Rev. 2018. PMID: 29897294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Germline and sporadic mTOR pathway mutations in low-grade oncocytic tumor of the kidney.Mod Pathol. 2022 Mar;35(3):333-343. doi: 10.1038/s41379-021-00896-6. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Mod Pathol. 2022. PMID: 34538873 Free PMC article.
-
Brain somatic mutations in MTOR reveal translational dysregulations underlying intractable focal epilepsy.J Clin Invest. 2019 Oct 1;129(10):4207-4223. doi: 10.1172/JCI127032. J Clin Invest. 2019. PMID: 31483294 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting mTOR for cancer therapy.J Hematol Oncol. 2019 Jul 5;12(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s13045-019-0754-1. J Hematol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31277692 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sato Y, Yoshizato T, Shiraishi Y, Maekawa S, Okuno Y, Kamura T, Shimamura T, Sato-Otsubo A, Nagae G, Suzuki H, Nagata Y, Yoshida K, Kon A, Suzuki Y, Chiba K, Tanaka H, et al. Integrated molecular analysis of clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Nat Genet. 2013;45:860–867. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

