ARM-seq: AlkB-facilitated RNA methylation sequencing reveals a complex landscape of modified tRNA fragments
- PMID: 26237225
- PMCID: PMC4553111
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.3508
ARM-seq: AlkB-facilitated RNA methylation sequencing reveals a complex landscape of modified tRNA fragments
Abstract
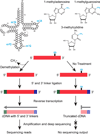
High-throughput RNA sequencing has accelerated discovery of the complex regulatory roles of small RNAs, but RNAs containing modified nucleosides may escape detection when those modifications interfere with reverse transcription during RNA-seq library preparation. Here we describe AlkB-facilitated RNA methylation sequencing (ARM-seq), which uses pretreatment with Escherichia coli AlkB to demethylate N(1)-methyladenosine (m(1)A), N(3)-methylcytidine (m(3)C) and N(1)-methylguanosine (m(1)G), all commonly found in tRNAs. Comparative methylation analysis using ARM-seq provides the first detailed, transcriptome-scale map of these modifications and reveals an abundance of previously undetected, methylated small RNAs derived from tRNAs. ARM-seq demonstrates that tRNA fragments accurately recapitulate the m(1)A modification state for well-characterized yeast tRNAs and generates new predictions for a large number of human tRNAs, including tRNA precursors and mitochondrial tRNAs. Thus, ARM-seq provides broad utility for identifying previously overlooked methyl-modified RNAs, can efficiently monitor methylation state and may reveal new roles for tRNA fragments as biomarkers or signaling molecules.
Figures


Comment in
-
Removing roadblocks to deep sequencing of modified RNAs.Nat Methods. 2015 Sep;12(9):821-2. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3516. Nat Methods. 2015. PMID: 26317237 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
High-Throughput Small RNA Sequencing Enhanced by AlkB-Facilitated RNA de-Methylation (ARM-Seq).Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1562:231-243. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6807-7_15. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28349464 Free PMC article.
-
Removing roadblocks to deep sequencing of modified RNAs.Nat Methods. 2015 Sep;12(9):821-2. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3516. Nat Methods. 2015. PMID: 26317237 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleotide resolution profiling of m7G tRNA modification by TRAC-Seq.Nat Protoc. 2019 Nov;14(11):3220-3242. doi: 10.1038/s41596-019-0226-7. Epub 2019 Oct 16. Nat Protoc. 2019. PMID: 31619810 Free PMC article.
-
Quantifying the 'escapers' among RNA species.Biochem Soc Trans. 2015 Dec;43(6):1215-20. doi: 10.1042/BST20150158. Biochem Soc Trans. 2015. PMID: 26614663 Review.
-
Noncanonical Roles of tRNAs: tRNA Fragments and Beyond.Annu Rev Genet. 2020 Nov 23;54:47-69. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-022620-101840. Epub 2020 Aug 25. Annu Rev Genet. 2020. PMID: 32841070 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epitranscriptome: Review of Top 25 Most-Studied RNA Modifications.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 10;23(22):13851. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213851. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small non-coding RNA signatures in atrial appendages of patients with atrial fibrillation.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Jun;28(12):e18483. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18483. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39051629 Free PMC article.
-
ALKBH1-Mediated tRNA Demethylation Regulates Translation.Cell. 2016 Oct 20;167(3):816-828.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.09.038. Epub 2016 Oct 13. Cell. 2016. PMID: 27745969 Free PMC article.
-
OncotRF: an online resource for exploration of tRNA-derived fragments in human cancers.RNA Biol. 2020 Aug;17(8):1081-1091. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1776506. Epub 2020 Jun 28. RNA Biol. 2020. PMID: 32597311 Free PMC article.
-
Processing by RNase 1 forms tRNA halves and distinct Y RNA fragments in the extracellular environment.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Aug 20;48(14):8035-8049. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa526. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32609822 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

