High-Density Genotypes of Inbred Mouse Strains: Improved Power and Precision of Association Mapping
- PMID: 26224782
- PMCID: PMC4592984
- DOI: 10.1534/g3.115.020784
High-Density Genotypes of Inbred Mouse Strains: Improved Power and Precision of Association Mapping
Abstract
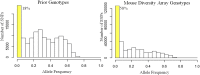
Human genome-wide association studies have identified thousands of loci associated with disease phenotypes. Genome-wide association studies also have become feasible using rodent models and these have some important advantages over human studies, including controlled environment, access to tissues for molecular profiling, reproducible genotypes, and a wide array of techniques for experimental validation. Association mapping with common mouse inbred strains generally requires 100 or more strains to achieve sufficient power and mapping resolution; in contrast, sample sizes for human studies typically are one or more orders of magnitude greater than this. To enable well-powered studies in mice, we have generated high-density genotypes for ∼175 inbred strains of mice using the Mouse Diversity Array. These new data increase marker density by 1.9-fold, have reduced missing data rates, and provide more accurate identification of heterozygous regions compared with previous genotype data. We report the discovery of new loci from previously reported association mapping studies using the new genotype data. The data are freely available for download, and Web-based tools provide easy access for association mapping and viewing of the underlying intensity data for individual loci.
Keywords: HMDP; genotyping; mouse; mouse diversity array.
Copyright © 2015 Rau et al.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fine mapping in 94 inbred mouse strains using a high-density haplotype resource.Genetics. 2010 Jul;185(3):1081-95. doi: 10.1534/genetics.110.115014. Epub 2010 May 3. Genetics. 2010. PMID: 20439770 Free PMC article.
-
Large-scale discovery and genotyping of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the mouse.Nat Genet. 2000 Apr;24(4):381-6. doi: 10.1038/74215. Nat Genet. 2000. PMID: 10742102
-
Segmental phylogenetic relationships of inbred mouse strains revealed by fine-scale analysis of sequence variation across 4.6 mb of mouse genome.Genome Res. 2004 Aug;14(8):1493-500. doi: 10.1101/gr.2627804. Genome Res. 2004. PMID: 15289472 Free PMC article.
-
Haplotype association mapping in mice.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;573:213-22. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-247-6_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19763930 Review.
-
QTL mapping using high-throughput sequencing.Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1284:257-85. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2444-8_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25757777 Review.
Cited by
-
Hybrid Mouse Diversity Panel Identifies Genetic Architecture Associated with the Acute Antisense Oligonucleotide-Mediated Inflammatory Response to a 2'-O-Methoxyethyl Antisense Oligonucleotide.Nucleic Acid Ther. 2019 Oct;29(5):266-277. doi: 10.1089/nat.2019.0797. Epub 2019 Aug 1. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2019. PMID: 31368839 Free PMC article.
-
Frequency of mononuclear diploid cardiomyocytes underlies natural variation in heart regeneration.Nat Genet. 2017 Sep;49(9):1346-1353. doi: 10.1038/ng.3929. Epub 2017 Aug 7. Nat Genet. 2017. PMID: 28783163 Free PMC article.
-
Gene-by-Sex Interactions in Mitochondrial Functions and Cardio-Metabolic Traits.Cell Metab. 2019 Apr 2;29(4):932-949.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.12.013. Epub 2019 Jan 10. Cell Metab. 2019. PMID: 30639359 Free PMC article.
-
Genomewide Association Study Identifies Cxcl Family Members as Partial Mediators of LPS-Induced Periodontitis.J Bone Miner Res. 2018 Aug;33(8):1450-1463. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3440. Epub 2018 May 22. J Bone Miner Res. 2018. PMID: 29637625 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in heart mitochondria regulate diastolic dysfunction.Nat Commun. 2022 Jul 4;13(1):3850. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31544-5. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35787630 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brittsan A. G., Kiss E., Edes I., Grupp I. L., Grupp G., et al. , 1999. The effect of isoproterenol on phospholamban-deficient mouse hearts with altered thyroid conditions. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 31: 1725–1737. - PubMed
-
- Chu, G., and E. G. Kranias, 2006 Phospholamban as a therapeutic modality in heart failure. Novartis Found. Symp. 274: 156–171; discussion 172–5, 272–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 HL126753/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- GM076468/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- D094311/PHS HHS/United States
- HL28481/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA034196/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL028481/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL123295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HL123021/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL123295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL30568/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL030568/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM076468/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HL126753/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
