Acquisition of cancer stem cell-like properties in non-small cell lung cancer with acquired resistance to afatinib
- PMID: 26202045
- PMCID: PMC4638008
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.12749
Acquisition of cancer stem cell-like properties in non-small cell lung cancer with acquired resistance to afatinib
Abstract
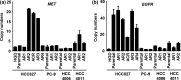
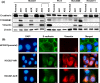
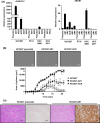
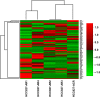
Afatinib is an irreversible epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) that is known to be effective against the EGFR T790M variant, which accounts for half of the mechanisms of acquired resistance to reversible EGFR-TKIs. However, acquired resistance to afatinib was also observed in clinical use. Thus, elucidating and overcoming the mechanisms of resistance are important issues in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. In this study, we established various afatinib-resistant cell lines and investigated the resistance mechanisms. EGFR T790M mutations were not detected using direct sequencing in established resistant cells. Several afatinib-resistant cell lines displayed MET amplification, and these cells were sensitive to the combination of afatinib plus crizotinib. As a further investigation, a cell line that acquired resistance to afatinib plus crizotinib, HCC827-ACR, was established from one of the MET amplified-cell lines. Several afatinib-resistant cell lines including HCC827-ACR displayed epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) features and epigenetic silencing of miR-200c, which is a suppresser of EMT. In addition, these cell lines also exhibited overexpression of ALDH1A1 and ABCB1, which are putative stem cell markers, and resistance to docetaxel. In conclusion, we established afatinib-resistant cells and found that MET amplification, EMT, and stem cell-like features are observed in cells with acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs. This finding may provide clues to overcoming resistance to EGFR-TKIs.
Keywords: Afatinib; EGFR-TKI; cancer stem cells; drug resistance; non-small cell lung cancer.
© 2015 The Authors. Cancer Science published by Wiley Publishing Asia Pty Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic strategies for afatinib-resistant lung cancer harboring HER2 alterations.Cancer Sci. 2018 May;109(5):1493-1502. doi: 10.1111/cas.13571. Epub 2018 Apr 15. Cancer Sci. 2018. PMID: 29532558 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitivity to chemotherapeutics of NSCLC cells with acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs is mediated by T790M mutation or epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Oncol Rep. 2018 Apr;39(4):1783-1792. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6242. Epub 2018 Feb 1. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29393480
-
Efficacy of continuous EGFR-inhibition and role of Hedgehog in EGFR acquired resistance in human lung cancer cells with activating mutation of EGFR.Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 4;8(14):23020-23032. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15479. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28416737 Free PMC article.
-
Afatinib: a second-generation EGF receptor and ErbB tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer.Future Oncol. 2015 Sep;11(18):2525-40. doi: 10.2217/fon.15.183. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Future Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26314834 Review.
-
Acquired resistance of non-small cell lung cancer to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Respir Investig. 2014 Mar;52(2):82-91. doi: 10.1016/j.resinv.2013.07.007. Epub 2013 Aug 30. Respir Investig. 2014. PMID: 24636263 Review.
Cited by
-
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) causing acquired resistance to afatinib in a patient with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutant lung adenocarcinoma.J Thorac Dis. 2018 Jul;10(7):E560-E563. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2018.06.122. J Thorac Dis. 2018. PMID: 30174934 Free PMC article.
-
The interplay of reactive oxygen species and the epidermal growth factor receptor in tumor progression and drug resistance.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Mar 16;37(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0728-0. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29548337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of acquired resistance to afatinib clarified with liquid biopsy.PLoS One. 2018 Dec 14;13(12):e0209384. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0209384. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30550608 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical efficacy and safety of afatinib in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer in Chinese patients.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 Jan 24;11:529-538. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S136579. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. PMID: 29416353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monitoring EGFR-lung cancer evolution: a possible beginning of a "methylation era" in TKI resistance prediction.Front Oncol. 2023 Apr 20;13:1137384. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1137384. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37152062 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129–39. - PubMed
-
- Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:121–8. - PubMed
-
- Sequist LV, Martins RG, Spigel D, et al. First-line gefitinib in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harboring somatic EGFR mutations. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:2442–9. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi S, Boggon TJ, Dayaram T, et al. EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:786–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

