Simultaneous deletion of Bax and Bak is required to prevent apoptosis and interstitial fibrosis in obstructive nephropathy
- PMID: 26180237
- PMCID: PMC4572396
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00170.2015
Simultaneous deletion of Bax and Bak is required to prevent apoptosis and interstitial fibrosis in obstructive nephropathy
Abstract
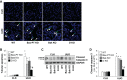
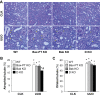
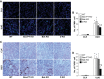
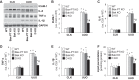
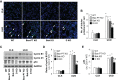
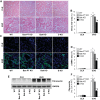
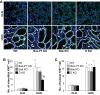
Proximal tubular injury and apoptosis are key mediators of the development of kidney fibrosis, a hallmark of chronic kidney disease. However, the molecular mechanism by which tubular apoptotic cell death leads to kidney fibrosis is poorly understood. In the present study, we tested the roles of Bcl-2-associated X (Bax) and Bcl-2 antagonist/killer (Bak), two crucial proteins involved in intrinsic apoptotic cell death, in the progression of kidney fibrosis. Mice with proximal tubule-specific Bax deletion, systemic deletion of Bak, and dual deletion of Bax and Bak were subjected to unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO). Dual deficiency of Bax and Bak inhibited tubular apoptosis and atrophy. Consistent with decreased tubular injury, dual ablation of Bax and Bak suppressed UUO-induced inflammation and kidney fibrosis with decreased tubular cell cycle arrest, expression of fibrogenic and inflammatory cytokines, and oxidative stress in the kidney. Bax or Bak deficiency was insufficient to prevent apoptosis and all other aforementioned malevolent effects, suggesting compensatory mediation by each other in the respective signaling pathways. These data suggest that dual ablation of Bax and Bak in the kidney is required to prevent UUO-induced tubular apoptosis and the consequent kidney inflammation and fibrosis.
Keywords: Bcl-2 antagonist/killer; Bcl-2-associated X; apoptosis; chronic kidney disease; fibrosis; inflammation; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures

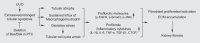
Similar articles
-
Double knockout of Bax and Bak from kidney proximal tubules reduces unilateral urethral obstruction associated apoptosis and renal interstitial fibrosis.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 20;7:44892. doi: 10.1038/srep44892. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28317867 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocyte growth factor gene therapy retards the progression of chronic obstructive nephropathy.Kidney Int. 2002 Oct;62(4):1238-48. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2002.kid579.x. Kidney Int. 2002. PMID: 12234294
-
Bax and Bak have critical roles in ischemic acute kidney injury in global and proximal tubule-specific knockout mouse models.Kidney Int. 2013 Jul;84(1):138-48. doi: 10.1038/ki.2013.68. Epub 2013 Mar 6. Kidney Int. 2013. PMID: 23466994 Free PMC article.
-
Deficiency in apoptotic effectors Bax and Bak reveals an autophagic cell death pathway initiated by photodamage to the endoplasmic reticulum.Autophagy. 2006 Jul-Sep;2(3):238-40. doi: 10.4161/auto.2730. Epub 2006 Jul 22. Autophagy. 2006. PMID: 16874066 Review.
-
Obstructive nephropathy: lessons from cystic kidney disease.Nephron. 2000 Jan;84(1):6-12. doi: 10.1159/000045532. Nephron. 2000. PMID: 10644902 Review.
Cited by
-
Melatonin preconditioning of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells promotes their engraftment and improves renal regeneration in a rat model of chronic kidney disease.J Mol Histol. 2019 Apr;50(2):129-140. doi: 10.1007/s10735-019-09812-4. Epub 2019 Jan 22. J Mol Histol. 2019. PMID: 30671880
-
Double knockout of Bax and Bak from kidney proximal tubules reduces unilateral urethral obstruction associated apoptosis and renal interstitial fibrosis.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 20;7:44892. doi: 10.1038/srep44892. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28317867 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Nootkatone on Renal Inflammation, Apoptosis, and Fibrosis in a Unilateral Ureteral Obstructive Mouse Model.Nutrients. 2021 Nov 1;13(11):3921. doi: 10.3390/nu13113921. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34836176 Free PMC article.
-
Proximal tubule cyclophilin D mediates kidney fibrogenesis in obstructive nephropathy.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2021 Oct 1;321(4):F431-F442. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00171.2021. Epub 2021 Aug 16. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34396791 Free PMC article.
-
Directly targeting BAX for drug discovery: Therapeutic opportunities and challenges.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Jun;14(6):2378-2401. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.02.010. Epub 2024 Feb 10. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 38828138 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bakris G, Vassalotti J, Ritz E, Wanner C, Stergiou G, Molitch M, Nesto R, Kaysen GA, Sowers JR; CKD Consensus Working Group. National Kidney Foundation consensus conference on cardiovascular and kidney diseases and diabetes risk: an integrated therapeutic approach to reduce events. Kidney Int 78: 726–736, 2010. - PubMed
-
- Bonventre JV. Maladaptive proximal tubule repair: cell cycle arrest. Nephron Clin Pract 127: 61–64, 2014. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

