Pten Mutations Alter Brain Growth Trajectory and Allocation of Cell Types through Elevated β-Catenin Signaling
- PMID: 26180201
- PMCID: PMC6605343
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5272-14.2015
Pten Mutations Alter Brain Growth Trajectory and Allocation of Cell Types through Elevated β-Catenin Signaling
Abstract
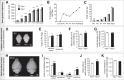
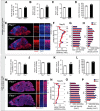
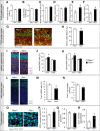
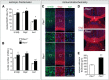
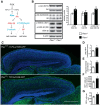
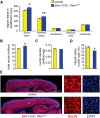
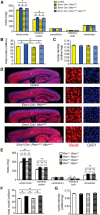
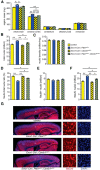
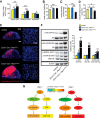
Abnormal patterns of head and brain growth are a replicated finding in a subset of individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). It is not known whether risk factors associated with ASD and abnormal brain growth (both overgrowth and undergrowth) converge on common biological pathways and cellular mechanisms in the developing brain. Heterozygous mutations in PTEN (PTEN(+/-)), which encodes a negative regulator of the PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway, are a risk factor for ASD and macrocephaly. Here we use the developing cerebral cortex of Pten(+/-) mice to investigate the trajectory of brain overgrowth and underlying cellular mechanisms. We find that overgrowth is detectable from birth to adulthood, is driven by hyperplasia, and coincides with excess neurons at birth and excess glia in adulthood. β-Catenin signaling is elevated in the developing Pten(+/-) cortex, and a heterozygous mutation in Ctnnb1 (encoding β-catenin), itself a candidate gene for ASD and microcephaly, can suppress Pten(+/-) cortical overgrowth. Thus, a balance of Pten and β-catenin signaling regulates normal brain growth trajectory by controlling cell number, and imbalance in this relationship can result in abnormal brain growth.
Significance statement: We report that Pten haploinsufficiency leads to a dynamic trajectory of brain overgrowth during development and altered scaling of neuronal and glial cell populations. β-catenin signaling is elevated in the developing cerebral cortex of Pten haploinsufficient mice, and a heterozygous mutation in β-catenin, itself a candidate gene for ASD and microcephaly, suppresses Pten(+/-) cortical overgrowth. This leads to the new insight that Pten and β-catenin signaling act in a common pathway to regulate normal brain growth trajectory by controlling cell number, and disruption of this pathway can result in abnormal brain growth.
Keywords: Pten; autism; brain growth; cell types; macrocephaly; β-catenin.
Copyright © 2015 the authors 0270-6474/15/3510252-16$15.00/0.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic Suppression of mTOR Rescues Synaptic and Social Behavioral Abnormalities in a Mouse Model of Pten Haploinsufficiency.Autism Res. 2019 Oct;12(10):1463-1471. doi: 10.1002/aur.2186. Epub 2019 Aug 23. Autism Res. 2019. PMID: 31441226 Free PMC article.
-
Pten haploinsufficient mice show broad brain overgrowth but selective impairments in autism-relevant behavioral tests.Hum Mol Genet. 2014 Jul 1;23(13):3490-505. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu057. Epub 2014 Feb 4. Hum Mol Genet. 2014. PMID: 24497577
-
PTEN Regulates Dendritic Arborization by Decreasing Microtubule Polymerization Rate.J Neurosci. 2022 Mar 9;42(10):1945-1957. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1835-21.2022. Epub 2022 Jan 31. J Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35101965 Free PMC article.
-
Balancing Proliferation and Connectivity in PTEN-associated Autism Spectrum Disorder.Neurotherapeutics. 2015 Jul;12(3):609-19. doi: 10.1007/s13311-015-0356-8. Neurotherapeutics. 2015. PMID: 25916396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PTEN signaling in autism spectrum disorders.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2012 Oct;22(5):873-9. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2012.05.004. Epub 2012 Jun 2. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2012. PMID: 22664040 Review.
Cited by
-
Dyrk1a Mutations Cause Undergrowth of Cortical Pyramidal Neurons via Dysregulated Growth Factor Signaling.Biol Psychiatry. 2021 Sep 1;90(5):295-306. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2021.01.012. Epub 2021 Apr 8. Biol Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33840455 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Suppression of mTOR Rescues Synaptic and Social Behavioral Abnormalities in a Mouse Model of Pten Haploinsufficiency.Autism Res. 2019 Oct;12(10):1463-1471. doi: 10.1002/aur.2186. Epub 2019 Aug 23. Autism Res. 2019. PMID: 31441226 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperconnectivity of prefrontal cortex to amygdala projections in a mouse model of macrocephaly/autism syndrome.Nat Commun. 2016 Nov 15;7:13421. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13421. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27845329 Free PMC article.
-
Linking Autism Risk Genes to Disruption of Cortical Development.Cells. 2020 Nov 18;9(11):2500. doi: 10.3390/cells9112500. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33218123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deleterious ZNRF3 germline variants cause neurodevelopmental disorders with mirror brain phenotypes via domain-specific effects on Wnt/β-catenin signaling.Am J Hum Genet. 2024 Sep 5;111(9):1994-2011. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2024.07.016. Epub 2024 Aug 20. Am J Hum Genet. 2024. PMID: 39168120 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

