Applying refinement to the use of mice and rats in rheumatoid arthritis research
- PMID: 26168847
- PMCID: PMC4508365
- DOI: 10.1007/s10787-015-0241-4
Applying refinement to the use of mice and rats in rheumatoid arthritis research
Abstract
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a painful, chronic disorder and there is currently an unmet need for effective therapies that will benefit a wide range of patients. The research and development process for therapies and treatments currently involves in vivo studies, which have the potential to cause discomfort, pain or distress. This Working Group report focuses on identifying causes of suffering within commonly used mouse and rat 'models' of RA, describing practical refinements to help reduce suffering and improve welfare without compromising the scientific objectives. The report also discusses other, relevant topics including identifying and minimising sources of variation within in vivo RA studies, the potential to provide pain relief including analgesia, welfare assessment, humane endpoints, reporting standards and the potential to replace animals in RA research.
Figures
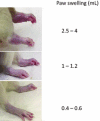
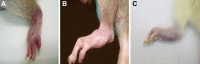

Similar articles
-
Utility of animal models for identification of potential therapeutics for rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2008 Nov;67(11):1505-15. doi: 10.1136/ard.2007.076430. Epub 2007 Nov 29. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008. PMID: 18055474 Review.
-
Rheumatoid arthritis research in the 21st century: Limitations of traditional models, new technologies, and opportunities for a human biology-based approach.ALTEX. 2020;37(2):223-242. doi: 10.14573/altex.1910011. Epub 2019 Dec 17. ALTEX. 2020. PMID: 31854453 Review.
-
Opportunities for improving animal welfare in rodent models of epilepsy and seizures.J Neurosci Methods. 2016 Feb 15;260:2-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2015.09.007. Epub 2015 Sep 12. J Neurosci Methods. 2016. PMID: 26376175 Review.
-
Possibilities for refinement and reduction: future improvements within regulatory testing.ILAR J. 2002;43 Suppl:S74-9. doi: 10.1093/ilar.43.suppl_1.s74. ILAR J. 2002. PMID: 12388856 Review.
-
Analysis of patents on anti-rheumatoid arthritis therapies issued in China.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2015;25(8):909-30. doi: 10.1517/13543776.2015.1044972. Epub 2015 Jun 12. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2015. PMID: 26066366 Review.
Cited by
-
Determining the preferred liquid reward in adult C57BL/6 mice.Lab Anim. 2023 Jun;57(3):332-335. doi: 10.1177/00236772221138628. Epub 2022 Dec 6. Lab Anim. 2023. PMID: 36474418 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of the Effects of Pain and Analgesia on Immune System Function and Inflammation: Relevance for Preclinical Studies.Comp Med. 2019 Dec 1;69(6):520-534. doi: 10.30802/AALAS-CM-19-000041. Epub 2019 Dec 20. Comp Med. 2019. PMID: 31896389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Refinement and validation of infrared thermal imaging (IRT): a non-invasive technique to measure disease activity in a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2020 Nov 30;22(1):281. doi: 10.1186/s13075-020-02367-w. Arthritis Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 33256854 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo anti-arthritic and anti-nociceptive effects of ethanol extract of Moringa oleifera leaves on complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA)-induced arthritis in rats.Integr Med Res. 2018 Mar;7(1):85-94. doi: 10.1016/j.imr.2017.11.002. Epub 2017 Dec 23. Integr Med Res. 2018. PMID: 29629295 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-Acting Peripherally Restricted Delta/Kappa Opioid (CAV1001) Produces Antinociception in Animal Models of Sub-Acute and Chronic Pain.J Pain Res. 2020 Oct 6;13:2461-2474. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S262303. eCollection 2020. J Pain Res. 2020. PMID: 33116788 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersen ML, Tufik S. Altered sleep and behavioural patterns of arthritic rats. Sleep Res Online. 2000;3:161–167. - PubMed
-
- Bas DB, Su J, Sandor K, Agalave NM, Lundberg J, Codeluppi S, Baharpoor A, Nandakumar KS, Holmdahl R, Svensson CI. Collagen antibody-induced arthritis evokes persistent pain with spinal glial involvement and transient prostaglandin dependency. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64:3886–3996. doi: 10.1002/art.37686. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
