A Single miRNA-mRNA Interaction Affects the Immune Response in a Context- and Cell-Type-Specific Manner
- PMID: 26163372
- PMCID: PMC4529747
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.04.022
A Single miRNA-mRNA Interaction Affects the Immune Response in a Context- and Cell-Type-Specific Manner
Abstract
MicroRNA (miRNA)-dependent regulation of gene expression confers robustness to cellular phenotypes and controls responses to extracellular stimuli. Although a single miRNA can regulate expression of hundreds of target genes, it is unclear whether any of its distinct biological functions can be due to the regulation of a single target. To explore in vivo the function of a single miRNA-mRNA interaction, we mutated the 3' UTR of a major miR-155 target (SOCS1) to specifically disrupt its regulation by miR-155. We found that under physiologic conditions and during autoimmune inflammation or viral infection, some immunological functions of miR-155 were fully or largely attributable to the regulation of SOCS1, whereas others could be accounted only partially or not at all by this interaction. Our data suggest that the role of a single miRNA-mRNA interaction is dependent on cell type and biological context.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
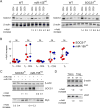
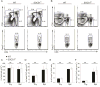
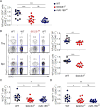
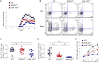


Comment in
-
miR-155-SOCS1 as a Functional Axis: Satisfying the Burden of Proof.Immunity. 2015 Jul 21;43(1):3-4. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.06.020. Immunity. 2015. PMID: 26200005
Similar articles
-
miR-155-SOCS1 as a Functional Axis: Satisfying the Burden of Proof.Immunity. 2015 Jul 21;43(1):3-4. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.06.020. Immunity. 2015. PMID: 26200005
-
MicroRNA-155 is required for effector CD8+ T cell responses to virus infection and cancer.Immunity. 2013 Apr 18;38(4):742-53. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.12.006. Immunity. 2013. PMID: 23601686 Free PMC article.
-
Stage-specific regulation of natural killer cell homeostasis and response against viral infection by microRNA-155.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Apr 23;110(17):6967-72. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1304410110. Epub 2013 Apr 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23572582 Free PMC article.
-
NK cells controlling virus-specific T cells: Rheostats for acute vs. persistent infections.Virology. 2013 Jan 5;435(1):37-45. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2012.10.005. Virology. 2013. PMID: 23217614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL12 in acute viral infectious disease.Res Immunol. 1995 Sep-Oct;146(7-8):590-600. doi: 10.1016/0923-2494(96)83036-7. Res Immunol. 1995. PMID: 8839166 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Tissue-Specific Expression Patterns of MicroRNA during Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease in the Rat.Front Immunol. 2016 Sep 16;7:361. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00361. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27695455 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-155 enhances T cell trafficking and antiviral effector function in a model of coronavirus-induced neurologic disease.J Neuroinflammation. 2016 Sep 7;13(1):240. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0699-z. J Neuroinflammation. 2016. PMID: 27604627 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Unconventional T Cells Controlled by MicroRNA.Front Immunol. 2019 Oct 23;10:2520. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02520. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31708931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a miRNA-based classifier for detection of colorectal cancer molecular subtypes.Mol Oncol. 2022 Jul;16(14):2693-2709. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13210. Epub 2022 Apr 29. Mol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35298091 Free PMC article.
-
miR-664a-3p functions as an oncogene by targeting Hippo pathway in the development of gastric cancer.Cell Prolif. 2019 May;52(3):e12567. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12567. Epub 2019 Mar 18. Cell Prolif. 2019. Retraction in: Cell Prolif. 2024 Jul;57(7):e13681. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13681 PMID: 30883979 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Alexander WS, Starr R, Fenner JE, Scott CL, Handman E, Sprigg NS, Corbin JE, Cornish AL, Darwiche R, Owczarek CM, et al. SOCS1 is a critical inhibitor of interferon gamma signaling and prevents the potentially fatal neonatal actions of this cytokine. Cell. 1999;98:597–608. - PubMed
-
- Arase H, Mocarski ES, Campbell AE, Hill AB, Lanier LL. Direct recognition of cytomegalovirus by activating and inhibitory NK cell receptors. Science. 2002;296:1323–1326. - PubMed
-
- Baltimore D, Boldin MP, O’Connell RM, Rao DS, Taganov KD. MicroRNAs: new regulators of immune cell development and function. Nat Immunol. 2008;9:839–845. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- AI034206/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI100874/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007893/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- AI085034/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI108651/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI108651/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI089935/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K99 AI089935/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI034206/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI103646/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI034206/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R00 AI089935/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI_/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- AI100874/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI103646/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R00 AI085034/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

