M-Trap: Exosome-Based Capture of Tumor Cells as a New Technology in Peritoneal Metastasis
- PMID: 26150590
- PMCID: PMC4836824
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djv184
M-Trap: Exosome-Based Capture of Tumor Cells as a New Technology in Peritoneal Metastasis
Abstract
Background: Remodeling targeted tissues for reception of tumor cells metastasizing from primary lesions is a consequence of communication between the tumor and the environment that governs metastasis. This study describes a novel approach that aims to disrupt the process of metastasis by interfering with this intense dialogue.
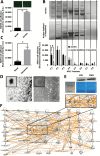
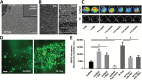
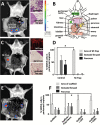
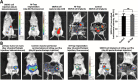
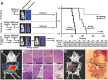
Methods: Proteomics and adhesion assays identified exosomes purified from the ascitic fluid of ovarian cancer patients (n = 9) as intermediaries of tumor cell attachment. A novel tumor cell capture device was fabricated by embedding exosomes onto a 3D scaffold (metastatic trap [M-Trap]). Murine models of ovarian metastasis (n = 3 to 34 mice per group) were used to demonstrate the efficacy of M-Trap to capture metastatic cells disseminating in the peritoneal cavity. Kaplan-Meier survival curves were used to estimate cumulative survival probabilities. All statistical tests were two-sided.
Results: The exosome-based M-Trap device promoted tumor cell adhesion with a nonpharmacological mode of action. M-Trap served as a preferential site for metastasis formation and completely remodeled the pattern of peritoneal metastasis in clinically relevant models of ovarian cancer. Most importantly, M-Trap demonstrated a statistically significant benefit in survival outcomes, with mean survival increasing from 117.5 to 198.8 days in the presence of M-Trap; removal of the device upon tumor cell capture further improved survival to a mean of 309.4 days (P < .001).
Conclusions: A potent artificial premetastatic niche based on exosomes is an effective approach to impair the crosstalk between metastatic cells and their environment. In the clinical setting, the capacity to modulate the pattern of dissemination represents an opportunity to control the process of metastasis. In summary, M-Trap transforms a systemic, fatal disease into a focalized disease where proven therapeutic approaches such as surgery can extend survival.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biomimetic device and foreign body reaction cooperate for efficient tumour cell capture in murine advanced ovarian cancer.Dis Model Mech. 2020 Jun 17;13(6):dmm043653. doi: 10.1242/dmm.043653. Dis Model Mech. 2020. PMID: 32764154 Free PMC article.
-
Mesothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Exosomes in Peritoneal Metastasis of Ovarian Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 25;22(21):11496. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111496. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34768926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor-environment biomimetics delay peritoneal metastasis formation by deceiving and redirecting disseminated cancer cells.Biomaterials. 2015 Jun;54:148-57. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.03.012. Epub 2015 Apr 2. Biomaterials. 2015. PMID: 25907048
-
Exosome-derived miRNAs and ovarian carcinoma progression.Carcinogenesis. 2014 Sep;35(9):2113-20. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgu130. Epub 2014 Jun 12. Carcinogenesis. 2014. PMID: 24925027
-
Malignant ascites in ovarian cancer and the role of targeted therapeutics.Anticancer Res. 2014 Apr;34(4):1553-61. Anticancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24692682 Review.
Cited by
-
Exosomes: novel implications in diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal cancer.Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2016 Dec;401(8):1097-1110. doi: 10.1007/s00423-016-1468-2. Epub 2016 Jun 24. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2016. PMID: 27342853 Review.
-
Epigenetic Landscape of Liquid Biopsy in Colorectal Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Feb 5;9:622459. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.622459. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33614651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CXCL12 loaded-dermal filler captures CXCR4 expressing melanoma circulating tumor cells.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Jul 22;10(8):562. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1796-6. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31332163 Free PMC article.
-
Reversing the Tumor Target: Establishment of a Tumor Trap.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Aug 12;10:887. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00887. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31456685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isolation and characterization of exosomes for cancer research.J Hematol Oncol. 2020 Nov 10;13(1):152. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00987-y. J Hematol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33168028 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144 (5):646–674. - PubMed
-
- Sleeman JP, Christofori G, Fodde R, et al. Concepts of metastasis in flux: the stromal progression model. Semin Cancer Biol. 2012;22 (3):174–186. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen DX, Bos PD, Massague J. Metastasis: from dissemination to organ-specific colonization. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9 (4):274–284. - PubMed
-
- Peinado H, Lavotshkin S, Lyden D. The secreted factors responsible for pre-metastatic niche formation: old sayings and new thoughts. Semin Cancer Biol. 2011;21 (2):139–146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

