Biased Brownian motion as a mechanism to facilitate nanometer-scale exploration of the microtubule plus end by a kinesin-8
- PMID: 26150501
- PMCID: PMC4517267
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1500272112
Biased Brownian motion as a mechanism to facilitate nanometer-scale exploration of the microtubule plus end by a kinesin-8
Abstract
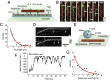
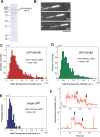
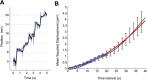
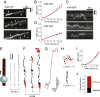
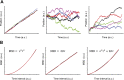
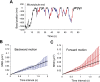
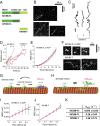
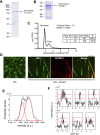
Kinesin-8s are plus-end-directed motors that negatively regulate microtubule (MT) length. Well-characterized members of this subfamily (Kip3, Kif18A) exhibit two important properties: (i) They are "ultraprocessive," a feature enabled by a second MT-binding site that tethers the motors to a MT track, and (ii) they dissociate infrequently from the plus end. Together, these characteristics combined with their plus-end motility cause Kip3 and Kif18A to enrich preferentially at the plus ends of long MTs, promoting MT catastrophes or pausing. Kif18B, an understudied human kinesin-8, also limits MT growth during mitosis. In contrast to Kif18A and Kip3, localization of Kif18B to plus ends relies on binding to the plus-end tracking protein EB1, making the relationship between its potential plus-end-directed motility and plus-end accumulation unclear. Using single-molecule assays, we show that Kif18B is only modestly processive and that the motor switches frequently between directed and diffusive modes of motility. Diffusion is promoted by the tail domain, which also contains a second MT-binding site that decreases the off rate of the motor from the MT lattice. In cells, Kif18B concentrates at the extreme tip of a subset of MTs, superseding EB1. Our data demonstrate that kinesin-8 motors use diverse design principles to target MT plus ends, which likely target them to the plus ends of distinct MT subpopulations in the mitotic spindle.
Keywords: EB1; Kif18B; kinesin-8; microtubule; mitosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Spatial regulation of astral microtubule dynamics by Kif18B in PtK cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 Oct 15;27(20):3021-3030. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E16-04-0254. Epub 2016 Aug 24. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27559136 Free PMC article.
-
Kif18B interacts with EB1 and controls astral microtubule length during mitosis.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Sep;22(17):3070-80. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-04-0363. Epub 2011 Jul 7. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21737685 Free PMC article.
-
A non-motor microtubule binding site is essential for the high processivity and mitotic function of kinesin-8 Kif18A.PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27471. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027471. Epub 2011 Nov 10. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22102900 Free PMC article.
-
Move in for the kill: motile microtubule regulators.Trends Cell Biol. 2012 Nov;22(11):567-75. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2012.08.003. Epub 2012 Sep 6. Trends Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22959403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Insights into the Function of Kinesin-8 Proteins in Microtubule Length Regulation.Biomolecules. 2018 Dec 20;9(1):1. doi: 10.3390/biom9010001. Biomolecules. 2018. PMID: 30577528 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Spatial regulation of astral microtubule dynamics by Kif18B in PtK cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 Oct 15;27(20):3021-3030. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E16-04-0254. Epub 2016 Aug 24. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27559136 Free PMC article.
-
The Proliferation of Glioblastoma Is Contributed to Kinesin Family Member 18A and Medical Data Analysis of GBM.Front Genet. 2022 Apr 8;13:858882. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.858882. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35464837 Free PMC article.
-
Processive Kinesin-14 HSET Exhibits Directional Flexibility Depending on Motor Traffic.Curr Biol. 2018 Jul 23;28(14):2356-2362.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.06.055. Epub 2018 Jul 12. Curr Biol. 2018. PMID: 30017484 Free PMC article.
-
Microtubule end tethering of a processive kinesin-8 motor Kif18b is required for spindle positioning.J Cell Biol. 2018 Jul 2;217(7):2403-2416. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201705209. Epub 2018 Apr 16. J Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29661912 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosomally unstable tumor cells specifically require KIF18A for proliferation.Nat Commun. 2021 Feb 22;12(1):1213. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21447-2. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33619254 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

