SSRI-associated optic neuropathy
- PMID: 26139049
- PMCID: PMC4565945
- DOI: 10.1038/eye.2015.119
SSRI-associated optic neuropathy
Abstract
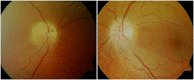
Purpose: We report five cases of optic neuropathy (ON) identified over a 2-year period within an island population of 140 000. These cases display characteristics possibly related to long-term treatment with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
Methods: Retrospective analysis of casenotes. Each case has been assessed using the Naranjo algorithm to indicate likelihood of adverse drug reaction (ADR).
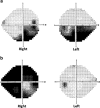
Results: Clinical assessment and investigation confirmed ON in all cases with a vascular origin suspected. SSRI cessation may help protect the unaffected eye and in some cases recovery of vision seems possible. The Naranjo scores indicated possible ADR in four cases and probable ADR in one case.
Conclusions: In 2004, ~7% of the UK adult population was receiving SSRI treatment for a range of 4.8-7.7 years. The most common ophthalmic side effect is acute glaucoma. Currently, there remain no reports of SSRI associated ON, although papilloedema has been reported. A potential mechanism for ischaemic optic neuropathy (ION) has been described in relation to raised serotonin levels. A single case of central retinal vein occlusion exists along with reports of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and ischaemic stroke. We recommend a review of SSRI treatment in cases of acute ON.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SSRI treatment-associated stroke: causality assessment in two cases.Ann Pharmacother. 2004 Jul-Aug;38(7-8):1197-201. doi: 10.1345/aph.1D624. Epub 2004 May 18. Ann Pharmacother. 2004. PMID: 15150381
-
Cerebrovascular effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors: a systematic review.J Clin Psychiatry. 2004 Dec;65(12):1642-53. doi: 10.4088/jcp.v65n1209. J Clin Psychiatry. 2004. PMID: 15641869 Review.
-
Assessment of adverse drug reactions in psychiatric inpatients with the AMSP drug safety program: methods and first results for tricyclic antidepressants and SSRI.Pharmacopsychiatry. 1999 Jan;32(1):21-8. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-979184. Pharmacopsychiatry. 1999. PMID: 10071179 Clinical Trial.
-
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors and Cataract Risk: A Case-Control Analysis.Ophthalmology. 2017 Nov;124(11):1635-1639. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2017.05.002. Epub 2017 May 29. Ophthalmology. 2017. PMID: 28571893
-
Linezolid-associated peripheral and optic neuropathy, lactic acidosis, and serotonin syndrome.Pharmacotherapy. 2007 Aug;27(8):1189-97. doi: 10.1592/phco.27.8.1189. Pharmacotherapy. 2007. PMID: 17655517 Review.
Cited by
-
Keep an eye on the SSRI: help avoid possible sight-threatening adverse events.Br J Gen Pract. 2016 Feb;66(643):91. doi: 10.3399/bjgp16X683641. Br J Gen Pract. 2016. PMID: 26823253 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Sertraline-Induced Optic Nerve Dysfunction.Cureus. 2023 Mar 31;15(3):e36976. doi: 10.7759/cureus.36976. eCollection 2023 Mar. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37139272 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Naranjo CA, Busto U, Sellers EM, Sandor P, Ruiz I, Roberts EA, et al. A method for estimating the probability of adverse drug reactions. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981;30 (2:239–245. - PubMed
-
- Petty R, House A, Knapp P, Raynor T, Zermansky A. Prevalence, duration and indications for prescribing of antidepressants in primary care. Age Ageing. 2006;35 (5:523–526. - PubMed
-
- Hutcheon ML. An unexpected case of swollen optic nerves. Am J Ther. 2011;18 (4:e126–e129. - PubMed
-
- Hayreh SS. Retinal and optic nerve head ischemic disorders and atherosclerosis: role of serotonin. Prog Retin Eye Res. 1999;18:191–221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous