InChI, the IUPAC International Chemical Identifier
- PMID: 26136848
- PMCID: PMC4486400
- DOI: 10.1186/s13321-015-0068-4
InChI, the IUPAC International Chemical Identifier
Abstract
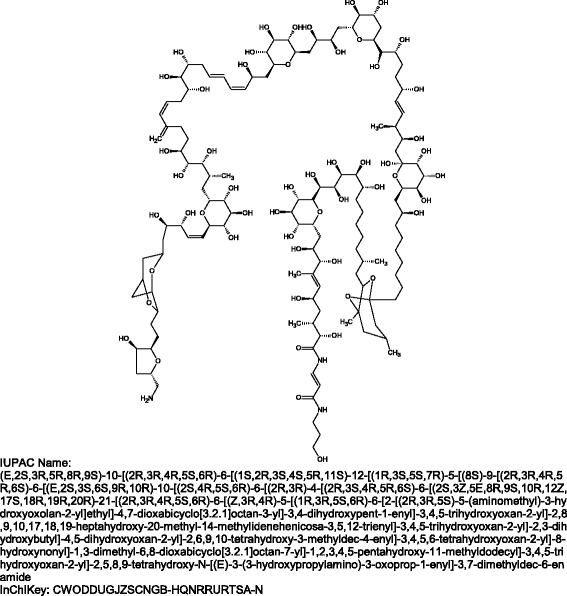
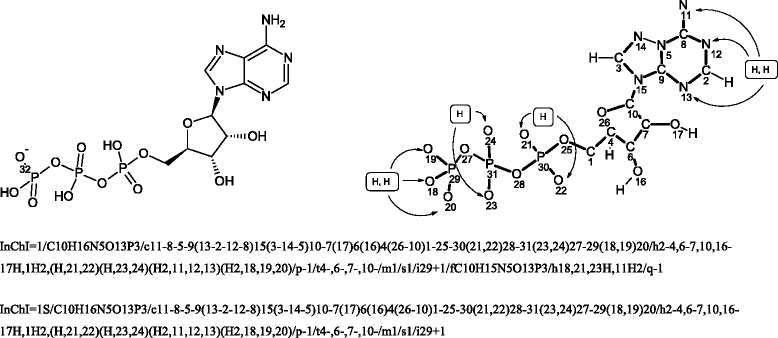
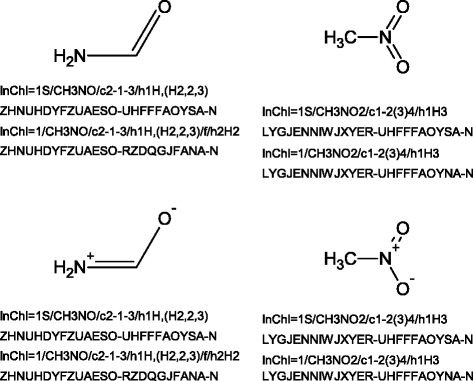
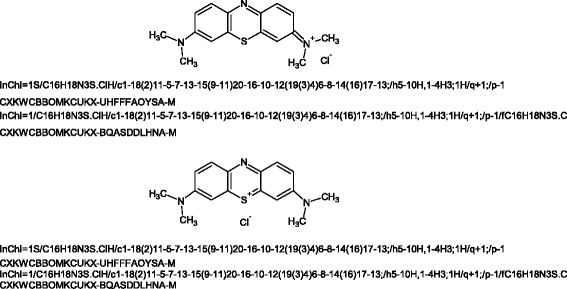
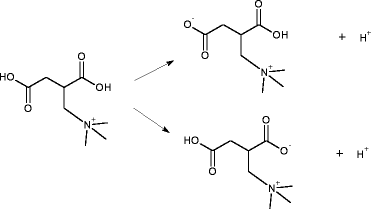
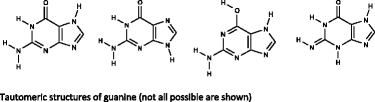
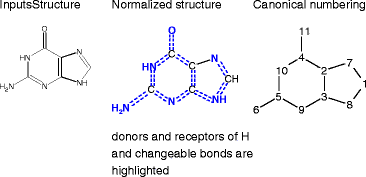
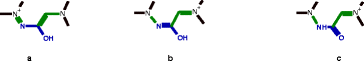
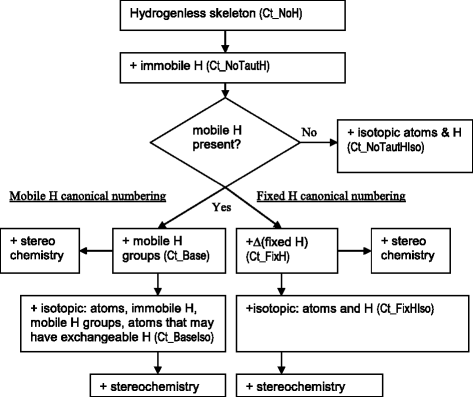
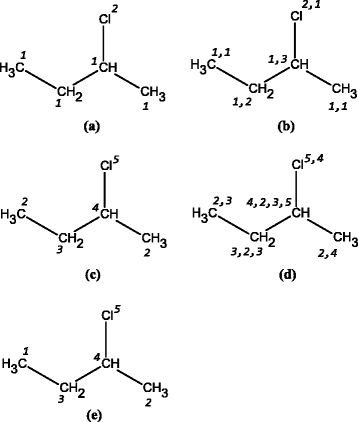
This paper documents the design, layout and algorithms of the IUPAC International Chemical Identifier, InChI.
Keywords: Chemical identifier; Chemical structure linear notation; IUPAC standard; InChI; InChIKey.
Figures
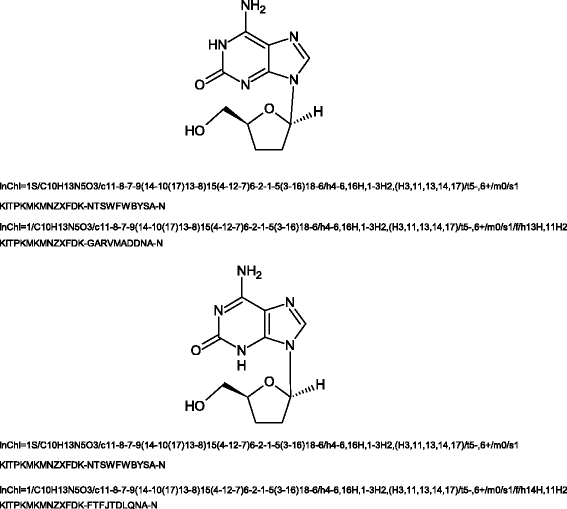
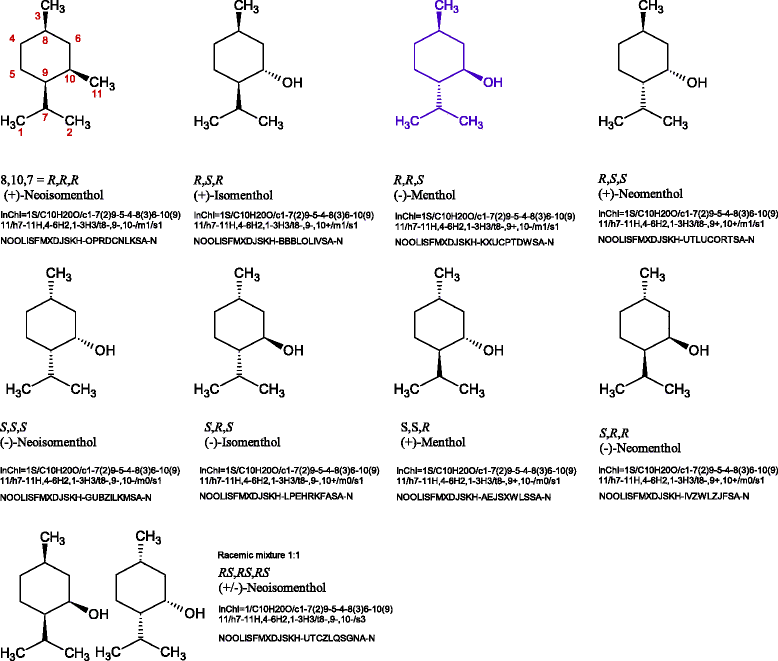
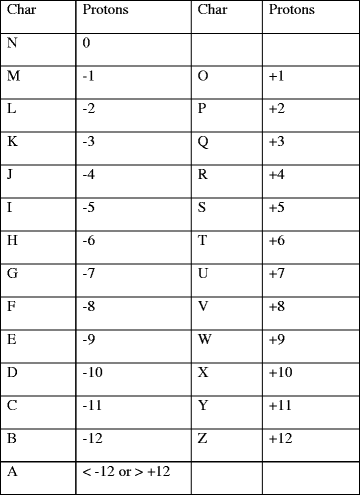
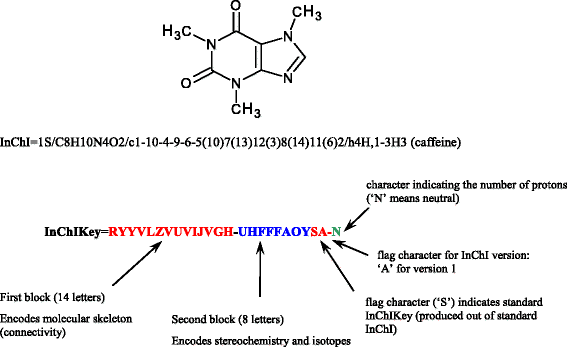
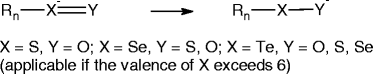

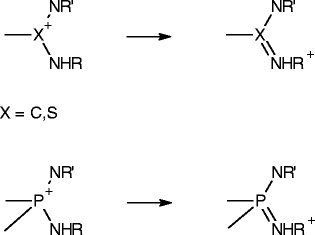
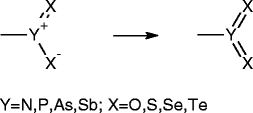
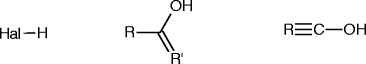


Similar articles
-
IUPAC International Chemical Identifier (InChI)-related education and training materials through InChI Open Education Resource (OER).Chem Teach Int. 2024 Jan 3;6(1):77-91. doi: 10.1515/cti-2023-0009. eCollection 2024 Mar. Chem Teach Int. 2024. PMID: 38601265 Free PMC article.
-
InChI - the worldwide chemical structure identifier standard.J Cheminform. 2013 Jan 24;5(1):7. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-5-7. J Cheminform. 2013. PMID: 23343401 Free PMC article.
-
Translating the InChI: adapting neural machine translation to predict IUPAC names from a chemical identifier.J Cheminform. 2021 Oct 7;13(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s13321-021-00535-x. J Cheminform. 2021. PMID: 34620215 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical structure indexing of toxicity data on the internet: moving toward a flat world.Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2006 May;9(3):314-25. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2006. PMID: 16729727 Review.
-
Distance learning in toxicology: resident and remote; Scotland, IPCS, IUPAC, and the world.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2005 Sep 1;207(2 Suppl):746-9. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2005.02.021. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15982692 Review.
Cited by
-
Experimental and Chemoinformatics Study of Tautomerism in a Database of Commercially Available Screening Samples.J Chem Inf Model. 2016 Nov 28;56(11):2149-2161. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.6b00338. Epub 2016 Oct 16. J Chem Inf Model. 2016. PMID: 27669079 Free PMC article.
-
mergem: merging, comparing, and translating genome-scale metabolic models using universal identifiers.NAR Genom Bioinform. 2024 Feb 2;6(1):lqae010. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqae010. eCollection 2024 Mar. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 38312936 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in coordination of rhenium organometallic complexes in the Protein Data Bank.IUCrJ. 2022 Feb 25;9(Pt 2):180-193. doi: 10.1107/S2052252522000665. eCollection 2022 Mar 1. IUCrJ. 2022. PMID: 35371500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retrosynthetic accessibility score (RAscore) - rapid machine learned synthesizability classification from AI driven retrosynthetic planning.Chem Sci. 2021 Jan 22;12(9):3339-3349. doi: 10.1039/d0sc05401a. Chem Sci. 2021. PMID: 34164104 Free PMC article.
-
RampDB: a web application and database for the exploration and prediction of receptor activity modifying protein interactions.Database (Oxford). 2017 Jan 1;2017:bax067. doi: 10.1093/database/bax067. Database (Oxford). 2017. PMID: 29220456 Free PMC article.
References
-
- IUPAC - International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Home. [http://www.iupac.org/]
-
- National Institute of Standards and Technology. [http://www.nist.gov/]
-
- InChI Trust: Home. [http://www.inchi-trust.org/]
-
- Stein S, Heller S, Tchekhovskoi D, Pletnev I. IUPAC International Chemical Identifier (InChI) InChI version 1, software version 1.04 (2011) Technical Manual. [http://www.inchi-trust.org/download/104/InChI_TechMan.pdf] - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

