Activation of IL-8 via PI3K/Akt-dependent pathway is involved in leptin-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human breast cancer cells
- PMID: 26121010
- PMCID: PMC4622725
- DOI: 10.1080/15384047.2015.1056409
Activation of IL-8 via PI3K/Akt-dependent pathway is involved in leptin-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human breast cancer cells
Abstract
Background information: Previous studies have revealed that leptin may be involved in epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), a crucial initiator of cancer progression to facilitate metastatic cascade, increase tumor recurrence, and ultimately cause poor prognosis. However, the underlying mechanism remains unclear. The aim of our present study was to investigate the effect of leptin on EMT of breast cancer cells and the underlying mechanism.
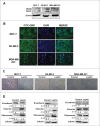
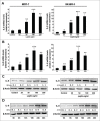
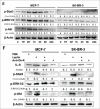
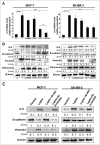
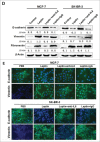
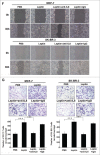
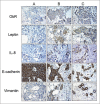
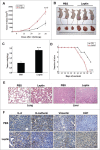
Results: Our data demonstrated that leptin significantly increased the phosphorylation of STAT3, Akt, and ERK1/2, elevated the expression of IL-8, and induced breast cancer cells to undergo EMT. The effect of leptin on IL-8 could visibly abolished by the inhibitor of PI3K LY294002. In addition, leptin-induced EMT of breast cancer cells was blocked by anti-IL-8 antibodies. Examination of the expression of ObR, leptin, IL-8 and EMT-related biomarkers in patient specimens demonstrated that malignant breast carcinoma with lymph node metastases (LNM), which represents poor prognosis, expressed higher levels of ObR, leptin, IL-8 than other types of breast cancer, and displayed more obvious EMT transversion. In vivo xenograft experiment revealed that leptin signally promoted tumor growth and metastasis and increased the expressions of IL-8 and EMT-related biomarkers.
Conclusions: Our results support that leptin-induced EMT in breast cancer cells requires IL-8 activation via the PI3K/Akt signal pathway.
Keywords: AKT, Protein Kinase B; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; EMT; EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; IFN, interferon; IL-8; IL-8, Interleukin 8; JAK, Junas Kinase; LNM, lymph node metastases; MAPK, Mitogen-activated protein kinase; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; NF-κB, Nuclear factor kappa B; Ob-R, Ob receptor; PI-3K, phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase; PI3K/Akt; STAT, signal transduction and activators of transcription; TGF, transforming growth factor; TNF, tumor necorsis factor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; breast cancer; leptin; mTOR, Mammalian Target Of Rapamycin; qRT-PCR, quantify reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Leptin promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer via the upregulation of pyruvate kinase M2.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Oct 21;35(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0446-4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27769315 Free PMC article.
-
Leptin induces functional activation of cyclooxygenase-2 through JAK2/STAT3, MAPK/ERK, and PI3K/AKT pathways in human endometrial cancer cells.Cancer Sci. 2009 Mar;100(3):389-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.01053.x. Epub 2008 Dec 16. Cancer Sci. 2009. PMID: 19154413 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of metastatic potential by TrkB via activation of IL6/JAK2/STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling in breast cancer.Oncotarget. 2015 Nov 24;6(37):40158-71. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5522. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26515594 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling Pathways Induced by Leptin during Epithelial⁻Mesenchymal Transition in Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 6;19(11):3493. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113493. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30404206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PI3K/AKT signaling pathway as a critical regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal tumor cells.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Aug 14;21(1):201. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01225-x. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37580737 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic Syndrome and Breast Cancer: Prevalence, Treatment Response, and Prognosis.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 25;11:629666. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.629666. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33842335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leptin promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer via the upregulation of pyruvate kinase M2.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Oct 21;35(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0446-4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27769315 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Four Interleukin-8 Polymorphisms (-251 A>T, +781 C>T, +1633 C>T, +2767 A>T) with Ovarian Cancer Risk: Focus on Menopausal Status and Endometriosis-Related Subtypes.Biomedicines. 2024 Jan 30;12(2):321. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12020321. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38397923 Free PMC article.
-
Leptin secreted by adipocytes promotes EMT transition and endometrial cancer progression via the JAK2/STAT3 signalling pathway.Adipocyte. 2024 Dec;13(1):2293273. doi: 10.1080/21623945.2023.2293273. Epub 2023 Dec 13. Adipocyte. 2024. PMID: 38090745 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the multifaceted role of obesity in breast cancer progression.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jul 8;12:1408844. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1408844. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39040042 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- de Azambuja E, McCaskill-Stevens W, Francis P, Quinaux E, Crown JP, Vicente M, Giuliani R, Nordenskjöld B, Gutiérez J, Andersson M, et al.. The effect of body mass index on overall and disease-free survival in node-positive breast cancer patients treated with docetaxel and doxorubicin-containing adjuvant chemotherapy: the experience of the BIG 02-98 trial. Breast CancerRes Treat. 2010;119:145-53; http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10549-009-0512-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Renehan AG, Tyson M, Egger M, Heller RF, Zwahlen M. Body-mass index and incidence of cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. Lancet. 2008;371:569-78; PMID:18280327; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60269-X - DOI - PubMed
-
- Majed B, Moreau T, Senouci K, Sigal B, Salmon RJ, Fourquet A, Asselain B. Stoutness and prognosis of female non-metastatic breast cancer: results from a French observational cohort study. Bull Cancer. 2009;96:531-41; PMID:19467984 - PubMed
-
- Wolin KY, Carson K, Colditz GA. Obesity and cancer. Oncologist. 2010;15:556-65; PMID:20507889; http://dx.doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2009-0285 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Simpson ER, Brown KA. Obesity and breast cancer: role of inflammation and aromatase. J Mol Endocrinol. 2013; 51(3):T51-9; PMID:24163427; http://dx.doi.org/10.1530/JME-13-0217 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
