RhoB is a component of the human cytomegalovirus assembly complex and is required for efficient viral production
- PMID: 26114383
- PMCID: PMC4613856
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1066535
RhoB is a component of the human cytomegalovirus assembly complex and is required for efficient viral production
Abstract
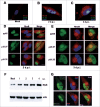
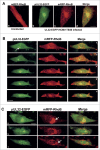
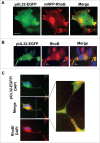
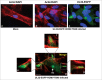
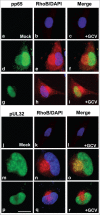
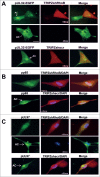
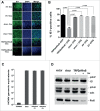
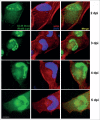
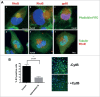
Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV), an ubiquitous β-herpesvirus, is a significant pathogen that causes medically severe diseases in immunocompromised individuals and in congenitally infected neonates. RhoB belongs to the family of Rho GTPases, which regulates diverse cellular processes. Rho proteins are implicated in the entry and egress from the host cell of mainly α- and γ-herpesviruses, whereas β-herpesviruses are the least studied in this regard. Here, we studied the role of RhoB GTPase during HCMV lytic infection. Microscopy analysis, both in fixed and live infected cells showed that RhoB was translocated to the assembly complex/compartment (AC) of HCMV, a cytoplasmic zone in infected cells where many viral structural proteins are known to accumulate and assembly of new virions takes place. Furthermore, RhoB was localized at the AC even when the expression of the late HCMV AC proteins was inhibited. At the very late stages of infection, cellular projections were formed containing RhoB and HCMV virions, potentially contributing to the successful viral spread. Interestingly, the knockdown of RhoB in HCMV-infected cells resulted in a significant reduction of the virus titer and could also affect the accumulation of AC viral proteins at this subcellular compartment. RhoB knockdown also affected actin fibers' structure. Actin reorganization was observed at late stages of infection originating from the viral AC and surrounding the cellular projections, implying a potential interplay between RhoB and actin during HCMV assembly and egress. In conclusion, our results demonstrate for the first time that RhoB is a constituent of the viral AC and is required for HCMV productive infection.
Keywords: HCMV; RhoB; actin; assembly compartment; assembly complex; cellular projections; cytoskeleton; pUL32; pUL97; pp65.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of RhoA, RhoB and RhoC GTPases in Cell Morphology, Proliferation and Migration in Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV) Infected Glioblastoma Cells.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;38(1):94-109. doi: 10.1159/000438612. Epub 2016 Jan 8. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26741994
-
Phosphorylation of Golgi Peripheral Membrane Protein Grasp65 Is an Integral Step in the Formation of the Human Cytomegalovirus Cytoplasmic Assembly Compartment.mBio. 2016 Oct 4;7(5):e01554-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01554-16. mBio. 2016. PMID: 27703074 Free PMC article.
-
Potent Inhibition of Human Cytomegalovirus by Modulation of Cellular SNARE Syntaxin 5.J Virol. 2016 Dec 16;91(1):e01637-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01637-16. Print 2017 Jan 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27795424 Free PMC article.
-
Tegument proteins of human cytomegalovirus.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2008 Jun;72(2):249-65, table of contents. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00040-07. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2008. PMID: 18535146 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus Egress: Overcoming Barriers and Co-Opting Cellular Functions.Viruses. 2021 Dec 22;14(1):15. doi: 10.3390/v14010015. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 35062219 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Efficient proliferation and mitosis of glioblastoma cells infected with human cytomegalovirus is mediated by RhoA GTPase.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Oct;22(4):3066-3072. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11434. Epub 2020 Aug 19. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32945485 Free PMC article.
-
Virus-host protein interactions as footprints of human cytomegalovirus replication.Curr Opin Virol. 2022 Feb;52:135-147. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2021.11.016. Epub 2021 Dec 16. Curr Opin Virol. 2022. PMID: 34923282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple Roles of the Cytoplasmic Domain of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Envelope Glycoprotein D in Infected Cells.J Virol. 2016 Oct 28;90(22):10170-10181. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01396-16. Print 2016 Nov 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27581980 Free PMC article.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus Hijacks WD Repeat Domain 11 for Virion Assembly Compartment Formation and Virion Morphogenesis.J Virol. 2022 Mar 9;96(5):e0182721. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01827-21. Epub 2022 Jan 12. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35020472 Free PMC article.
-
The RhoB small GTPase in physiology and disease.Small GTPases. 2018 Sep 3;9(5):384-393. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2016.1253528. Epub 2016 Nov 22. Small GTPases. 2018. PMID: 27875099 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boeckh M, Geballe AP. Cytomegalovirus: pathogen, paradigm, and puzzle. J Clin Invest 2011; 121:1673-80; PMID:21659716; http://dx.doi.org/10.1172/JCI45449 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bate SL, Dollard SC, Cannon MJ. Cytomegalovirus seroprevalence in the United States: the national health and nutrition examination surveys, 1988–2004. Clin Infect Dis 2010; 50:1439-47; PMID:20426575; http://dx.doi.org/10.1086/652438 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fowler KB, Stagno S, Pass RF, Britt WJ, Boll TJ, Alford CA. The outcome of congenital cytomegalovirus infection in relation to maternal antibody status. N Engl J Med 1992; 326:663-7; PMID:1310525; http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199203053261003 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hyde TB, Schmid DS, Cannon MJ. Cytomegalovirus seroconversion rates and risk factors: implications for congenital CMV. Rev Med Virol 2010; 20:311-26; PMID:20645278; http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/rmv.659 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Landolfo S, Gariglio M, Gribaudo G, Lembo D. The human cytomegalovirus. Pharmacol Ther 2003; 98:269-97; PMID:12782241; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0163-7258(03)00034-2 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
