BASiCS: Bayesian Analysis of Single-Cell Sequencing Data
- PMID: 26107944
- PMCID: PMC4480965
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004333
BASiCS: Bayesian Analysis of Single-Cell Sequencing Data
Abstract
Single-cell mRNA sequencing can uncover novel cell-to-cell heterogeneity in gene expression levels in seemingly homogeneous populations of cells. However, these experiments are prone to high levels of unexplained technical noise, creating new challenges for identifying genes that show genuine heterogeneous expression within the population of cells under study. BASiCS (Bayesian Analysis of Single-Cell Sequencing data) is an integrated Bayesian hierarchical model where: (i) cell-specific normalisation constants are estimated as part of the model parameters, (ii) technical variability is quantified based on spike-in genes that are artificially introduced to each analysed cell's lysate and (iii) the total variability of the expression counts is decomposed into technical and biological components. BASiCS also provides an intuitive detection criterion for highly (or lowly) variable genes within the population of cells under study. This is formalised by means of tail posterior probabilities associated to high (or low) biological cell-to-cell variance contributions, quantities that can be easily interpreted by users. We demonstrate our method using gene expression measurements from mouse Embryonic Stem Cells. Cross-validation and meaningful enrichment of gene ontology categories within genes classified as highly (or lowly) variable supports the efficacy of our approach.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
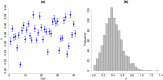
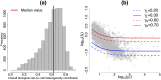
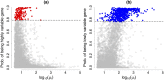
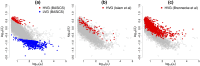
Similar articles
-
BASiCS workflow: a step-by-step analysis of expression variability using single cell RNA sequencing data.F1000Res. 2024 May 7;11:59. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.74416.1. eCollection 2022. F1000Res. 2024. PMID: 38779464 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond comparisons of means: understanding changes in gene expression at the single-cell level.Genome Biol. 2016 Apr 15;17:70. doi: 10.1186/s13059-016-0930-3. Genome Biol. 2016. PMID: 27083558 Free PMC article.
-
Bayesian approach to single-cell differential expression analysis.Nat Methods. 2014 Jul;11(7):740-2. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2967. Epub 2014 May 18. Nat Methods. 2014. PMID: 24836921 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding development and stem cells using single cell-based analyses of gene expression.Development. 2017 Jan 1;144(1):17-32. doi: 10.1242/dev.133058. Development. 2017. PMID: 28049689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical downstream analysis steps for single-cell RNA sequencing data.Brief Bioinform. 2021 Sep 2;22(5):bbab105. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbab105. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 33822873 Review.
Cited by
-
Statistical and Bioinformatics Analysis of Data from Bulk and Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Experiments.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2194:143-175. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0849-4_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 32926366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SDImpute: A statistical block imputation method based on cell-level and gene-level information for dropouts in single-cell RNA-seq data.PLoS Comput Biol. 2021 Jun 17;17(6):e1009118. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009118. eCollection 2021 Jun. PLoS Comput Biol. 2021. PMID: 34138847 Free PMC article.
-
Correcting the Mean-Variance Dependency for Differential Variability Testing Using Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Data.Cell Syst. 2018 Sep 26;7(3):284-294.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2018.06.011. Epub 2018 Aug 29. Cell Syst. 2018. PMID: 30172840 Free PMC article.
-
Using single nucleotide variations in single-cell RNA-seq to identify subpopulations and genotype-phenotype linkage.Nat Commun. 2018 Nov 20;9(1):4892. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07170-5. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30459309 Free PMC article.
-
SCRaPL: A Bayesian hierarchical framework for detecting technical associates in single cell multiomics data.PLoS Comput Biol. 2022 Jun 21;18(6):e1010163. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010163. eCollection 2022 Jun. PLoS Comput Biol. 2022. PMID: 35727848 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

