Mitochondrial Morphology and Fundamental Parameters of the Mitochondrial Respiratory Chain Are Altered in Caenorhabditis elegans Strains Deficient in Mitochondrial Dynamics and Homeostasis Processes
- PMID: 26106885
- PMCID: PMC4480853
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130940
Mitochondrial Morphology and Fundamental Parameters of the Mitochondrial Respiratory Chain Are Altered in Caenorhabditis elegans Strains Deficient in Mitochondrial Dynamics and Homeostasis Processes
Erratum in
-
Correction: Mitochondrial Morphology and Fundamental Parameters of the Mitochondrial Respiratory Chain Are Altered in Caenorhabditis elegans Strains Deficient in Mitochondrial Dynamics and Homeostasis Processes.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 15;11(12):e0168738. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168738. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27977805 Free PMC article.
Abstract
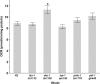
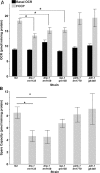
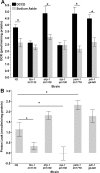
Mitochondrial dysfunction has been linked to myriad human diseases and toxicant exposures, highlighting the need for assays capable of rapidly assessing mitochondrial health in vivo. Here, using the Seahorse XFe24 Analyzer and the pharmacological inhibitors dicyclohexylcarbodiimide and oligomycin (ATP-synthase inhibitors), carbonyl cyanide 4-(trifluoromethoxy) phenylhydrazone (mitochondrial uncoupler) and sodium azide (cytochrome c oxidase inhibitor), we measured the fundamental parameters of mitochondrial respiratory chain function: basal oxygen consumption, ATP-linked respiration, maximal respiratory capacity, spare respiratory capacity and proton leak in the model organism Caenhorhabditis elegans. Since mutations in mitochondrial homeostasis genes cause mitochondrial dysfunction and have been linked to human disease, we measured mitochondrial respiratory function in mitochondrial fission (drp-1)-, fusion (fzo-1)-, mitophagy (pdr-1, pink-1)-, and electron transport chain complex III (isp-1)-deficient C. elegans. All showed altered function, but the nature of the alterations varied between the tested strains. We report increased basal oxygen consumption in drp-1; reduced maximal respiration in drp-1, fzo-1, and isp-1; reduced spare respiratory capacity in drp-1 and fzo-1; reduced proton leak in fzo-1 and isp-1; and increased proton leak in pink-1 nematodes. As mitochondrial morphology can play a role in mitochondrial energetics, we also quantified the mitochondrial aspect ratio for each mutant strain using a novel method, and for the first time report increased aspect ratios in pdr-1- and pink-1-deficient nematodes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

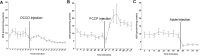
Similar articles
-
Seahorse Xfe 24 Extracellular Flux Analyzer-Based Analysis of Cellular Respiration in Caenorhabditis elegans.Curr Protoc Toxicol. 2015 Nov 2;66:25.7.1-25.7.15. doi: 10.1002/0471140856.tx2507s66. Curr Protoc Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 26523474 Free PMC article.
-
Deficiencies in mitochondrial dynamics sensitize Caenorhabditis elegans to arsenite and other mitochondrial toxicants by reducing mitochondrial adaptability.Toxicology. 2017 Jul 15;387:81-94. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2017.05.018. Epub 2017 Jun 8. Toxicology. 2017. PMID: 28602540 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of mitochondrial dynamics affects behaviour and lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 May;76(10):1967-1985. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03024-5. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30840087 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the mitochondrial respiratory chain on longevity in C. elegans.Exp Gerontol. 2014 Aug;56:245-55. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2014.03.028. Epub 2014 Apr 5. Exp Gerontol. 2014. PMID: 24709342 Review.
-
Mitochondrial ATP-Pi exchange complex and the site of uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation.Fed Proc. 1975 Jul;34(8):1699-706. Fed Proc. 1975. PMID: 1093889 Review.
Cited by
-
From the Cover: Arsenite Uncouples Mitochondrial Respiration and Induces a Warburg-like Effect in Caenorhabditis elegans.Toxicol Sci. 2016 Aug;152(2):349-62. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfw093. Epub 2016 May 20. Toxicol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27208080 Free PMC article.
-
Bioenergetic Health Assessment of a Single Caenorhabditis elegans from Postembryonic Development to Aging Stages via Monitoring Changes in the Oxygen Consumption Rate within a Microfluidic Device.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Jul 28;18(8):2453. doi: 10.3390/s18082453. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30060586 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposing of an old drug: In vitro and in vivo efficacies of buparvaquone against Echinococcus multilocularis.Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2018 Dec;8(3):440-450. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2018.10.011. Epub 2018 Oct 31. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2018. PMID: 30396011 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Defects in Mitochondrial Dynamics in Caenorhabditis elegans Impact Ultraviolet C Radiation- and 6-hydroxydopamine-Induced Neurodegeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 29;20(13):3202. doi: 10.3390/ijms20133202. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31261893 Free PMC article.
-
Oxygen consumption rate of Caenorhabditis elegans as a high-throughput endpoint of toxicity testing using the Seahorse XFe96 Extracellular Flux Analyzer.Sci Rep. 2020 Mar 6;10(1):4239. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-61054-7. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32144330 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Susin SA, Lorenzo HK, Zamzami N, Marzo I, Snow BE, Brothers GM, et al. Molecular characterization of mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor. Nature. 1999;397(6718):441–6. - PubMed
-
- Liu Z, Butow RA. Mitochondrial retrograde signaling. Annu Rev Genet. 2006;40:159–85. - PubMed
-
- Nicholls DG. Mitochondria and calcium signaling. Cell calcium. 2005;38(3):311–7. - PubMed
-
- Fernie AR, Carrari F, Sweetlove LJ. Respiratory metabolism: glycolysis, the TCA cycle and mitochondrial electron transport. Current opinion in plant biology. 2004;7(3):254–61. - PubMed
-
- Schaefer AM, Taylor RW, Turnbull DM, Chinnery PF. The epidemiology of mitochondrial disorders—past, present and future. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics. 2004;1659(2):115–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

