DMXL2 drives epithelial to mesenchymal transition in hormonal therapy resistant breast cancer through Notch hyper-activation
- PMID: 26093085
- PMCID: PMC4673176
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.4164
DMXL2 drives epithelial to mesenchymal transition in hormonal therapy resistant breast cancer through Notch hyper-activation
Abstract
The acquisition of endocrine therapy resistance in estrogen receptor α (ERα) breast cancer patients represents a major clinical problem. Notch signalling has been extensively linked to breast cancer especially in patients who fail to respond to endocrine therapy. Following activation, Notch intracellular domain is released and enters the nucleus where activates transcription of target genes. The numerous steps that cascade after activation of the receptor complicate using Notch as biomarker. Hence, this warrants the development of reliable indicators of Notch activity. DMXL2 is a novel regulator of Notch signalling not yet investigated in breast cancer. Here, we demonstrate that DMXL2 is overexpressed in a subset of endocrine therapy resistant breast cancer cell lines where it promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition through hyper-activation of Notch signalling via V-ATPase dependent acidification. Following DMXL2 depletion or treatment with Bafilomycin A1, both EMT targets and Notch signalling pathway significantly decrease. We show for the first time that DMXL2 protein levels are significantly increased in ERα positive breast cancer patients that progress after endocrine therapy. Finally, we demonstrate that DMXL2 is a transmembrane protein with a potential extra-cellular domain. These findings identify DMXL2 as a novel, functional biomarker for ERα positive breast cancer.
Keywords: DMXL2; EMT; Notch; breast cancer; endocrine therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
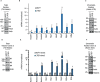
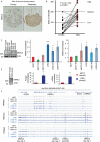
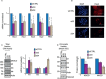
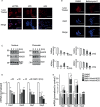

Similar articles
-
Nicastrin and Notch4 drive endocrine therapy resistance and epithelial to mesenchymal transition in MCF7 breast cancer cells.Breast Cancer Res. 2014 Jun 11;16(3):R62. doi: 10.1186/bcr3675. Breast Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24919951 Free PMC article.
-
The mitotic kinase Aurora--a promotes distant metastases by inducing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in ERα(+) breast cancer cells.Oncogene. 2014 Jan 30;33(5):599-610. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.628. Epub 2013 Jan 21. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 23334326 Free PMC article.
-
Notch activation stimulates migration of breast cancer cells and promotes tumor growth.Breast Cancer Res. 2013;15(4):R54. doi: 10.1186/bcr3447. Breast Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23826634 Free PMC article.
-
Notch Signaling in Breast Cancer: A Role in Drug Resistance.Cells. 2020 Sep 29;9(10):2204. doi: 10.3390/cells9102204. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33003540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk between Notch, HIF-1α and GPER in Breast Cancer EMT.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jul 10;19(7):2011. doi: 10.3390/ijms19072011. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29996493 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Short- and long-term effects of radiation exposure at low dose and low dose rate in normal human VH10 fibroblasts.Front Public Health. 2023 Dec 15;11:1297942. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1297942. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 38162630 Free PMC article.
-
Monoamine oxidase-A activity is required for clonal tumorsphere formation by human breast tumor cells.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2019 Nov 12;24:59. doi: 10.1186/s11658-019-0183-8. eCollection 2019. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31754354 Free PMC article.
-
SREBP1 drives Keratin-80-dependent cytoskeletal changes and invasive behavior in endocrine-resistant ERα breast cancer.Nat Commun. 2019 May 9;10(1):2115. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09676-y. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31073170 Free PMC article.
-
Overcoming Endocrine Resistance in Breast Cancer.Cancer Cell. 2020 Apr 13;37(4):496-513. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.03.009. Cancer Cell. 2020. PMID: 32289273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid unleashing of macrophage efferocytic capacity via transcriptional pause release.Nature. 2024 Apr;628(8007):408-415. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07172-y. Epub 2024 Mar 13. Nature. 2024. PMID: 38480883
References
-
- Stylianou S, Clarke RB, Brennan K. Aberrant activation of notch signaling in human breast cancer. Cancer research. 2006;66:1517–25. - PubMed
-
- Andersson ER, Lendahl U. Therapeutic modulation of Notch signalling--are we there yet? Nature reviews Drug discovery. 2014;13:357–78. - PubMed
-
- Le Borgne R. Regulation of Notch signalling by endocytosis and endosomal sorting. Current opinion in cell biology. 2006;18:213–22. - PubMed
-
- Tolcher AW, Chugh R, Chambers G, Thorpe V, Dupont J, Hill D, et al. A first-in-human phase I study to evaluate the fully human monoclonal antibody OMP-59R5 (anti-Notch2/3) administered intravenously to patients with advanced solid tumors. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2012;30
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

