WASH and Tsg101/ALIX-dependent diversion of stress-internalized EGFR from the canonical endocytic pathway
- PMID: 26066081
- PMCID: PMC4490399
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms8324
WASH and Tsg101/ALIX-dependent diversion of stress-internalized EGFR from the canonical endocytic pathway
Abstract
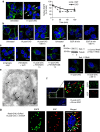
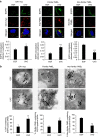
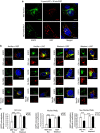
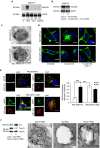
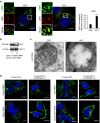
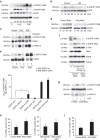
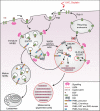
Stress exposure triggers ligand-independent EGF receptor (EGFR) endocytosis, but its post-endocytic fate and role in regulating signalling are unclear. We show that the p38 MAP kinase-dependent, EGFR tyrosine kinase (TK)-independent EGFR internalization induced by ultraviolet light C (UVC) or the cancer therapeutic cisplatin, is followed by diversion from the canonical endocytic pathway. Instead of lysosomal degradation or plasma membrane recycling, EGFR accumulates in a subset of LBPA-rich perinuclear multivesicular bodies (MVBs) distinct from those carrying EGF-stimulated EGFR. Stress-internalized EGFR co-segregates with exogenously expressed pre-melanosomal markers OA1 and fibrillar PMEL, following early endosomal sorting by the actin polymerization-promoting WASH complex. Stress-internalized EGFR is retained intracellularly by continued p38 activity in a mechanism involving ubiquitin-independent, ESCRT/ALIX-dependent incorporation onto intraluminal vesicles (ILVs) of MVBs. In contrast to the internalization-independent EGF-stimulated activation, UVC/cisplatin-triggered EGFR activation depends on EGFR internalization and intracellular retention. EGFR signalling from this MVB subpopulation delays apoptosis and might contribute to chemoresistance.
Figures
Comment in
-
Stress reveals new destination for EGF receptor.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(21):3343-4. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1093432. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 26418166 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
AP-3 regulates PAR1 ubiquitin-independent MVB/lysosomal sorting via an ALIX-mediated pathway.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Sep;23(18):3612-23. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-03-0251. Epub 2012 Jul 25. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22833563 Free PMC article.
-
RAB7 and TSG101 are required for the constitutive recycling of unliganded EGFRs via distinct mechanisms.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013 Dec 5;381(1-2):188-97. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2013.07.029. Epub 2013 Aug 7. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23933150 Free PMC article.
-
Roles for ER:endosome membrane contact sites in ligand-stimulated intraluminal vesicle formation.Biochem Soc Trans. 2018 Oct 19;46(5):1055-1062. doi: 10.1042/BST20170432. Epub 2018 Sep 20. Biochem Soc Trans. 2018. PMID: 30242114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ALIX binds a YPX(3)L motif of the GPCR PAR1 and mediates ubiquitin-independent ESCRT-III/MVB sorting.J Cell Biol. 2012 Apr 30;197(3):407-19. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201110031. J Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22547407 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signalling within multivesicular bodies.Biochem Soc Trans. 2009 Feb;37(Pt 1):173-7. doi: 10.1042/BST0370173. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009. PMID: 19143625 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of EGF Receptor Regulatory Networks in the Host Response to Viral Infections.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jan 10;11:820355. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.820355. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35083168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TGFβ overcomes FGF-induced transinhibition of EGFR in lens cells to enable fibrotic secondary cataract.Mol Biol Cell. 2024 Jun 1;35(6):ar75. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E24-01-0040. Epub 2024 Apr 10. Mol Biol Cell. 2024. PMID: 38598298 Free PMC article.
-
A new paradigm for epidermal growth factor receptor expression exists in PTC and NIFTP regulated by microRNAs.Front Oncol. 2023 Apr 11;13:1080008. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1080008. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37114127 Free PMC article.
-
Stress-induced endocytosis and degradation of epidermal growth factor receptor are two independent processes.Cancer Cell Int. 2016 Mar 31;16:25. doi: 10.1186/s12935-016-0301-x. eCollection 2016. Cancer Cell Int. 2016. PMID: 27034618 Free PMC article.
-
Tyrosine Kinase Receptors in Oncology.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 12;21(22):8529. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228529. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33198314 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jones S. & Rappoport J. Z. Interdependent epidermal growth factor receptor signalling and trafficking. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 51, 23–28 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Sorkin A. & Goh L. K. Endocytosis and intracellular trafficking of ErbBs. Exp. Cell Res. 315, 683–696 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Scaltriti M. & Baselga J. The epidermal growth factor receptor pathway: a model for targeted therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 12, 5268–5272 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

