microRNA regulation of the embryonic hypoxic response in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 26063315
- PMCID: PMC4462753
- DOI: 10.1038/srep11284
microRNA regulation of the embryonic hypoxic response in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
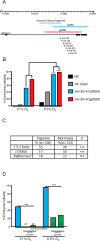
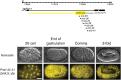
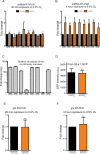
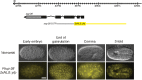
Layered strategies to combat hypoxia provide flexibility in dynamic oxygen environments. Here we show that multiple miRNAs are required for hypoxic survival responses during C. elegans embryogenesis. Certain miRNAs promote while others antagonize the hypoxic survival response. We found that expression of the mir-35 family is regulated by hypoxia in a HIF-1-independent manner and loss of mir-35-41 weakens hypoxic survival mechanisms in embryos. In addition, correct regulation of the RNA binding protein, SUP-26, a mir-35 family target, is needed for survival in chronic hypoxia. The identification of the full mRNA target repertoire of these miRNAs will reveal the miRNA-regulated network of hypoxic survival mechanisms in C. elegans.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A microRNA family exerts maternal control on sex determination in C. elegans.Genes Dev. 2017 Feb 15;31(4):422-437. doi: 10.1101/gad.290155.116. Epub 2017 Mar 9. Genes Dev. 2017. PMID: 28279983 Free PMC article.
-
A negative regulatory loop between microRNA and Hox gene controls posterior identities in Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS Genet. 2010 Sep 2;6(9):e1001089. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001089. PLoS Genet. 2010. PMID: 20824072 Free PMC article.
-
HRPK-1, a conserved KH-domain protein, modulates microRNA activity during Caenorhabditis elegans development.PLoS Genet. 2019 Oct 4;15(10):e1008067. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008067. eCollection 2019 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 31584932 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal effects of microRNAs in early embryogenesis.RNA Biol. 2018 Feb 1;15(2):165-169. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1402999. Epub 2017 Dec 8. RNA Biol. 2018. PMID: 29120257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic analysis of hypoxia signaling and response in C elegans.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003 May;995:191-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb03222.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003. PMID: 12814951 Review.
Cited by
-
In vivo CRISPR screening for phenotypic targets of the mir-35-42 family in C. elegans.Genes Dev. 2020 Sep 1;34(17-18):1227-1238. doi: 10.1101/gad.339333.120. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Genes Dev. 2020. PMID: 32820039 Free PMC article.
-
The mir-35 Family Links Maternal Germline Sex to Embryonic Viability in Caenorhabditis elegans.G3 (Bethesda). 2019 Mar 7;9(3):901-909. doi: 10.1534/g3.118.200863. G3 (Bethesda). 2019. PMID: 30679246 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Molecular Genetic Explorations of Caenorhabditis elegans MicroRNAs.Genetics. 2018 Jul;209(3):651-673. doi: 10.1534/genetics.118.300291. Genetics. 2018. PMID: 29967059 Free PMC article.
-
miRNAs cooperate in apoptosis regulation during C. elegans development.Genes Dev. 2017 Jan 15;31(2):209-222. doi: 10.1101/gad.288555.116. Epub 2017 Feb 6. Genes Dev. 2017. PMID: 28167500 Free PMC article.
-
Parkinson's disease and microRNAs - Lessons from model organisms and human studies.Exp Gerontol. 2021 Nov;155:111585. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2021.111585. Epub 2021 Oct 8. Exp Gerontol. 2021. PMID: 34634413 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Semenza G. L. Oxygen homeostasis. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med 2, 336–61 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Pocock R. Invited review: decoding the microRNA response to hypoxia. Pflugers Archiv : European journal of physiology 461, 307–15 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Dunwoodie S. L. The role of hypoxia in development of the Mammalian embryo. Dev Cell 17, 755–73 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

