Heterogeneity of epigenetic changes at ischemia/reperfusion- and endotoxin-induced acute kidney injury genes
- PMID: 26061546
- PMCID: PMC4589440
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2015.164
Heterogeneity of epigenetic changes at ischemia/reperfusion- and endotoxin-induced acute kidney injury genes
Abstract
Aberrant gene expression is a molecular hallmark of acute kidney injury (AKI). As epigenetic processes control gene expression in a cell- and environment-defined manner, understanding the epigenetic pathways that regulate genes altered by AKI may open vital new insights into the complexities of disease pathogenesis and identify possible therapeutic targets. Here we used matrix chromatin immunoprecipitation and integrative analysis to study 20 key permissive and repressive epigenetic histone marks at transcriptionally induced Tnf, Ngal, Kim-1, and Icam-1 genes in mouse models of AKI; unilateral renal ischemia/reperfusion, lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and their synergistically injurious combination. Results revealed unexpected heterogeneity of transcriptional and epigenetic responses. Tnf and Ngal were transcriptionally upregulated in response to both treatments individually, and to combination treatment. Kim-1 was induced by ischemia/reperfusion and Icam-1 by LPS only. Epigenetic alterations at these genes exhibited distinct time-dependent changes that shared some similarities, such as reduction in repressive histone modifications, and also had major ischemia/reperfusion versus endotoxin differences. Thus, diversity of changes at AKI genes in response to different insults indicates involvement of several epigenetic pathways. This could be exploited pharmacologically through rational-drug design to alter the course and improve clinical outcomes of this syndrome.
Figures
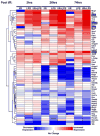
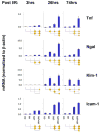
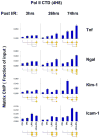
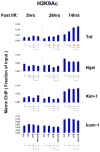
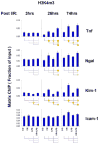
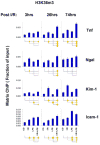
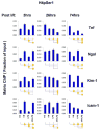
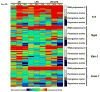
Comment in
-
Epigenetic regulation in acute kidney injury: new light in a dark area.Kidney Int. 2015 Oct;88(4):665-8. doi: 10.1038/ki.2015.229. Kidney Int. 2015. PMID: 26422622 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Transcriptional analysis of kidneys during repair from AKI reveals possible roles for NGAL and KIM-1 as biomarkers of AKI-to-CKD transition.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010 Jun;298(6):F1472-83. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00619.2009. Epub 2010 Feb 24. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20181666
-
Synchronous recruitment of epigenetic modifiers to endotoxin synergistically activated Tnf-α gene in acute kidney injury.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 30;8(7):e70322. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070322. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23936185 Free PMC article.
-
Renal neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin expression in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury in the rat.BMC Nephrol. 2012 Jun 27;13:25. doi: 10.1186/1471-2369-13-25. BMC Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22564340 Free PMC article.
-
NGAL-Siderocalin in kidney disease.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Sep;1823(9):1451-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.06.014. Epub 2012 Jun 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22728330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin-mediated iron traffic in kidney epithelia.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2006 Jul;15(4):442-9. doi: 10.1097/01.mnh.0000232886.81142.58. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2006. PMID: 16775460 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Gene Expression Profiling of Randall's Plaques in Calcium Oxalate Stone Formers.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017 Jan;28(1):333-347. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2015111271. Epub 2016 Jun 13. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 27297950 Free PMC article.
-
Renoprotective approaches and strategies in acute kidney injury.Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Jul;163:58-73. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.03.015. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27108948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PIXUL-ChIP: integrated high-throughput sample preparation and analytical platform for epigenetic studies.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jul 9;47(12):e69. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz222. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30927002 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omic approaches to acute kidney injury and repair.Curr Opin Biomed Eng. 2021 Dec;20:100344. doi: 10.1016/j.cobme.2021.100344. Epub 2021 Sep 21. Curr Opin Biomed Eng. 2021. PMID: 35005326 Free PMC article.
-
EZH2 plays a crucial role in ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury by regulating p38 signaling.Inflamm Res. 2019 Apr;68(4):325-336. doi: 10.1007/s00011-019-01221-3. Epub 2019 Feb 28. Inflamm Res. 2019. PMID: 30820607
References
-
- Chawla LS, Kimmel PL. Acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease: an integrated clinical syndrome. Kidney Int. 2012;82:516–524. - PubMed
-
- Lameire NH, Bagga A, Cruz D, et al. Acute kidney injury: an increasing global concern. Lancet. 2013;382:170–179. - PubMed
-
- Chertow GM, Burdick E, Honour M, et al. Acute kidney injury, mortality, length of stay, and costs in hospitalized patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:3365–3370. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

