NF-κB2/p52:c-Myc:hnRNPA1 Pathway Regulates Expression of Androgen Receptor Splice Variants and Enzalutamide Sensitivity in Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 26056150
- PMCID: PMC4529751
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-1057
NF-κB2/p52:c-Myc:hnRNPA1 Pathway Regulates Expression of Androgen Receptor Splice Variants and Enzalutamide Sensitivity in Prostate Cancer
Abstract
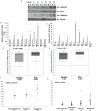
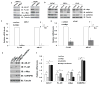
Castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) remains dependent on androgen receptor (AR) signaling. Alternative splicing of the AR to generate constitutively active, ligand-independent variants is one of the principal mechanisms that promote the development of resistance to next-generation antiandrogens such as enzalutamide. Here, we demonstrate that the splicing factor heterogeneous nuclear RNA-binding protein A1 (hnRNPA1) plays a pivotal role in the generation of AR splice variants such as AR-V7. hnRNPA1 is overexpressed in prostate tumors compared with benign prostates, and its expression is regulated by NF-κB2/p52 and c-Myc. CRPC cells resistant to enzalutamide exhibit higher levels of NF-κB2/p52, c-Myc, hnRNPA1, and AR-V7. Levels of hnRNPA1 and AR-V7 are positively correlated with each other in prostate cancer. The regulatory circuit involving NF-κB2/p52, c-Myc, and hnRNPA1 plays a central role in the generation of AR splice variants. Downregulation of hnRNPA1 and consequently of AR-V7 resensitizes enzalutamide-resistant cells to enzalutamide, indicating that enhanced expression of hnRNPA1 may confer resistance to AR-targeted therapies by promoting the generation of splice variants. These findings may provide a rationale for cotargeting these pathways to achieve better efficacy through AR blockade.
©2015 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
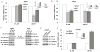
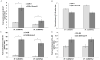

Similar articles
-
NF-κB2/p52 induces resistance to enzalutamide in prostate cancer: role of androgen receptor and its variants.Mol Cancer Ther. 2013 Aug;12(8):1629-37. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0027. Epub 2013 May 22. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013. PMID: 23699654 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin Targets hnRNPA1 to Overcome Enzalutamide Resistance in Prostate Cancer Cells.Mol Cancer Ther. 2017 Dec;16(12):2770-2779. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-17-0030. Epub 2017 Jul 20. Mol Cancer Ther. 2017. PMID: 28729398 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of glucose metabolism by NF-κB2/p52 mediates enzalutamide resistance in castration-resistant prostate cancer cells.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2014 May 6;21(3):435-42. doi: 10.1530/ERC-14-0107. Print 2014 Jun. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24659479 Free PMC article.
-
Androgen receptor splice variants in the era of enzalutamide and abiraterone.Horm Cancer. 2014 Oct;5(5):265-73. doi: 10.1007/s12672-014-0190-1. Epub 2014 Jul 22. Horm Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25048254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AR-V7 and prostate cancer: The watershed for treatment selection?Cancer Treat Rev. 2016 Feb;43:27-35. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2015.12.003. Epub 2015 Dec 18. Cancer Treat Rev. 2016. PMID: 26827690 Review.
Cited by
-
Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Prostate Cancer Development: Therapeutic Implications.Medicines (Basel). 2019 Jul 30;6(3):82. doi: 10.3390/medicines6030082. Medicines (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31366128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Splicing Factors Have an Essential Role in Prostate Cancer Progression and Androgen Receptor Signaling.Biomolecules. 2019 Apr 1;9(4):131. doi: 10.3390/biom9040131. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 30939845 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Androgen receptor variants: RNA-based mechanisms and therapeutic targets.Hum Mol Genet. 2020 Sep 30;29(R1):R19-R26. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddaa089. Hum Mol Genet. 2020. PMID: 32412639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the Lnc-OPHN1-5/androgen receptor/hnRNPA1 complex increases Enzalutamide sensitivity to better suppress prostate cancer progression.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Sep 20;12(10):855. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03966-4. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34545067 Free PMC article.
-
Allosteric alterations in the androgen receptor and activity in prostate cancer.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2017 Sep;24(9):R335-R348. doi: 10.1530/ERC-17-0108. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28808043 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

