Glutaminolysis and autophagy in cancer
- PMID: 26054373
- PMCID: PMC4590661
- DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1053680
Glutaminolysis and autophagy in cancer
Abstract
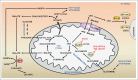
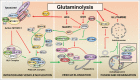
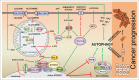
The remarkable metabolic differences between cancer cells and normal cells result in the potential for targeted cancer therapy. The upregulation of glutaminolysis provides energetic advantages to cancer cells. The recently described link between glutaminolysis and autophagy, mediated by MTORC1, may constitute an attractive target for therapeutic strategies. A combination of therapies targeting simultane-ously cell signaling, cancer metabolism, and autophagy can solve therapy resistance and tumor relapse problems, commonly observed in patients treated with most of the current targeted therapies. In this review we summarize the mechanistic link between glutaminolysis and autophagy, and discuss the impacts of these processes on cancer progression and the potential for therapeutic intervention.
Keywords: MTOR; ROS; autophagy; cancer; glutaminolysis; prolyl hydroxylases; α-ketoglutarate.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of Glutaminolysis Inhibits Cell Growth via Down-regulating Mtorc1 Signaling in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Anticancer Res. 2016 Nov;36(11):6021-6029. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.11191. Anticancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27793929
-
Glutaminolysis feeds mTORC1.Cell Cycle. 2012 Nov 15;11(22):4107-8. doi: 10.4161/cc.22632. Epub 2012 Oct 24. Cell Cycle. 2012. PMID: 23095634 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
mTORC1 regulates glutamine metabolism.Cancer Discov. 2013 Jul;3(7):OF25. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-RW2013-106. Epub 2013 May 16. Cancer Discov. 2013. PMID: 23847369
-
Targeting autophagy to overcome drug resistance in cancer therapy.Future Med Chem. 2015 Aug;7(12):1535-42. doi: 10.4155/fmc.15.88. Epub 2015 Aug 26. Future Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 26334206 Review.
-
Reactive oxygen species regulation of autophagy in cancer: implications for cancer treatment.Free Radic Biol Med. 2012 Oct 1;53(7):1399-410. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.07.011. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012. PMID: 22820461 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting glutaminase-mediated glutamine dependence in papillary thyroid cancer.J Mol Med (Berl). 2018 Aug;96(8):777-790. doi: 10.1007/s00109-018-1659-0. Epub 2018 Jun 25. J Mol Med (Berl). 2018. PMID: 29942976
-
Tumor Microenvironment Characteristics of Pancreatic Cancer to Determine Prognosis and Immune-Related Gene Signatures.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Jun 8;8:645024. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.645024. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34169093 Free PMC article.
-
mTORC1 inhibition in cancer cells protects from glutaminolysis-mediated apoptosis during nutrient limitation.Nat Commun. 2017 Jan 23;8:14124. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14124. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28112156 Free PMC article.
-
Restricting Glutamine Uptake Enhances NSCLC Sensitivity to Third-Generation EGFR-TKI Almonertinib.Front Pharmacol. 2021 May 14;12:671328. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.671328. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34054543 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative metabolomic analysis of polyphenic horn development in the dung beetle Onthophagus taurus.PLoS One. 2022 Mar 17;17(3):e0265222. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265222. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35298496 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 2011; 144:646-74; PMID:21376230; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Menon S, Manning BD. Common corruption of the mTOR signaling network in human tumors. Oncogene 2008; 27(Suppl 2):S43-51; PMID:19956179; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.352 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cheong H, Lu C, Lindsten T, Thompson CB. Therapeutic targets in cancer cell metabolism and autophagy. Nat Biotechnol 2012; 30:671-8; PMID:22781696; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2285 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Matés JM, Segura JA, Campos-Sandoval JA, Lobo C, Alonso L, Alonso FJ, Márquez J. Glutamine homeostasis and mitochondrial dynamics. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2009; 41:2051-61; PMID:19703661; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2009.03.003 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wise DR, Thompson CB. Glutamine addiction: a new therapeutic target in cancer. Trends Biochem Sci 2010; 35:427-33; PMID:20570523; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2010.05.003 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
