Glutamine promotes ovarian cancer cell proliferation through the mTOR/S6 pathway
- PMID: 26045471
- PMCID: PMC4500469
- DOI: 10.1530/ERC-15-0192
Glutamine promotes ovarian cancer cell proliferation through the mTOR/S6 pathway
Abstract
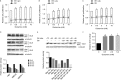
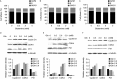
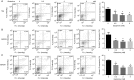
Glutamine is one of the main nutrients used by tumor cells for biosynthesis. Therefore, targeted inhibition of glutamine metabolism may have anti-tumorigenic implications. In the present study, we aimed to evaluate the effects of glutamine on ovarian cancer cell growth. Three ovarian cancer cell lines, HEY, SKOV3, and IGROV-1, were assayed for glutamine dependence by analyzing cytotoxicity, cell cycle progression, apoptosis, cell stress, and glucose/glutamine metabolism. Our results revealed that administration of glutamine increased cell proliferation in all three ovarian cancer cell lines in a dose dependent manner. Depletion of glutamine induced reactive oxygen species and expression of endoplasmic reticulum stress proteins. In addition, glutamine increased the activity of glutaminase (GLS) and glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) by modulating the mTOR/S6 and MAPK pathways. Inhibition of mTOR activity by rapamycin or blocking S6 expression by siRNA inhibited GDH and GLS activity, leading to a decrease in glutamine-induced cell proliferation. These studies suggest that targeting glutamine metabolism may be a promising therapeutic strategy in the treatment of ovarian cancer.
Keywords: glutamate dehydrogenase; glutaminase; mTOR/S6; ovarian cancer; siRNA.
© 2015 The authors.
Figures
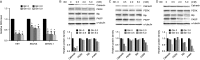
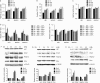
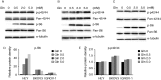
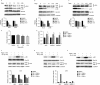
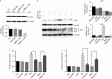
Similar articles
-
Glucose promotes cell proliferation, glucose uptake and invasion in endometrial cancer cells via AMPK/mTOR/S6 and MAPK signaling.Gynecol Oncol. 2015 Sep;138(3):668-75. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2015.06.036. Epub 2015 Jun 30. Gynecol Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26135947 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamine promotes the proliferation of epithelial cells via mTOR/S6 pathway in oral lichen planus.J Oral Pathol Med. 2023 Feb;52(2):150-160. doi: 10.1111/jop.13391. Epub 2022 Dec 19. J Oral Pathol Med. 2023. PMID: 36459062
-
The HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, simvastatin, exhibits anti-metastatic and anti-tumorigenic effects in ovarian cancer.Oncotarget. 2016 Jan 5;7(1):946-60. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5834. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26503475 Free PMC article.
-
Hopefully devoted to Q: targeting glutamine addiction in cancer.Br J Cancer. 2017 May 23;116(11):1375-1381. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2017.113. Epub 2017 Apr 25. Br J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28441384 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New progress of glutamine metabolism in the occurrence, development, and treatment of ovarian cancer from mechanism to clinic.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 29;12:1018642. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1018642. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36523985 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dual inhibition of glycolysis and glutaminolysis as a therapeutic strategy in the treatment of ovarian cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 29;8(38):63551-63561. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18854. eCollection 2017 Sep 8. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28969010 Free PMC article.
-
Branched-chain amino acid catabolism promotes ovarian cancer cell proliferation via phosphorylation of mTOR.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 18:2024.10.15.618560. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.15.618560. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39464074 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Dual contribution of the mTOR pathway and of the metabolism of amino acids in prostate cancer.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2022 Oct;45(5):831-859. doi: 10.1007/s13402-022-00706-4. Epub 2022 Aug 29. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2022. PMID: 36036882 Review.
-
Glutamine supplementation enhances development of in vitro-produced porcine embryos and increases leucine consumption from the medium.Biol Reprod. 2018 Nov 1;99(5):938-948. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioy129. Biol Reprod. 2018. PMID: 29860318 Free PMC article.
-
MUC1 facilitates metabolomic reprogramming in triple-negative breast cancer.PLoS One. 2017 May 2;12(5):e0176820. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176820. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28464016 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

