Activation of transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 induces apoptosis in hippocampus through downregulating PI3K/Akt and upregulating p38 MAPK signaling pathways
- PMID: 26043075
- PMCID: PMC4669828
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2015.146
Activation of transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 induces apoptosis in hippocampus through downregulating PI3K/Akt and upregulating p38 MAPK signaling pathways
Abstract
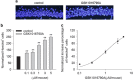
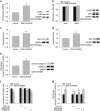
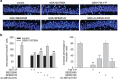
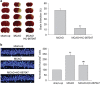
Transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) is a calcium-permeable cation channel that is sensitive to cell swelling, arachidonic acid and its metabolites, epoxyeicosatrienoic acids, which are associated with cerebral ischemia. The activation of TRPV4 induces cytotoxicity in many types of cells, accompanied by an increase in the intracellular free calcium concentration. TRPV4 activation modulates the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and phosphatidyl inositol 3 kinase (PI3K)/ protein kinase B (Akt) signaling pathways that regulate cell death and survival. Herein, we examined TRPV4-induced neuronal apoptosis by intracerebroventricular (ICV) injection of a TRPV4 agonist (GSK1016790A) and assessed its involvement in cerebral ischemic injury. ICV injection of GSK1016790A dose-dependently induced apoptosis in the mouse hippocampi (GSK-injected mice). The protein level of phosphorylated p38 MAPK (p-p38 MAPK) was markedly increased and that of phosphorylated c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase (p-JNK) was virtually unchanged. TRPV4 activation also decreased Bcl-2/Bax protein ratio and increased the cleaved caspase-3 protein level, and these effects were blocked by a PI3K agonist and a p38 MAPK antagonist, but were unaffected by a JNK antagonist. ICV injection of the TRPV4 antagonist HC-067047 reduced brain infarction after reperfusion for 48 h in mice with middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). In addition, HC-067047 treatment attenuated the decrease in the phosphorylated Akt protein level and the increase in p-p38 MAPK protein level at 48 h after MCAO, while the increase in p-JNK protein level remained unchanged. Finally, the decreased Bcl-2/Bax protein ratio and the increased cleaved caspase-3 protein level at 48 h after MCAO were markedly attenuated by HC-067047. We conclude that activation of TRPV4 induces apoptosis by downregulating PI3K/Akt and upregulating p38 MAPK signaling pathways, which is involved in cerebral ischemic injury.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 4 is Involved in Neuronal Injury in Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion in Mice.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Jan;53(1):8-17. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-8992-2. Epub 2014 Nov 18. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 25399955
-
Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 4 Activation-Induced Increase in Glycine-Activated Current in Mouse Hippocampal Pyramidal Neurons.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;45(3):1084-1096. doi: 10.1159/000487350. Epub 2018 Feb 7. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29439248
-
Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 4-Induced Modulation of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels in Hippocampal Neurons.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Jan;53(1):759-768. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-9038-5. Epub 2014 Dec 15. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 25502461
-
Medicinal Herbs and Their Derived Ingredients Protect against Cognitive Decline in In Vivo Models of Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 25;23(19):11311. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911311. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kinase Signaling in Apoptosis Induced by Saturated Fatty Acids in Pancreatic β-Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Sep 12;17(9):1400. doi: 10.3390/ijms17091400. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27626409 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nrf2 Regulates Oxidative Stress and Its Role in Cerebral Ischemic Stroke.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Nov 30;11(12):2377. doi: 10.3390/antiox11122377. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36552584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancement in research on the role of the transient receptor potential vanilloid channel in cerebral ischemic injury (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2021 Aug;22(2):881. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10313. Epub 2021 Jun 15. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34194559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of TRPV4 in Regulating Innate Immune Cell Function in Lung Inflammation.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 26;11:1211. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01211. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32676078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elevated TRPV4 Levels Contribute to Endothelial Damage and Scarring in Experimental Spinal Cord Injury.J Neurosci. 2020 Feb 26;40(9):1943-1955. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2035-19.2020. Epub 2020 Jan 23. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31974206 Free PMC article.
-
Methylglyoxal Causes Cell Death in Neural Progenitor Cells and Impairs Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis.Neurotox Res. 2016 Apr;29(3):419-31. doi: 10.1007/s12640-015-9588-y. Epub 2015 Dec 21. Neurotox Res. 2016. PMID: 26690780
References
-
- Garcia-Elias A, Mrkonjić S, Jung C, Pardo-Pastor C, Vicente R, Valverde MA. The TRPV4 channel. Handb Exp Pharmacol 2014; 222: 293–319. - PubMed
-
- Vincent F, Duncton MA. TRPV4 agonists and antagonists. Curr Top Med Chem 2011; 11: 2216–2226. - PubMed
-
- Lee JC, Choe SY. Age-related changes in the distribution of transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 channel (TRPV4) in the central nervous system of rats. J Mol Histol 2014; 45: 497–505. - PubMed
-
- Shi M, Du F, Liu Y, Li L, Cai J, Zhang GF et al. Glial cell-expressed mechanosensitive channel TRPV4 mediates infrasound-induced neuronal impairment. Acta Neuropathol 2013; 126: 725–739. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

