Cell or cell membrane-based drug delivery systems
- PMID: 26000058
- PMCID: PMC4440443
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.11852
Cell or cell membrane-based drug delivery systems
Abstract
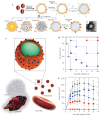
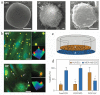
Natural cells have been explored as drug carriers for a long period. They have received growing interest as a promising drug delivery system (DDS) until recently along with the development of biology and medical science. The synthetic materials, either organic or inorganic, are found to be with more or less immunogenicity and/or toxicity. The cells and extracellular vesicles (EVs), are endogenous and thought to be much safer and friendlier. Furthermore, in view of their host attributes, they may achieve different biological effects and/or targeting specificity, which can meet the needs of personalized medicine as the next generation of DDS. In this review, we summarized the recent progress in cell or cell membrane-based DDS and their fabrication processes, unique properties and applications, including the whole cells, EVs and cell membrane coated nanoparticles. We expect the continuing development of this cell or cell membrane-based DDS will promote their clinic applications.
Keywords: cell membrane; drug delivery system; extracellular vesicle; nanoparticle; tumor.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Research Progress in Bioinspired Drug Delivery Systems.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2020 Sep;17(9):1269-1288. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2020.1783235. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2020. PMID: 32543953 Review.
-
Prospects and challenges of extracellular vesicle-based drug delivery system: considering cell source.Drug Deliv. 2020 Dec;27(1):585-598. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2020.1748758. Drug Deliv. 2020. PMID: 32264719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell membrane capsule: a novel natural tool for antitumour drug delivery.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2019 Mar;16(3):251-269. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2019.1581762. Epub 2019 Mar 7. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2019. PMID: 30742557 Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles for drug delivery.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016 Nov 15;106(Pt A):148-156. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2016.02.006. Epub 2016 Feb 27. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016. PMID: 26928656 Review.
-
Membrane Derived Vesicles as Biomimetic Carriers for Targeted Drug Delivery System.Curr Top Med Chem. 2020;20(27):2472-2492. doi: 10.2174/1568026620666200922113054. Curr Top Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32962615 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioactive nanotherapeutic trends to combat triple negative breast cancer.Bioact Mater. 2021 Mar 13;6(10):3269-3287. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.02.037. eCollection 2021 Oct. Bioact Mater. 2021. PMID: 33778204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maximizing liposome tumor delivery by hybridizing with tumor-derived extracellular vesicles.Nanoscale. 2024 Sep 12;16(35):16652-16663. doi: 10.1039/d4nr02191f. Nanoscale. 2024. PMID: 39171636
-
Simultaneously Modulating HIF-1α and HIF-2α and Optimizing Macrophage Polarization through the Biomimetic Gene Vector toward the Treatment of Osteoarthritis.Biomater Res. 2024 Jul 29;28:0059. doi: 10.34133/bmr.0059. eCollection 2024. Biomater Res. 2024. PMID: 39076894 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinspired and Biomimetic Nanomedicines for Targeted Cancer Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2022 May 23;14(5):1109. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14051109. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35631695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PD-1 Cellular Nanovesicles Carrying Gemcitabine to Inhibit the Proliferation of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cell.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jun 14;14(6):1263. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14061263. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35745835 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hubbell JA, Langer R. Translating materials design to the clinic. Nat Mater. 2013;12:963–6. - PubMed
-
- Hu C-MJ, Fang RH, Luk BT. et al. Polymeric nanotherapeutics: clinical development and advances in stealth functionalization strategies. Nanoscale. 2013;6:65–75. - PubMed
-
- Wicki A, Witzigmann D, Balasubramanian V. et al. Nanomedicine in cancer therapy: Challenges, opportunities, and clinical applications. J Control Release. 2015;200:138–157. - PubMed
-
- Tan SW, Li X, Guo Y. et al. Lipid-enveloped hybrid nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nanoscale. 2013;5:860–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

