Processing Body Formation Limits Proinflammatory Cytokine Synthesis in Endotoxin-Tolerant Monocytes and Murine Septic Macrophages
- PMID: 25998849
- PMCID: PMC4618041
- DOI: 10.1159/000381915
Processing Body Formation Limits Proinflammatory Cytokine Synthesis in Endotoxin-Tolerant Monocytes and Murine Septic Macrophages
Abstract
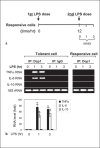
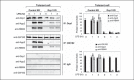
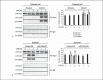
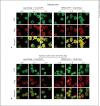
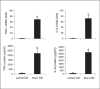
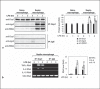
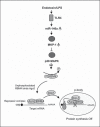
An anti-inflammatory phenotype with pronounced immunosuppression develops during sepsis, during which time neutrophils and monocytes/macrophages limit their Toll-like receptor 4 responses to bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS/endotoxin). We previously reported that during this endotoxin-tolerant state, distinct signaling pathways differentially repress transcription and translation of proinflammatory cytokines such as TNFα and IL-6. Sustained endotoxin tolerance contributes to sepsis mortality. While transcription repression requires chromatin modifications, a translational repressor complex of Argonaute 2 (Ago2) and RNA-binding motif protein 4 (RBM4), which bind the 3'-UTR of TNFα and IL-6 mRNA, limits protein synthesis. Here, we show that Dcp1 supports the assembly of the Ago2 and RBM4 repressor complex into cytoplasmic processing bodies (p-bodies) in endotoxin-tolerant THP-1 human monocytes following stimulation with LPS, resulting in translational repression and limiting protein synthesis. Importantly, this translocation process is reversed by Dcp1 knockdown, which restores TNFα and IL-6 protein levels. We also find this translational repression mechanism in primary macrophages of septic mice. Because p-body formation is a critical step in mRNA translation repression, we conclude that Dcp1 is a major component of the translational repression machinery of endotoxin tolerance and may contribute to sepsis outcome.
© 2015 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-146a and RBM4 form a negative feed-forward loop that disrupts cytokine mRNA translation following TLR4 responses in human THP-1 monocytes.Immunol Cell Biol. 2013 Sep;91(8):532-40. doi: 10.1038/icb.2013.37. Epub 2013 Jul 30. Immunol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23897118 Free PMC article.
-
Immune responsive gene 1 (IRG1) promotes endotoxin tolerance by increasing A20 expression in macrophages through reactive oxygen species.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jun 7;288(23):16225-16234. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.454538. Epub 2013 Apr 22. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23609450 Free PMC article.
-
Endotoxin tolerance in rats: expression of TNF-alpha, IL-6, IL-10, VCAM-1 AND HSP 70 in lung and liver during endotoxin shock.Cytokine. 1999 Oct;11(10):796-804. doi: 10.1006/cyto.1998.0490. Cytokine. 1999. PMID: 10525319
-
Immune Mechanisms Underlying Susceptibility to Endotoxin Shock in Aged Hosts: Implication in Age-Augmented Generalized Shwartzman Reaction.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jul 2;20(13):3260. doi: 10.3390/ijms20133260. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31269748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endotoxin tolerance: a review.Crit Care Med. 2002 Jan;30(1 Suppl):S64-73. Crit Care Med. 2002. PMID: 11782563 Review.
Cited by
-
RBM4 modulates the proliferation and expression of inflammatory factors via the alternative splicing of regulatory factors in HeLa cells.Mol Genet Genomics. 2020 Jan;295(1):95-106. doi: 10.1007/s00438-019-01606-3. Epub 2019 Sep 5. Mol Genet Genomics. 2020. PMID: 31489484
-
Transcriptomic profile investigations highlight a putative role for NUDT16 in sepsis.J Cell Mol Med. 2022 Mar;26(5):1714-1721. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17240. Epub 2022 Feb 17. J Cell Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35174610 Free PMC article.
-
AMP-Activated Protein Kinase and Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3β Modulate the Severity of Sepsis-Induced Lung Injury.Mol Med. 2016 Apr;21(1):937-950. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2015.00198. Epub 2015 Nov 30. Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 26650187 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of novel genes related to immune microenvironment in polycystic ovary syndrome.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Oct 25;103(43):e40229. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040229. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39470566 Free PMC article.
-
Forsythoside A Modulates Zymosan-Induced Peritonitis in Mice.Molecules. 2018 Mar 6;23(3):593. doi: 10.3390/molecules23030593. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29509714 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bianchi ME. Editorial: A recipe for inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. 2009;86:471–472. - PubMed
-
- Biswas SK, Lopez-Collazo E. Endotoxin tolerance: new mechanisms, molecules and clinical significance. Trends Immunol. 2009;30:475–487. - PubMed
-
- Hotchkiss RS, Karl IE. The pathophysiology and treatment of sepsis. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:138–150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

