Increased production of BDNF in colonic epithelial cells induced by fecal supernatants from diarrheic IBS patients
- PMID: 25998025
- PMCID: PMC4441152
- DOI: 10.1038/srep10121
Increased production of BDNF in colonic epithelial cells induced by fecal supernatants from diarrheic IBS patients
Abstract
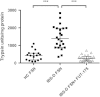
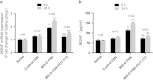
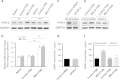
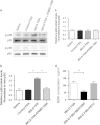
Colonic brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) plays an essential role in pathogenesis of abdominal pain in diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-D), but regulation on its expression remains unclear. We investigated the role of fecal supernatants (FSN) from IBS-D patients on regulating BDNF expression in colonic epithelial cells of human and mice. Using human Caco-2 cells, we found that IBS-D FSN significantly increased BDNF mRNA and protein levels compared to control FSN, which were remarkably suppressed by the serine protease inhibitor. To further explore the potential mechanisms, we investigated the impact of protease-activated receptor-2 (PAR-2) on BDNF expression. We found a significant increase in PAR-2 expression in Caco-2 after IBS-D FSN stimulation. Knockdown of PAR-2 significantly inhibited IBS-D FSN-induced upregulation of BDNF. Moreover, we found that phosphorylation of p38 MAPK, not NF-κB p65, contributed to PAR-2-mediated BDNF overexpression. To confirm these results, we intracolonically infused IBS-D or control FSN in mice and found that IBS-D FSN significantly elevated colonic BDNF and visceral hypersensitivity in mice, which were both suppressed by the inhibitor of serine protease or antagonist of PAR-2. Together, our data indicate that activation of PAR-2 signaling by IBS-D FSN promotes expression of colonic BDNF, thereby contributing to IBS-like visceral hypersensitivity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protease Activated Receptor-2 Induces Immune Activation and Visceral Hypersensitivity in Post-infectious Irritable Bowel Syndrome Mice.Dig Dis Sci. 2019 Mar;64(3):729-739. doi: 10.1007/s10620-018-5367-y. Epub 2018 Nov 16. Dig Dis Sci. 2019. PMID: 30446929
-
Luminal cysteine-proteases degrade colonic tight junction structure and are responsible for abdominal pain in constipation-predominant IBS.Am J Gastroenterol. 2013 Aug;108(8):1322-31. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2013.152. Epub 2013 May 28. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23711626
-
Colonic N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor contributes to visceral hypersensitivity in irritable bowel syndrome.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Apr;32(4):828-836. doi: 10.1111/jgh.13588. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 27575648
-
Protease activated receptor 2: a new target for IBS treatment.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2008 Aug;12 Suppl 1:95-102. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2008. PMID: 18924448 Review.
-
Updates on the epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management of postinfectious irritable bowel syndrome.Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2020 Oct;33(5):411-418. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0000000000000666. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32833689 Review.
Cited by
-
Somatization in patients with predominant diarrhoea irritable bowel syndrome: the role of the intestinal barrier function and integrity.BMC Gastroenterol. 2021 May 22;21(1):235. doi: 10.1186/s12876-021-01820-7. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 34022802 Free PMC article.
-
Newly developed serine protease inhibitors decrease visceral hypersensitivity in a post-inflammatory rat model for irritable bowel syndrome.Br J Pharmacol. 2018 Sep;175(17):3516-3533. doi: 10.1111/bph.14396. Epub 2018 Jul 23. Br J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29911328 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Variations in TrkB.T1 Isoform and Their Association With Somatic and Psychological Symptoms in Individuals With IBS.J Pain. 2024 Nov;25(11):104634. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2024.104634. Epub 2024 Jul 14. J Pain. 2024. PMID: 39004388
-
A review of dorsal root ganglia and primary sensory neuron plasticity mediating inflammatory and chronic neuropathic pain.Neurobiol Pain. 2024 Jan 20;15:100151. doi: 10.1016/j.ynpai.2024.100151. eCollection 2024 Jan-Jun. Neurobiol Pain. 2024. PMID: 38314104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Probiotic modulation of the microbiota-gut-brain axis and behaviour in zebrafish.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 15;6:30046. doi: 10.1038/srep30046. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27416816 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gralnek I. M., Hays R. D., Kilbourne A., Naliboff B. & Mayer E. A. The impact of irritable bowel syndrome on health-related quality of life. Gastroenterology 119, 654–60 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Drossman D. A., Camilleri M., Mayer E. A. & Whitehead W. E. AGA technical review on irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 123, 2108–31 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Cremon C. et al. Intestinal serotonin release, sensory neuron activation, and abdominal pain in irritable bowel syndrome. Am J. Gastroenterol 106, 1290–8 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Barbara G. et al. Mast cell-dependent excitation of visceral-nociceptive sensory neurons in irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 132, 26–37 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Merighi A. et al. BDNF as a pain modulator. Prog. Neurobiol. 85, 297–317 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

