Diabetes induces GABA receptor plasticity in murine vagal motor neurons
- PMID: 25995347
- PMCID: PMC4512246
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00209.2015
Diabetes induces GABA receptor plasticity in murine vagal motor neurons
Abstract
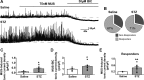
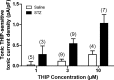
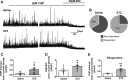
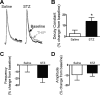
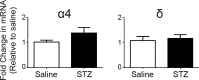
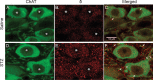
Autonomic dysregulation accompanies type-1 diabetes, and synaptic regulation of parasympathetic preganglionic motor neurons in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus (DMV) is altered after chronic hyperglycemia/hypoinsulinemia. Tonic gamma-aminobutyric acid A (GABAA) inhibition prominently regulates DMV neuron activity, which contributes to autonomic control of energy homeostasis. This study investigated persistent effects of chronic hyperglycemia/hypoinsulinemia on GABAA receptor-mediated inhibition in the DMV after streptozotocin-induced type-1 diabetes using electrophysiological recordings in vitro, quantitative (q)RT-PCR, and immunohistochemistry. Application of the nonspecific GABAA receptor agonist muscimol evoked an outward current of significantly larger amplitude in DMV neurons from diabetic mice than controls. Results from application of 4,5,6,7-tetrahydroisoxazolo[5,4-c]pyridin-3-ol hydrochloride (THIP), a δ-subunit agonist, suggested that GABAA receptors containing δ-subunits contributed to the enhanced inducible tonic GABA current in diabetic mice. Sensitivity to THIP of inhibitory postsynaptic currents in DMV neurons from diabetic mice was also increased. Results from qRT-PCR and immunohistochemical analyses indicated that the altered GABAergic inhibition may be related to increased trafficking of GABAA receptors that contain the δ-subunit, rather than an expression change. Overall these findings suggest increased sensitivity of δ-subunit containing GABAA receptors after several days of hyperglycemia/hypoinsulinemia, which dramatically alters GABAergic inhibition of DMV neurons and could contribute to diabetic autonomic dysregulation.
Keywords: GABA; diabetes; tonic current.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional and molecular plasticity of γ and α1 GABAA receptor subunits in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus after experimentally induced diabetes.J Neurophysiol. 2017 Nov 1;118(5):2833-2841. doi: 10.1152/jn.00085.2017. Epub 2017 Aug 23. J Neurophysiol. 2017. PMID: 28835522 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamatergic drive facilitates synaptic inhibition of dorsal vagal motor neurons after experimentally induced diabetes in mice.J Neurophysiol. 2016 Sep 1;116(3):1498-506. doi: 10.1152/jn.00325.2016. Epub 2016 Jul 6. J Neurophysiol. 2016. PMID: 27385796 Free PMC article.
-
GABAA receptor currents in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus in females: influence of ovarian cycle and 5α-reductase inhibition.J Neurophysiol. 2019 Nov 1;122(5):2130-2141. doi: 10.1152/jn.00039.2019. Epub 2019 Oct 9. J Neurophysiol. 2019. PMID: 31596653 Free PMC article.
-
Extrasynaptic GABAA receptors are critical targets for sedative-hypnotic drugs.J Clin Sleep Med. 2006 Apr 15;2(2):S12-8. J Clin Sleep Med. 2006. PMID: 17557502 Review.
-
Postsynaptic plasticity of GABAergic synapses.Neuropharmacology. 2020 Jun 1;169:107643. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.05.020. Epub 2019 May 17. Neuropharmacology. 2020. PMID: 31108109 Review.
Cited by
-
Early central cardiovagal dysfunction after high fat diet in a murine model.Sci Rep. 2023 Apr 21;13(1):6550. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-32492-w. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37085567 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast Growth Factor 19 Increases the Excitability of Pre-Motor Glutamatergic Dorsal Vagal Complex Neurons From Hyperglycemic Mice.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Nov 11;12:765359. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.765359. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34858337 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Neuroplasticity in the Nucleus Tractus Solitarius and Increased Risk of Sudden Death in Mice with Acquired Temporal Lobe Epilepsy.eNeuro. 2017 Oct 30;4(5):ENEURO.0319-17.2017. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0319-17.2017. eCollection 2017 Sep-Oct. eNeuro. 2017. PMID: 29085908 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Kinase C-Dependent Effects of Neurosteroids on Synaptic GABAA Receptor Inhibition Require the δ-Subunit.Front Physiol. 2021 Oct 25;12:742838. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.742838. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34759836 Free PMC article.
-
BHF177 Suppresses Diabetic Neuropathic Pain by Blocking PKC/CaMKII/ERK1/2/CREB Signaling Pathway through Activating GABAB Receptor.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Nov 17;2022:4661519. doi: 10.1155/2022/4661519. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 36439691 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahren B. Autonomic regulation of islet hormone secretion–implications for health and disease. Diabetologia 43: 393–410, 2000. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

