IMP3 promotes stem-like properties in triple-negative breast cancer by regulating SLUG
- PMID: 25982283
- PMCID: PMC5784260
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2015.164
IMP3 promotes stem-like properties in triple-negative breast cancer by regulating SLUG
Abstract
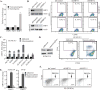
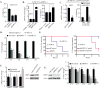
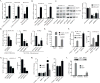
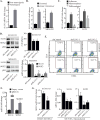
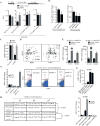
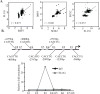
IMP3 (insulin-like growth factor-2 mRNA binding protein 3) is an oncofetal protein whose expression is prognostic for poor outcome in several cancers. Although IMP3 is expressed preferentially in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), its function is poorly understood. We observed that IMP3 expression is significantly higher in tumor initiating than in non-tumor initiating breast cancer cells and we demonstrate that IMP3 contributes to self-renewal and tumor initiation, properties associated with cancer stem cells (CSCs). The mechanism by which IMP3 contributes to this phenotype involves its ability to induce the stem cell factor SOX2. IMP3 does not interact with SOX2 mRNA significantly or regulate SOX2 expression directly. We discovered that IMP3 binds avidly to SNAI2 (SLUG) mRNA and regulates its expression by binding to the 5' UTR. This finding is significant because SLUG has been implicated in breast CSCs and TNBC. Moreover, we show that SOX2 is a transcriptional target of SLUG. These data establish a novel mechanism of breast tumor initiation involving IMP3 and they provide a rationale for its association with aggressive disease and poor outcome.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
IMP3 promotes TNBC stem cell property through miRNA-34a regulation.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 May;22(9):2688-2696. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201805_14965. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29771420
-
Differential expression of epithelial–mesenchymal transition and stem cell markers in intrinsic subtypes of breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015 Nov;154(1):45-55. doi: 10.1007/s10549-015-3598-6. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015. PMID: 26467042
-
IMP3 Stabilization of WNT5B mRNA Facilitates TAZ Activation in Breast Cancer.Cell Rep. 2018 May 29;23(9):2559-2567. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.04.113. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 29847788 Free PMC article.
-
Oncofetal protein IMP3, a new cancer biomarker.Adv Anat Pathol. 2014 May;21(3):191-200. doi: 10.1097/PAP.0000000000000021. Adv Anat Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24713990 Review.
-
The Oncogenic Functions of Insulin-like Growth Factor 2 mRNA-Binding Protein 3 in Human Carcinomas.Curr Pharm Des. 2020;26(32):3939-3954. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666200413080936. Curr Pharm Des. 2020. PMID: 32282295 Review.
Cited by
-
The emerging role of RNA N6-methyladenosine methylation in breast cancer.Biomark Res. 2021 May 27;9(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s40364-021-00295-8. Biomark Res. 2021. PMID: 34044876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phenotypic Plasticity: Driver of Cancer Initiation, Progression, and Therapy Resistance.Cell Stem Cell. 2019 Jan 3;24(1):65-78. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2018.11.011. Epub 2018 Dec 13. Cell Stem Cell. 2019. PMID: 30554963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IGF2BP3 mediates the mRNA degradation of NF1 to promote triple-negative breast cancer progression via an m6A-dependent manner.Clin Transl Med. 2023 Sep;13(9):e1427. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1427. Clin Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37743642 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous Neoantigen-Specific CD8 T Cells Identified in Two Glioblastoma Models Using a Cancer Immunogenomics Approach.Cancer Immunol Res. 2016 Dec;4(12):1007-1015. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-16-0156. Epub 2016 Oct 31. Cancer Immunol Res. 2016. PMID: 27799140 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-like growth factor II mRNA-binding protein 3 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion in human glioblastoma.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 May 15;12:3661-3670. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S200901. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31190868 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bolos V, Peinado H, Perez-Moreno MA, Fraga MF, Esteller M, Cano A. The transcription factor Slug represses E-cadherin expression and induces epithelial to mesenchymal transitions: a comparison with Snail and E47 repressors. Journal of cell science. 2003;116:499–511. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

