miRNA expression atlas in male rat
- PMID: 25977763
- PMCID: PMC4322570
- DOI: 10.1038/sdata.2014.5
miRNA expression atlas in male rat
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small (~22 nucleotide) noncoding RNAs that play pivotal roles in regulation of gene expression. The value of miRNAs as circulating biomarkers is now broadly recognized; such tissue-specific biomarkers can be used to monitor tissue injury and several pathophysiological conditions in organs. In addition, miRNA profiles of normal organs and tissues are important for obtaining a better understanding of the source of modulated miRNAs in blood and how those modulations reflect various physiological and toxicological conditions. This work was aimed at creating an miRNA atlas in rats, as part of a collaborative effort with the Toxicogenomics Informatics Project in Japan (TGP2). We analyzed genome-wide miRNA profiles of 55 different organs and tissues obtained from normal male rats using miRNA arrays. The work presented herein represents a comprehensive dataset derived from normal samples profiled in a single study. Here we present the whole dataset with miRNA profiles of multiple organs, as well as precise information on experimental procedures and organ-specific miRNAs identified in this dataset.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
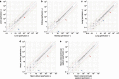

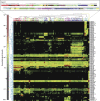

Similar articles
-
The beagle dog MicroRNA tissue atlas: identifying translatable biomarkers of organ toxicity.BMC Genomics. 2016 Aug 17;17:649. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2958-x. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27535741 Free PMC article.
-
The Rat microRNA body atlas; Evaluation of the microRNA content of rat organs through deep sequencing and characterization of pancreas enriched miRNAs as biomarkers of pancreatic toxicity in the rat and dog.BMC Genomics. 2016 Aug 30;17(1):694. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2956-z. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27576563 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of microRNA signatures of distinct mammary epithelial cell types with their gene expression and epigenetic portraits.Breast Cancer Res. 2015 Jun 18;17(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s13058-015-0585-0. Breast Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26080807 Free PMC article.
-
Small RNAs have a large impact: circulating microRNAs as biomarkers for human diseases.RNA Biol. 2012 Jun;9(6):850-9. doi: 10.4161/rna.20378. Epub 2012 Jun 1. RNA Biol. 2012. PMID: 22699556 Review.
-
Circulating miRNA profiling to identify biomarkers of dysmetabolism.Biomark Med. 2012 Dec;6(6):729-42. doi: 10.2217/bmm.12.91. Biomark Med. 2012. PMID: 23227838 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs as Guardians of the Prostate: Those Who Stand before Cancer. What Do We Really Know about the Role of microRNAs in Prostate Biology?Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 7;21(13):4796. doi: 10.3390/ijms21134796. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32645914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Co-sequencing and novel delayed anti-correlation identify function for pancreatic enriched microRNA biomarkers in a rat model of acute pancreatic injury.BMC Genomics. 2018 Apr 27;19(1):297. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4657-2. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29699496 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive microRNA-seq transcriptomic profiling across 11 organs, 4 ages, and 2 sexes of Fischer 344 rats.Sci Data. 2022 May 12;9(1):201. doi: 10.1038/s41597-022-01285-7. Sci Data. 2022. PMID: 35551205 Free PMC article.
-
miEAA 2.0: integrating multi-species microRNA enrichment analysis and workflow management systems.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jul 2;48(W1):W521-W528. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa309. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32374865 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of miRNA expression across human tissues.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 May 5;44(8):3865-77. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw116. Epub 2016 Feb 25. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 26921406 Free PMC article.
References
Data Citations
-
- Minami K., Uehara T. 2013. Gene Expression Omnibus. GSE52754
References
-
- Stefani G. & Slack F. J. Small noncoding RNAs in animal development. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9, 219–230 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Jordan S. D. et al. Obesity-induced overexpression of miRNA-143 inhibits insulin-stimulated AKT activation and impairs glucose metabolism. Nat. Cell Biol. 13, 434–446 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

