The Nuclear DNA Sensor IFI16 Acts as a Restriction Factor for Human Papillomavirus Replication through Epigenetic Modifications of the Viral Promoters
- PMID: 25972554
- PMCID: PMC4505635
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00013-15
The Nuclear DNA Sensor IFI16 Acts as a Restriction Factor for Human Papillomavirus Replication through Epigenetic Modifications of the Viral Promoters
Abstract
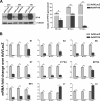
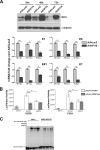
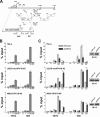
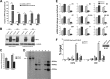
The human interferon-inducible IFI16 protein, an innate immune sensor of intracellular DNA, was recently demonstrated to act as a restriction factor for human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) and herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) infection by inhibiting both viral-DNA replication and transcription. Through the use of two distinct cellular models, this study provides strong evidence in support of the notion that IFI16 can also restrict human papillomavirus 18 (HPV18) replication. In the first model, an immortalized keratinocyte cell line (NIKS) was used, in which the IFI16 protein was knocked down through the use of small interfering RNA (siRNA) technology and overexpressed following transduction with the adenovirus IFI16 (AdVIFI16) vector. The second model consisted of U2OS cells transfected by electroporation with HPV18 minicircles. In differentiated IFI16-silenced NIKS-HPV18 cells, viral-load values were significantly increased compared with differentiated control cells. Consistent with this, IFI16 overexpression severely impaired HPV18 replication in both NIKS and U2OS cells, thus confirming its antiviral restriction activity. In addition to the inhibition of viral replication, IFI16 was also able to reduce viral transcription, as demonstrated by viral-gene expression analysis in U2OS cells carrying episomal HPV18 minicircles and HeLa cells. We also provide evidence that IFI16 promotes the addition of heterochromatin marks and the reduction of euchromatin marks on viral chromatin at both early and late promoters, thus reducing both viral replication and transcription. Altogether, these results argue that IFI16 restricts chromatinized HPV DNA through epigenetic modifications and plays a broad surveillance role against viral DNA in the nucleus that is not restricted to herpesviruses.
Importance: Intrinsic immunity is mediated by cellular restriction factors that are constitutively expressed and active even before a pathogen enters the cell. The host nuclear factor IFI16 acts as a sensor of foreign DNA and an antiviral restriction factor, as recently demonstrated by our group for human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) and herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1). Here, we provide the first evidence that IFI16 inhibits HPV18 replication by repressing viral-gene expression and replication. This antiviral restriction activity was observed in immortalized keratinocytes transfected with the religated genomes and in U2OS cells transfected with HPV18 minicircles, suggesting that it is not cell type specific. We also show that IFI16 promotes the assembly of heterochromatin on HPV DNA. These changes in viral chromatin structure lead to the generation of a repressive state at both early and late HPV18 promoters, thus implicating the protein in the epigenetic regulation of HPV gene expression and replication.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nuclear Innate Immune DNA Sensor IFI16 Is Degraded during Lytic Reactivation of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus (KSHV): Role of IFI16 in Maintenance of KSHV Latency.J Virol. 2016 Sep 12;90(19):8822-41. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01003-16. Print 2016 Oct 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27466416 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory Interaction between the Cellular Restriction Factor IFI16 and Viral pp65 (pUL83) Modulates Viral Gene Expression and IFI16 Protein Stability.J Virol. 2016 Aug 26;90(18):8238-50. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00923-16. Print 2016 Sep 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27384655 Free PMC article.
-
IFI16 restricts HSV-1 replication by accumulating on the hsv-1 genome, repressing HSV-1 gene expression, and directly or indirectly modulating histone modifications.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Nov 6;10(11):e1004503. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004503. eCollection 2014 Nov. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 25375629 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear sensing of viral DNA, epigenetic regulation of herpes simplex virus infection, and innate immunity.Virology. 2015 May;479-480:153-9. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2015.02.009. Epub 2015 Mar 3. Virology. 2015. PMID: 25742715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interferon-inducible DNA-sensor protein IFI16: a key player in the antiviral response.New Microbiol. 2015 Jan;38(1):5-20. Epub 2015 Jan 1. New Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25742143 Review.
Cited by
-
PYHIN Proteins and HPV: Role in the Pathogenesis of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Microorganisms. 2019 Dec 20;8(1):14. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8010014. Microorganisms. 2019. PMID: 31861809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human papillomaviruses sensitize cells to DNA damage induced apoptosis by targeting the innate immune sensor cGAS.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Jul 25;18(7):e1010725. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010725. eCollection 2022 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 35877778 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon Alpha Induces Multiple Cellular Proteins That Coordinately Suppress Hepadnaviral Covalently Closed Circular DNA Transcription.J Virol. 2020 Aug 17;94(17):e00442-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00442-20. Print 2020 Aug 17. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32581092 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Restriction Factors (eRFs) in Virus Infection.Viruses. 2024 Jan 25;16(2):183. doi: 10.3390/v16020183. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38399958 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation and Immune Regulation Mechanisms of PYHIN Family During Microbial Infection.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jan 25;12:809412. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.809412. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35145495 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

