Dengue Virus NS Proteins Inhibit RIG-I/MAVS Signaling by Blocking TBK1/IRF3 Phosphorylation: Dengue Virus Serotype 1 NS4A Is a Unique Interferon-Regulating Virulence Determinant
- PMID: 25968648
- PMCID: PMC4436066
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.00553-15
Dengue Virus NS Proteins Inhibit RIG-I/MAVS Signaling by Blocking TBK1/IRF3 Phosphorylation: Dengue Virus Serotype 1 NS4A Is a Unique Interferon-Regulating Virulence Determinant
Abstract
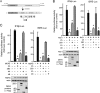
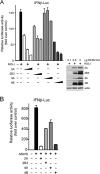
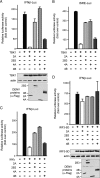
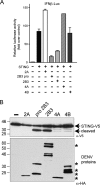
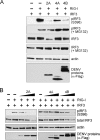
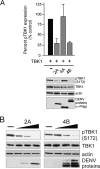
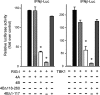
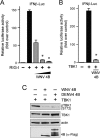
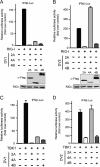
Dengue virus (DENV) replication is inhibited by the prior addition of type I interferon or by RIG-I agonists that elicit RIG-I/MAVS/TBK1/IRF3-dependent protective responses. DENV infection of primary human endothelial cells (ECs) results in a rapid increase in viral titer, which suggests that DENV inhibits replication-restrictive RIG-I/interferon beta (IFN-β) induction pathways within ECs. Our findings demonstrate that DENV serotype 4 (DENV4) nonstructural (NS) proteins NS2A and NS4B inhibited RIG-I-, MDA5-, MAVS-, and TBK1/IKKε-directed IFN-β transcription (>80%) but failed to inhibit IFN-β induction directed by STING or constitutively active IRF3-5D. Expression of NS2A and NS4B dose dependently inhibited the phosphorylation of TBK1 and IRF3, which suggests that they function at the level of TBK1 complex activation. NS2A and NS4B from DENV1/2/4, as well as the West Nile virus NS4B protein, commonly inhibited TBK1 phosphorylation and IFN-β induction. A comparative analysis of NS4A proteins across DENVs demonstrated that DENV1, but not DENV2 or DENV4, NS4A proteins uniquely inhibited TBK1. These findings indicate that DENVs contain conserved (NS2A/NS4B) and DENV1-specific (NS4A) mechanisms for inhibiting RIG-I/TBK1-directed IFN responses. Collectively, our results define DENV NS proteins that restrict IRF3 and IFN responses and thereby facilitate DENV replication and virulence. Unique DENV1-specific NS4A regulation of IFN induction has the potential to be a virulence determinant that contributes to the increased severity of DENV1 infections and the immunodominance of DENV1 responses during tetravalent DENV1-4 vaccination.
Importance: Our findings demonstrate that NS2A and NS4B proteins from dengue virus serotypes 1, 2, and 4 are inhibitors of RIG-I/MDA5-directed interferon beta (IFN-β) induction and that they accomplish this by blocking TBK1 activation. We determined that IFN inhibition is functionally conserved across NS4B proteins from West Nile virus and DENV1, -2, and -4 viruses. In contrast, DENV1 uniquely encodes an extra IFN regulating protein, NS4A, that inhibits TBK1-directed IFN induction. DENV1 is associated with an increase in severe patient disease, and added IFN regulation by the DENV1 NS4A protein may contribute to increased DENV1 replication, immunodominance, and virulence. The regulation of IFN induction by nonstructural (NS) proteins suggests their potential roles in enhancing viral replication and spread and as potential protein targets for viral attenuation. DENV1-specific IFN regulation needs to be considered in vaccine strategies where enhanced DENV1 replication may interfere with DENV2-4 seroconversion within coadministered tetravalent DENV1-4 vaccines.
Copyright © 2015 Dalrymple et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dengue Virus Subverts Host Innate Immunity by Targeting Adaptor Protein MAVS.J Virol. 2016 Jul 27;90(16):7219-7230. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00221-16. Print 2016 Aug 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27252539 Free PMC article.
-
Zika Virus Proteins NS2A and NS4A Are Major Antagonists that Reduce IFN-β Promoter Activity Induced by the MDA5/RIG-I Signaling Pathway.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Oct 28;29(10):1665-1674. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1909.09017. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31581385
-
Hantavirus GnT elements mediate TRAF3 binding and inhibit RIG-I/TBK1-directed beta interferon transcription by blocking IRF3 phosphorylation.J Virol. 2014 Feb;88(4):2246-59. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02647-13. Epub 2014 Jan 3. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24390324 Free PMC article.
-
Innate immunity to dengue virus infection and subversion of antiviral responses.J Mol Biol. 2014 Mar 20;426(6):1148-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.11.023. Epub 2013 Dec 3. J Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24316047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dengue Virus Control of Type I IFN Responses: A History of Manipulation and Control.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2015 Jun;35(6):421-30. doi: 10.1089/jir.2014.0129. Epub 2015 Jan 28. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2015. PMID: 25629430 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Who Regulates Whom? An Overview of RNA Granules and Viral Infections.Viruses. 2016 Jun 28;8(7):180. doi: 10.3390/v8070180. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27367717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dengue Virus 2 NS2B Targets MAVS and IKKε to Evade the Antiviral Innate Immune Response.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 May 28;33(5):600-606. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2210.10006. Epub 2023 Feb 15. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36788451 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Nucleic Acid Sensing in Controlling Microbial and Autoimmune Disorders.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2019;345:35-136. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2018.08.002. Epub 2018 Sep 25. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30904196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay between Zika Virus and Peroxisomes during Infection.Cells. 2019 Jul 15;8(7):725. doi: 10.3390/cells8070725. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31311201 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Response to Dengue and Zika.Annu Rev Immunol. 2018 Apr 26;36:279-308. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-042617-053142. Epub 2018 Jan 18. Annu Rev Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29345964 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lindenbach BD, Murray CL, Thiel H-J, Rice CM. 2013. Flaviviridae. In Knipe DM, Howley PM (ed), Field’s virology, vol 1, 6th ed, vol 1 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, New York, NY.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
