La-related Protein 1 (LARP1) Represses Terminal Oligopyrimidine (TOP) mRNA Translation Downstream of mTOR Complex 1 (mTORC1)
- PMID: 25940091
- PMCID: PMC4481205
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.621730
La-related Protein 1 (LARP1) Represses Terminal Oligopyrimidine (TOP) mRNA Translation Downstream of mTOR Complex 1 (mTORC1)
Abstract
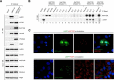
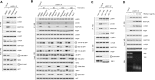
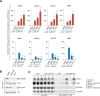
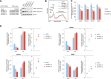
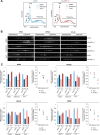
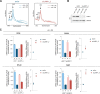
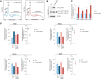
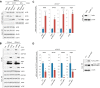
The mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) is a critical regulator of protein synthesis. The best studied targets of mTORC1 in translation are the eukaryotic initiation factor-binding protein 1 (4E-BP1) and ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 (S6K1). In this study, we identify the La-related protein 1 (LARP1) as a key novel target of mTORC1 with a fundamental role in terminal oligopyrimidine (TOP) mRNA translation. Recent genome-wide studies indicate that TOP and TOP-like mRNAs compose a large portion of the mTORC1 translatome, but the mechanism by which mTORC1 controls TOP mRNA translation is incompletely understood. Here, we report that LARP1 functions as a key repressor of TOP mRNA translation downstream of mTORC1. Our data show the following: (i) LARP1 associates with mTORC1 via RAPTOR; (ii) LARP1 interacts with TOP mRNAs in an mTORC1-dependent manner; (iii) LARP1 binds the 5'TOP motif to repress TOP mRNA translation; and (iv) LARP1 competes with the eukaryotic initiation factor (eIF) 4G for TOP mRNA binding. Importantly, from a drug resistance standpoint, our data also show that reducing LARP1 protein levels by RNA interference attenuates the inhibitory effect of rapamycin, Torin1, and amino acid deprivation on TOP mRNA translation. Collectively, our findings demonstrate that LARP1 functions as an important repressor of TOP mRNA translation downstream of mTORC1.
Keywords: 5'-terminal oligopyrimidine (5'TOP) motif; La-related protein 1 (LARP1); TOP mRNA translation; gene expression; mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1); mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR); protein synthesis; repressor protein; ribosome biogenesis; translation.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Proteomic analysis of cap-dependent translation identifies LARP1 as a key regulator of 5'TOP mRNA translation.Genes Dev. 2014 Feb 15;28(4):357-71. doi: 10.1101/gad.231407.113. Genes Dev. 2014. PMID: 24532714 Free PMC article.
-
LARP1 functions as a molecular switch for mTORC1-mediated translation of an essential class of mRNAs.Elife. 2017 Jun 26;6:e25237. doi: 10.7554/eLife.25237. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28650797 Free PMC article.
-
The amino acid sensor GCN2 suppresses terminal oligopyrimidine (TOP) mRNA translation via La-related protein 1 (LARP1).J Biol Chem. 2022 Sep;298(9):102277. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102277. Epub 2022 Jul 19. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35863436 Free PMC article.
-
LARP1 on TOP of ribosome production.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2018 Sep;9(5):e1480. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1480. Epub 2018 May 2. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2018. PMID: 29722158 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Controversies around the function of LARP1.RNA Biol. 2021 Feb;18(2):207-217. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1733787. Epub 2020 Apr 1. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 32233986 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The MYC-Regulated RNA-Binding Proteins hnRNPC and LARP1 Are Drivers of Multiple Myeloma Cell Growth and Disease Progression and Negatively Predict Patient Survival.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 21;15(23):5508. doi: 10.3390/cancers15235508. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38067212 Free PMC article.
-
mRNA 5' terminal sequences drive 200-fold differences in expression through effects on synthesis, translation and decay.PLoS Genet. 2022 Nov 28;18(11):e1010532. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010532. eCollection 2022 Nov. PLoS Genet. 2022. PMID: 36441824 Free PMC article.
-
LARP1 senses free ribosomes to coordinate supply and demand of ribosomal proteins.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 2:2023.11.01.565189. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.01.565189. bioRxiv. 2023. PMID: 37961604 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
The Alphaviral Capsid Protein Inhibits IRAK1-Dependent TLR Signaling.Viruses. 2021 Feb 27;13(3):377. doi: 10.3390/v13030377. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33673546 Free PMC article.
-
So close, no matter how far: multiple paths connecting transcription to mRNA translation in eukaryotes.EMBO Rep. 2020 Sep 3;21(9):e50799. doi: 10.15252/embr.202050799. Epub 2020 Aug 16. EMBO Rep. 2020. PMID: 32803873 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kim D. H., Sarbassov D. D., Ali S. M., King J. E., Latek R. R., Erdjument-Bromage H., Tempst P., Sabatini D. M. (2002) mTOR interacts with raptor to form a nutrient-sensitive complex that signals to the cell growth machinery. Cell 110, 163–175 - PubMed
-
- Hara K., Maruki Y., Long X., Yoshino K., Oshiro N., Hidayat S., Tokunaga C., Avruch J., Yonezawa K. (2002) Raptor, a binding partner of target of rapamycin (TOR), mediates TOR action. Cell 110, 177–189 - PubMed
-
- Loewith R., Jacinto E., Wullschleger S., Lorberg A., Crespo J. L., Bonenfant D., Oppliger W., Jenoe P., Hall M. N. (2002) Two TOR complexes, only one of which is rapamycin sensitive, have distinct roles in cell growth control. Mol. Cell 10, 457–468 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

