Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells as an Immune Parameter in Patients with Concurrent Sunitinib and Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy
- PMID: 25922428
- PMCID: PMC4720266
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-2742
Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells as an Immune Parameter in Patients with Concurrent Sunitinib and Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy
Abstract
Purpose: The clinical effects of sunitinib on human myeloid-derived suppressor cell (MDSC) subsets and correlation of the T-cell-mediated immune responses and clinical outcomes in patients with oligometastases treated by stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) have been evaluated.
Experimental design: The numbers of granulocytic and monocytic MDSC subsets, effector T cells, and regulatory T cells in the peripheral blood were evaluated pre- and post-sunitinib treatment and concurrent with SBRT. Correlations between MDSC, Treg, and T-cell responses and clinical outcomes were analyzed.
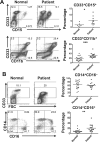
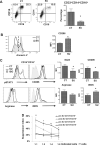
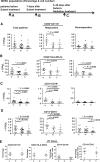
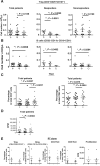
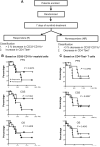
Results: Patients with oligometastases of various cancer types had elevated granulocytic MDSC and certain subsets of monocytic MDSC population. Sunitinib treatment resulted in a significant reduction in monocytic MDSC, phosphorylated STAT3, and arginase levels in monocytic MDSC (CD33(+)CD14(+)CD16(+)), and an increase in T-cell proliferative activity in cancer patients. Interestingly, the effects of sunitinib on reducing the accumulation and immune-suppressive function of MDSC were significantly correlated with Treg reduction, in responders but not in nonresponding patients. SBRT synergized the therapeutic effects of sunitinib, especially as related to decreased numbers of monocytic MDSC, Treg, and B cells, and augmented Tbet expression in primary CD4 and CD8 T cells. These effects were not observed in patients receiving radiation therapy alone. Most interestingly, the responders, defined by sunitinib-mediated reduction in CD33(+)CD11b(+) myeloid cell populations, tend to exhibit improved progression-free survival and cause-specific survival.
Conclusions: Sunitinib treatment increased the efficacy of SBRT in patients with oligometastases by reversing MDSC and Treg-mediated immune suppression and may enhance cancer immune therapy to prevent tumor recurrence post-SBRT.
©2015 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sunitinib mediates reversal of myeloid-derived suppressor cell accumulation in renal cell carcinoma patients.Clin Cancer Res. 2009 Mar 15;15(6):2148-57. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1332. Epub 2009 Mar 10. Clin Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19276286
-
MDSC as a mechanism of tumor escape from sunitinib mediated anti-angiogenic therapy.Int Immunopharmacol. 2011 Jul;11(7):856-61. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2011.01.030. Epub 2011 Feb 11. Int Immunopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21315783 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of concurrent chemoradiotherapy and radiotherapy alone on peripheral myeloid-derived suppressor and T regulatory cells in patients with nasopharyngeal cancer].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2017 Aug 23;39(8):579-583. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2017.08.004. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28835079 Chinese.
-
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells adhere to physiologic STAT3- vs STAT5-dependent hematopoietic programming, establishing diverse tumor-mediated mechanisms of immunologic escape.Immunol Invest. 2012;41(6-7):680-710. doi: 10.3109/08820139.2012.703745. Immunol Invest. 2012. PMID: 23017141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting immune suppressing myeloid-derived suppressor cells in oncology.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2011 Jan;77(1):12-9. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2010.02.004. Epub 2010 Mar 20. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2011. PMID: 20304669 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in gastrointestinal cancer.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2021 Jun;41(6):442-471. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12156. Epub 2021 Mar 27. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2021. PMID: 33773092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in Patients With Acute Pancreatitis With Increased Inhibitory Function.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 14;13:840620. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.840620. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35911709 Free PMC article.
-
Hypofractionated Irradiation Suppressed the Off-Target Mouse Hepatocarcinoma Growth by Inhibiting Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cell-Mediated Immune Suppression.Front Oncol. 2020 Feb 11;10:4. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00004. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32117702 Free PMC article.
-
The NEAT Predictive Model for Survival in Patients with Advanced Cancer.Cancer Res Treat. 2018 Oct;50(4):1433-1443. doi: 10.4143/crt.2017.223. Epub 2018 Jan 24. Cancer Res Treat. 2018. PMID: 29361815 Free PMC article.
-
Chemotherapeutic and targeted agents can modulate the tumor microenvironment and increase the efficacy of immune checkpoint blockades.Mol Cancer. 2021 Feb 4;20(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01317-7. Mol Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33541368 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tree AC, Khoo VS, Eeles RA, Ahmed M, Dearnaley DP, Hawkins MA, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for oligometastases. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:e28–37. - PubMed
-
- Milano MT, Katz AW, Zhang H, Okunieff P. Oligometastases treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy: long-term follow-up of prospective study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;83:878–86. - PubMed
-
- Seiwert TY, Salama JK, Vokes EE. The concurrent chemoradiation paradigm–general principles. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2007;4:86–100. - PubMed
-
- Roskoski R., Jr Sunitinib: a VEGF and PDGF receptor protein kinase and angiogenesis inhibitor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;356:323–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

