N-terminal modifications of cellular proteins: The enzymes involved, their substrate specificities and biological effects
- PMID: 25914051
- PMCID: PMC4692089
- DOI: 10.1002/pmic.201400619
N-terminal modifications of cellular proteins: The enzymes involved, their substrate specificities and biological effects
Abstract
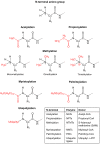
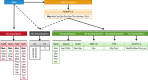
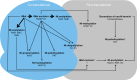
The vast majority of eukaryotic proteins are N-terminally modified by one or more processing enzymes. Enzymes acting on the very first amino acid of a polypeptide include different peptidases, transferases, and ligases. Methionine aminopeptidases excise the initiator methionine leaving the nascent polypeptide with a newly exposed amino acid that may be further modified. N-terminal acetyl-, methyl-, myristoyl-, and palmitoyltransferases may attach an acetyl, methyl, myristoyl, or palmitoyl group, respectively, to the α-amino group of the target protein N-terminus. With the action of ubiquitin ligases, one or several ubiquitin molecules are transferred, and hence, constitute the N-terminal modification. Modifications at protein N-termini represent an important contribution to proteomic diversity and complexity, and are essential for protein regulation and cellular signaling. Consequently, dysregulation of the N-terminal modifying enzymes is implicated in human diseases. We here review the different protein N-terminal modifications occurring co- or post-translationally with emphasis on the responsible enzymes and their substrate specificities.
Keywords: Acetylation; Cell biology; N-terminal; Protein modification; Substrate specificity; α-amino group.
© 2015 The Authors. PROTEOMICS Published by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Archaeal N-terminal protein maturation commonly involves N-terminal acetylation: a large-scale proteomics survey.J Mol Biol. 2006 Oct 6;362(5):915-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.07.086. Epub 2006 Aug 3. J Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16950390
-
Protein alpha-N-acetylation studied by N-terminomics.FEBS J. 2011 Oct;278(20):3822-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08230.x. Epub 2011 Aug 2. FEBS J. 2011. PMID: 21736701 Review.
-
Targeted large-scale analysis of protein acetylation.Proteomics. 2011 Feb;11(4):571-89. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201000397. Epub 2011 Jan 18. Proteomics. 2011. PMID: 21246731 Review.
-
Predicting N-terminal acetylation based on feature selection method.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008 Aug 8;372(4):862-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.05.143. Epub 2008 Jun 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008. PMID: 18533108
-
Characterization of N-terminal protein modifications in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA14.J Proteomics. 2015 Jan 30;114:214-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2014.11.006. Epub 2014 Nov 21. J Proteomics. 2015. PMID: 25464366
Cited by
-
Application of System Biology to Explore the Association of Neprilysin, Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2), and Carbonic Anhydrase (CA) in Pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2.Biol Proced Online. 2020 Jun 19;22:11. doi: 10.1186/s12575-020-00124-6. eCollection 2020. Biol Proced Online. 2020. PMID: 32572334 Free PMC article.
-
Protein cleavage influences surface protein presentation in Mycoplasma pneumoniae.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 24;11(1):6743. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86217-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33762641 Free PMC article.
-
A bipartite chromatophore transit peptide and N-terminal protein processing in the Paulinella chromatophore.Plant Physiol. 2022 May 3;189(1):152-164. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiac012. Plant Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35043947 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and Functional Basis of Potent Inhibition of Leishmanial Leucine Aminopeptidase by Peptidomimetics.ACS Omega. 2021 Jul 13;6(29):19076-19085. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c02386. eCollection 2021 Jul 27. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 34337246 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of native lens connexin 46/50 intercellular channels by cryo-EM.Nature. 2018 Dec;564(7736):372-377. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0786-7. Epub 2018 Dec 12. Nature. 2018. PMID: 30542154 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sherman F, Stewart JW, Tsunasawa S. Methionine or not methionine at the beginning of a protein. Bioessays. 1985;3:27–31. - PubMed
-
- Starheim KK, Gevaert K, Arnesen T. Protein N-terminal acetyltransferases: when the start matters. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2012;37:152–161. - PubMed
-
- Martin DD, Beauchamp E, Berthiaume LG. Post-translational myristoylation: Fat matters in cellular life and death. Biochimie. 2011;93:18–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

