Astrocyte NMDA receptors' activity sustains neuronal survival through a Cdk5-Nrf2 pathway
- PMID: 25909891
- PMCID: PMC4648333
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2015.49
Astrocyte NMDA receptors' activity sustains neuronal survival through a Cdk5-Nrf2 pathway
Abstract
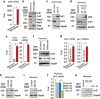
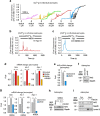
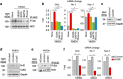
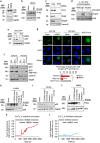
Neurotransmission unavoidably increases mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. However, the intrinsic antioxidant defense of neurons is weak and hence the mechanism whereby these cells are physiologically protected against oxidative damage is unknown. Here we found that the antioxidant defense of neurons is repressed owing to the continuous protein destabilization of the master antioxidant transcriptional activator, nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor-2 (Nrf2). By contrast, Nrf2 is highly stable in neighbor astrocytes explaining their robust antioxidant defense and resistance against oxidative stress. We also show that subtle and persistent stimulation of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors (NMDAR) in astrocytes, through a mechanism not requiring extracellular Ca²⁺ influx, upregulates a signal transduction pathway involving phospholipase C-mediated endoplasmic reticulum release of Ca²⁺ and protein kinase Cδ activation. Active protein kinase Cδ promotes, by phosphorylation, the stabilization of p35, a cyclin-dependent kinase-5 (Cdk5) cofactor. Active p35/Cdk5 complex in the cytosol phosphorylates Nrf2 at Thr(395), Ser(433) and Thr(439) that is sufficient to promote Nrf2 translocation to the nucleus and induce the expression of antioxidant genes. Furthermore, this Cdk5-Nrf2 transduction pathway boosts glutathione metabolism in astrocytes efficiently protecting closely spaced neurons against oxidative damage. Thus, intercellular communication through NMDAR couples neurotransmission with neuronal survival.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bioenergetics and redox adaptations of astrocytes to neuronal activity.J Neurochem. 2016 Oct;139 Suppl 2(Suppl Suppl 2):115-125. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13486. Epub 2016 Mar 10. J Neurochem. 2016. PMID: 26968531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GSK-3beta down-regulates the transcription factor Nrf2 after oxidant damage: relevance to exposure of neuronal cells to oxidative stress.J Neurochem. 2008 Apr;105(1):192-202. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.05124.x. Epub 2007 Nov 13. J Neurochem. 2008. PMID: 18005231
-
Prolactin is an Endogenous Antioxidant Factor in Astrocytes That Limits Oxidative Stress-Induced Astrocytic Cell Death via the STAT3/NRF2 Signaling Pathway.Neurochem Res. 2024 Jul;49(7):1879-1901. doi: 10.1007/s11064-024-04147-3. Epub 2024 May 17. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 38755517 Free PMC article.
-
The presence of active Cdk5 associated with p35 in astrocytes and its important role in process elongation of scratched astrocyte.Glia. 2007 Apr 15;55(6):573-83. doi: 10.1002/glia.20485. Glia. 2007. PMID: 17295212
-
The Nrf2-ARE cytoprotective pathway in astrocytes.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2009 Jun 3;11:e17. doi: 10.1017/S1462399409001094. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2009. PMID: 19490732 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hippocampal neurons require a large pool of glutathione to sustain dendrite integrity and cognitive function.Redox Biol. 2018 Oct;19:52-61. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.08.003. Epub 2018 Aug 7. Redox Biol. 2018. PMID: 30107295 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms and Genetics of Oxidative Stress in Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2019;72(4):981-1017. doi: 10.3233/JAD-190863. J Alzheimers Dis. 2019. PMID: 31744008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Persistent Overexposure to N-Methyl-D-Aspartate (NMDA) Calcium-Dependently Downregulates Glutamine Synthetase, Aquaporin 4, and Kir4.1 Channel in Mouse Cortical Astrocytes.Neurotox Res. 2019 Jan;35(1):271-280. doi: 10.1007/s12640-018-9958-3. Epub 2018 Sep 15. Neurotox Res. 2019. PMID: 30220059 Free PMC article.
-
Antidepressants, sertraline and paroxetine, increase calcium influx and induce mitochondrial damage-mediated apoptosis of astrocytes.Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 14;8(70):115490-115502. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23302. eCollection 2017 Dec 29. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29383176 Free PMC article.
-
Intertwined ROS and Metabolic Signaling at the Neuron-Astrocyte Interface.Neurochem Res. 2021 Jan;46(1):23-33. doi: 10.1007/s11064-020-02965-9. Epub 2020 Jan 27. Neurochem Res. 2021. PMID: 31989468
References
-
- 1Bossy-Wetzel E, Schwarzenbacher R, Lipton SA. Molecular pathways to neurodegeneration. Nat Med 2004; 10: S2–S9. - PubMed
-
- 4Herrero-Mendez A, Almeida A, Fernandez E, Maestre C, Moncada S, Bolanos JP. The bioenergetic and antioxidant status of neurons is controlled by continuous degradation of a key glycolytic enzyme by APC/C-Cdh1. Nat Cell Biol 2009; 11: 747–752. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

