Interaction between innate immunity and Ro52-induced antibody causes Sjögren's syndrome-like disorder in mice
- PMID: 25906316
- PMCID: PMC4526450
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206297
Interaction between innate immunity and Ro52-induced antibody causes Sjögren's syndrome-like disorder in mice
Abstract
Objectives: Autoantibodies reactive with Ro52 are often found in sera of patients with Sjögren's syndrome (SS). This study was undertaken to investigate the role of Ro52-induced immune responses in pathogenesis of SS.
Methods: New Zealand Mixed (NZM) 2758 mice were immunised with Ro52 in alum adjuvant. Control mice were immunised either with maltose-binding protein or injected with alum alone. Mice were monitored for anti-Ro52 antibody, sialoadenitis and pilocarpine-induced salivation. Antibody binding to salivary gland (SG) cells was analysed in vivo and in vitro by immunofluorescence. Sera from immunised mice were passively transferred into untreated or alum injected NZM2758 mice.
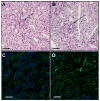
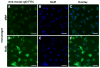
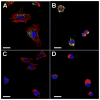
Results: By day 30 post-immunisation, Ro52 immunised mice generated immunoprecipitating anti-Ro52 antibodies and they had the maximum drop in saliva production. Both Ro52 immunised and control mice showed evidence of mild sialoadenitis. However, only Ro52 immunised mice had antibody deposition in their SG. Passive transfer of Ro52-immune sera induced SG dysfunction in recipient mice, only if the recipients were primed with alum. In vitro, antibodies from Ro52-immune sera were internalised by a SG cell line and this uptake was inhibited by cytochalasin D treatment.
Conclusions: Our data show for the first time that antibodies induced by Ro52 are capable of inducing SG dysfunction, and that this phenomenon is dependent on the activation of innate immunity. The mouse model described in this study implies that autoantibody deposition in the SG might be an important step in the induction of xerostomia and pathogenesis of SS.
Keywords: Autoantibodies; Autoimmunity; Sjögren's Syndrome.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/
Figures


Similar articles
-
Immune Response Targeting Sjögren's Syndrome Antigen Ro52 Suppresses Tear Production in Female Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 27;19(10):2935. doi: 10.3390/ijms19102935. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30261673 Free PMC article.
-
Immune response against the coiled coil domain of Sjögren's syndrome associated autoantigen Ro52 induces salivary gland dysfunction.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2018 May-Jun;36 Suppl 112(3):41-46. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29465352 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody deposition on vascular endothelial cells contributes to localized inflammation in salivary glands.J Oral Pathol Med. 2022 Aug;51(7):674-677. doi: 10.1111/jop.13330. Epub 2022 Jul 12. J Oral Pathol Med. 2022. PMID: 35766433 Free PMC article.
-
Autoantibodies in primary Sjögren's syndrome: new insights into mechanisms of autoantibody diversification and disease pathogenesis.Autoimmunity. 2001;34(2):123-32. doi: 10.3109/08916930109001960. Autoimmunity. 2001. PMID: 11905842 Review.
-
The role of M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor reactive T cells in Sjögren's syndrome: a critical review.J Autoimmun. 2014 Jun;51:44-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2013.12.012. Epub 2014 Jan 4. J Autoimmun. 2014. PMID: 24397962 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune Response Targeting Sjögren's Syndrome Antigen Ro52 Suppresses Tear Production in Female Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 27;19(10):2935. doi: 10.3390/ijms19102935. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30261673 Free PMC article.
-
The Toll-like Receptor 7-Mediated Ro52 Antigen-Presenting Pathway in the Salivary Gland Epithelial Cells of Sjögren's Syndrome.J Clin Med. 2023 Jun 30;12(13):4423. doi: 10.3390/jcm12134423. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37445456 Free PMC article.
-
Increased carotid intima-media thickening and antioxidized low-density lipoprotein in an anti-Ro60 SLE autoantibody subset.Front Lupus. 2023;1:1197309. doi: 10.3389/flupu.2023.1197309. Epub 2023 Sep 26. Front Lupus. 2023. PMID: 39055110 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical relevance of animal models in Sjögren's syndrome: the interferon signature from mouse to man.Arthritis Res Ther. 2015 Jul 3;17(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0678-2. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015. PMID: 26137972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LAMP3 induces apoptosis and autoantigen release in Sjögren's syndrome patients.Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 16;10(1):15169. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-71669-5. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32939030 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reksten TR, Jonsson MV. Sjögren’s syndrome: an update on epidemiology and current insights on pathophysiology. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2014;26:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Kyriakidis NC, Kapsogeorgou EK, Tzioufas AG. A comprehensive review of autoantibodies in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: Clinical phenotypes and regulatory mechanisms. J Autoimmunity. 2014;51:67–74. - PubMed
-
- Kong HJ, Anderson DE, Lee CH, Jang, et al. Cutting edge: autoantigen Ro52 is an interferon inducible E3 ligase that ubiquitinates IRF-8 and enhances cytokine expression in macrophages. J Immunol. 2007;179:26–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
