Neuronal polarization in the developing cerebral cortex
- PMID: 25904841
- PMCID: PMC4389351
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2015.00116
Neuronal polarization in the developing cerebral cortex
Abstract
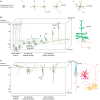
Cortical neurons consist of excitatory projection neurons and inhibitory GABAergic interneurons, whose connections construct highly organized neuronal circuits that control higher order information processing. Recent progress in live imaging has allowed us to examine how these neurons differentiate during development in vivo or in in vivo-like conditions. These analyses have revealed how the initial steps of polarization, in which neurons establish an axon, occur. Interestingly, both excitatory and inhibitory cortical neurons establish neuronal polarity de novo by undergoing a multipolar stage reminiscent of the manner in which polarity formation occurs in hippocampal neurons in dissociated culture. In this review, we focus on polarity formation in cortical neurons and describe their typical morphology and dynamic behavior during the polarization period. We also discuss cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying polarization, with reference to polarity formation in dissociated hippocampal neurons in vitro.
Keywords: axon; cerebral cortex; excitatory cortical neuron; imaging; inhibitory cortical neuron; neuron; polarization.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Excitatory cortical neurons with multipolar shape establish neuronal polarity by forming a tangentially oriented axon in the intermediate zone.Cereb Cortex. 2013 Jan;23(1):105-13. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhr383. Epub 2012 Jan 19. Cereb Cortex. 2013. PMID: 22267309
-
Neuronal Polarity in the Embryonic Mammalian Cerebral Cortex.Front Cell Neurosci. 2017 Jun 16;11:163. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2017.00163. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28670267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Formation of axon-dendrite polarity in situ: initiation of axons from polarized and non-polarized cells.Dev Growth Differ. 2012 Apr;54(3):398-407. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-169X.2012.01344.x. Dev Growth Differ. 2012. PMID: 22524609 Review.
-
Primary Culture of Dissociated Neurons from the Embryonic Cerebral Cortex.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2794:169-175. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3810-1_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38630228
-
Role of LKB1-SAD/MARK pathway in neuronal polarization.Dev Neurobiol. 2011 Jun;71(6):508-27. doi: 10.1002/dneu.20884. Dev Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21416623 Review.
Cited by
-
PDZ interaction of Vangl2 links PSD-95 and Prickle2 but plays only a limited role in the synaptic localisation of Vangl2.Sci Rep. 2015 Aug 10;5:12916. doi: 10.1038/srep12916. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26257100 Free PMC article.
-
Nestin Selectively Facilitates the Phosphorylation of the Lissencephaly-Linked Protein Doublecortin (DCX) by cdk5/p35 to Regulate Growth Cone Morphology and Sema3a Sensitivity in Developing Neurons.J Neurosci. 2020 May 6;40(19):3720-3740. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2471-19.2020. Epub 2020 Apr 9. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32273484 Free PMC article.
-
Igf1R/InsR function is required for axon extension and corpus callosum formation.PLoS One. 2019 Jul 18;14(7):e0219362. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0219362. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31318893 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant expression of LIMK1 impairs neuronal migration during neocortex development.Histochem Cell Biol. 2017 Apr;147(4):471-479. doi: 10.1007/s00418-016-1514-8. Epub 2016 Nov 14. Histochem Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 27844143
-
Axon-Targeting Motifs: Mechanisms and Applications of Enhancing Axonal Localisation of Transmembrane Proteins.Cells. 2022 Mar 9;11(6):937. doi: 10.3390/cells11060937. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35326388 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

