Inflammatory macrophages in pancreatic acinar cell metaplasia and initiation of pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 25897428
- PMCID: PMC4394130
- DOI: 10.18632/oncoscience.151
Inflammatory macrophages in pancreatic acinar cell metaplasia and initiation of pancreatic cancer
Abstract
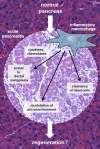
The roles of inflammatory macrophages in pancreatic tissue and the development of pancreatic cancer have not been well characterized. Recently it was shown that inflammatory macrophages, besides their function in clearing dead cells, also initiate pancreatic acinar cell metaplasia to duct-like progenitor cells. While in pancreatitis this is a reversible process, in context of an oncogenic stimulus this process is irreversible and can lead to the formation of precancerous lesions. Recent work now indicates that acquisition of an activating Kras mutation in acinar cells initiates signaling that leads to chemoattraction of M1-poliarized macrophages. This oncogene-caused chronic microinflammation can accelerate the pathogenesis of pancreatic cancers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The crosstalk between acinar cells with Kras mutations and M1-polarized macrophages leads to initiation of pancreatic precancerous lesions.Oncoimmunology. 2015 Mar 19;4(6):e1008794. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2015.1008794. eCollection 2015 Jun. Oncoimmunology. 2015. PMID: 26155420 Free PMC article.
-
Mutant KRAS-induced expression of ICAM-1 in pancreatic acinar cells causes attraction of macrophages to expedite the formation of precancerous lesions.Cancer Discov. 2015 Jan;5(1):52-63. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-14-0474. Epub 2014 Oct 31. Cancer Discov. 2015. PMID: 25361845 Free PMC article.
-
NFATc1 Links EGFR Signaling to Induction of Sox9 Transcription and Acinar-Ductal Transdifferentiation in the Pancreas.Gastroenterology. 2015 May;148(5):1024-1034.e9. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.01.033. Epub 2015 Jan 23. Gastroenterology. 2015. PMID: 25623042 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage-induced reactive oxygen species in the initiation of pancreatic cancer: a mini-review.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 21;15:1278807. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1278807. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38576613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The pancreatic duct cell: proliferative capabilities, specific characteristics, metaplasia, isolation, and culture.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1988 Jul-Aug;7(4):486-506. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1988. PMID: 2456383 Review.
Cited by
-
Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cells Regulate NLRP3 Activation to Generate a Tolerogenic Microenvironment.Cancer Res Commun. 2023 Sep 20;3(9):1899-1911. doi: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-23-0065. Cancer Res Commun. 2023. PMID: 37772994 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation and Wasting of Skeletal Muscles in Kras-p53-Mutant Mice with Intraepithelial Neoplasia and Pancreatic Cancer-When Does Cachexia Start?Cells. 2022 May 11;11(10):1607. doi: 10.3390/cells11101607. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35626644 Free PMC article.
-
Ibuprofen and diclofenac treatments reduce proliferation of pancreatic acinar cells upon inflammatory injury and mitogenic stimulation.Br J Pharmacol. 2018 Jan;175(2):335-347. doi: 10.1111/bph.13867. Epub 2017 Jun 16. Br J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28542719 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of differently polarized macrophages in the initiation and progressionof pancreatic cancer.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 11;14:1237711. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1237711. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37638028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophages and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2016 Oct 10;381(1):211-6. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.11.049. Epub 2015 Dec 18. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 26708507 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Forsmark CE. Management of chronic pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2013;144(6):1282–1291 e1283. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

