Hemispheric cortical dysplasia secondary to a mosaic somatic mutation in MTOR
- PMID: 25878179
- PMCID: PMC4442098
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000001594
Hemispheric cortical dysplasia secondary to a mosaic somatic mutation in MTOR
Abstract
Objective: To define causative somatic mutations in resected brain tissue from an infant with intractable epilepsy secondary to hemispheric cortical dysplasia.
Methods: Whole-exome sequencing was conducted on genomic DNA derived from both resected brain tissue and peripheral blood leukocytes. Comparison of the brain vs blood sequencing results was performed using bioinformatic methods designed to detect low-frequency genetic variation between tissue pairs.
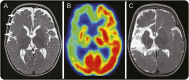
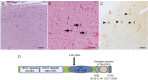
Results: Histopathology of the resected tissue showed dyslamination and dysmorphic neurons, but no balloon cells, consistent with focal cortical dysplasia type IIa. mTOR activation was observed by immunohistochemistry in the dysplasia. A missense mutation (c.4487T>G; p.W1456G) was detected in the FAT domain of MTOR in DNA from the dysplasia but not in lymphocytes. The mutation is predicted damaging (i.e., leading to mTOR activation) and was observed as a low-level mosaic with 8% of cells being heterozygous for the variant.
Conclusions: We report the novel finding of an MTOR mutation associated with nonsyndromic cortical dysplasia. Somatic-specific mutations in MTOR and related genes should be considered in a broader spectrum of patients with hemispheric malformations and more restricted forms of cortical dysplasia.
© 2015 American Academy of Neurology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cortical Dysplasia and the mTOR Pathway: How the Study of Human Brain Tissue Has Led to Insights into Epileptogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 25;23(3):1344. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031344. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain somatic mutations in MTOR cause focal cortical dysplasia type II leading to intractable epilepsy.Nat Med. 2015 Apr;21(4):395-400. doi: 10.1038/nm.3824. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Nat Med. 2015. PMID: 25799227
-
Somatic Mutations in the MTOR gene cause focal cortical dysplasia type IIb.Ann Neurol. 2015 Sep;78(3):375-86. doi: 10.1002/ana.24444. Epub 2015 Jul 3. Ann Neurol. 2015. PMID: 26018084
-
Association of MTOR Mutations With Developmental Brain Disorders, Including Megalencephaly, Focal Cortical Dysplasia, and Pigmentary Mosaicism.JAMA Neurol. 2016 Jul 1;73(7):836-845. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2016.0363. JAMA Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27159400 Free PMC article.
-
mTOR signaling in epilepsy: insights from malformations of cortical development.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2015 Apr 1;5(4):a022442. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a022442. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2015. PMID: 25833943 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cortical Dysplasia and the mTOR Pathway: How the Study of Human Brain Tissue Has Led to Insights into Epileptogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 25;23(3):1344. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031344. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypervascularization in mTOR-dependent focal and global cortical malformations displays differential rapamycin sensitivity.Epilepsia. 2019 Jun;60(6):1255-1265. doi: 10.1111/epi.15969. Epub 2019 May 24. Epilepsia. 2019. PMID: 31125447 Free PMC article.
-
Brain Tissue Low-Level Mosaicism for MTOR Mutation Causes Smith-Kingsmore Phenotype with Recurrent Hypoglycemia-A Novel Phenotype and a Further Proof for Testing of an Affected Tissue.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Jul 15;11(7):1269. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11071269. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34359351 Free PMC article.
-
CfDNA Measurement as a Diagnostic Tool for the Detection of Brain Somatic Mutations in Refractory Epilepsy.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 28;23(9):4879. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094879. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
mTOR Pathway Somatic Pathogenic Variants in Focal Malformations of Cortical Development: Novel Variants, Topographic Mapping, and Clinical Outcomes.Neurol Genet. 2023 Oct 26;9(6):e200103. doi: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000200103. eCollection 2023 Dec. Neurol Genet. 2023. PMID: 37900581 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen J, Tsai V, Parker WE, Aronica E, Baybis M, Crino PB. Detection of human papillomavirus in human focal cortical dysplasia type IIB. Ann Neurol 2012;72:881–892. - PubMed
-
- Leventer RJ, Jansen FE, Mandelstam SA, et al. Is focal cortical dysplasia sporadic? Family evidence for genetic susceptibility. Epilepsia 2014;55:e22–e26. - PubMed
-
- Crino PB. mTOR: a pathogenic signaling pathway in developmental brain malformations. Trends Mol Med 2011;17:734–742. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
