Hypoxia down-regulates expression of secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor in bronchial epithelial cells via TGF-β1
- PMID: 25851169
- PMCID: PMC4379733
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-015-0016-0
Hypoxia down-regulates expression of secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor in bronchial epithelial cells via TGF-β1
Abstract
Background: Secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor (SLPI) is a protein with anti-protease and antimicrobial properties that is constitutively secreted from the airway epithelium. The importance of maintaining a balance between proteases and anti-proteases, and robust innate defence mechanisms in the airways, is exemplified by inflammatory lung conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and cystic fibrosis (CF). Both conditions present with a high protease burden in the airways which leads to tissue destruction. These patients also have an impaired innate immune system in the lungs with bacterial colonization and frequent airway infections. Moreover, both diseases are associated with airway hypoxia due to inflammation and mucus plugs. The aim of the present study was to investigate the role of hypoxia on SLPI production from the airway epithelium.
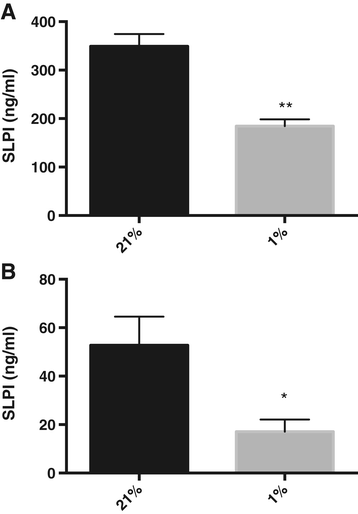
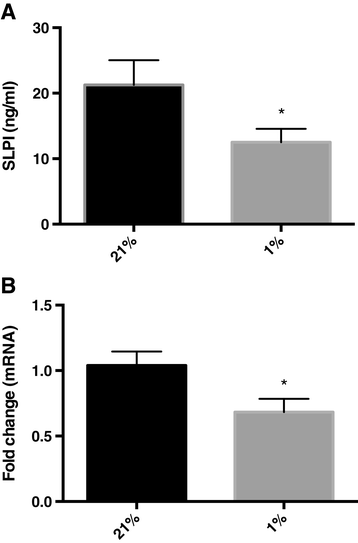
Methods: Primary human bronchial epithelial cells were grown in sub-immersed cultures or as differentiated epithelium in air liquid interface cultures. Cells were incubated at 21% O2 (normoxia) or 1% O2 (hypoxia), and the release of SLPI was analysed with ELISA. RT-PCR was used to study the expression of SLPI and transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1).
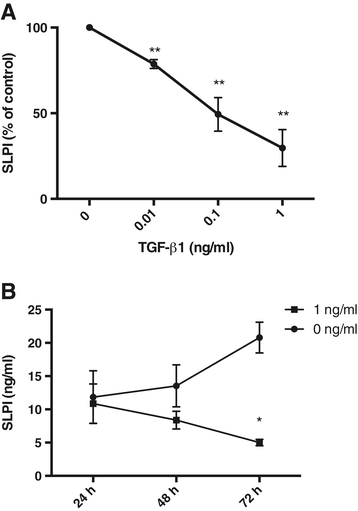
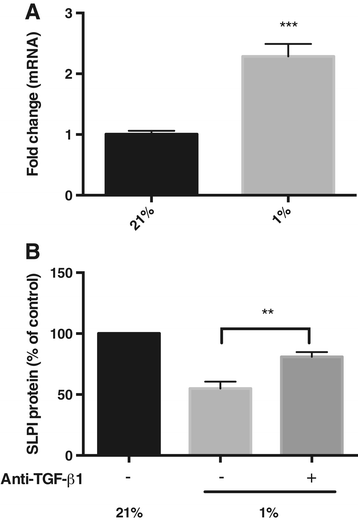
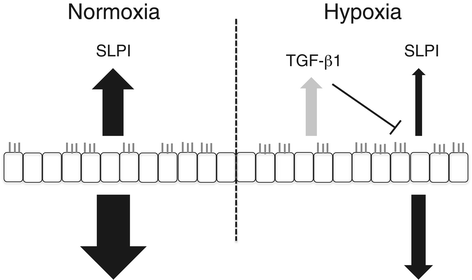
Results: Hypoxia decreased the constitutive production of SLPI by bronchial epithelial cells. The multifunctional cytokine TGF-β1, which is known to affect SLPI expression, showed increased expression in hypoxic bronchial epithelial cells. When bronchial epithelial cells were exposed to exogenous TGF-β1 during normoxia, the SLPI production was down-regulated. Addition of TGF-β1-neutralizing antibodies partially restored SLPI production during hypoxia, showing that TGF-β1 is an important regulator of SLPI during hypoxic conditions.
Conclusions: The mechanism described here adds to our knowledge of the pathogenesis of severe pulmonary diseases associated with hypoxia, e.g. COPD and CF. The hypoxic down-regulation of SLPI may help explain the protease/anti-protease imbalance associated with these conditions and vulnerability to airway infections. Furthermore, it provides an interesting target for the treatment and prevention of exacerbation in these patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transforming growth factor-beta1 is a potent inhibitor of secretory leukoprotease inhibitor expression in a bronchial epithelial cell line. Munich Lung Transplant Group.Eur Respir J. 2000 Jun;15(6):1052-7. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-3003.2000.01513.x. Eur Respir J. 2000. PMID: 10885424
-
[Expression of secretory leukocyte proteinase inhibitor in human bronchial epithelial cell is downregulated by transforming growth factor-beta1/Smads pathway].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2008 Aug 5;88(30):2117-21. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2008. PMID: 19080472 Chinese.
-
Effect of TGF-β on ocular surface epithelial cells.Exp Eye Res. 2013 Feb;107:88-100. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2012.11.017. Epub 2012 Dec 7. Exp Eye Res. 2013. PMID: 23220729
-
Secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor (SLPI), a multifunctional protein in the host defense response.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016 Apr;28:79-93. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2015.12.001. Epub 2015 Dec 15. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016. PMID: 26718149 Review.
-
Secretory leukocyte peptidase inhibitor and lung cancer.Cancer Sci. 2008 May;99(5):849-55. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.00772.x. Cancer Sci. 2008. PMID: 18380788 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
16S Metagenomics Reveals Dysbiosis of Nasal Core Microbiota in Children With Chronic Nasal Inflammation: Role of Adenoid Hypertrophy and Allergic Rhinitis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Sep 2;10:458. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00458. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32984078 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Early Nasopharyngeal Immune Markers With COVID-19 Clinical Outcome: Predictive Value of CCL2/MCP-1.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2020 Sep 3;7(10):ofaa407. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofaa407. eCollection 2020 Oct. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 33123608 Free PMC article.
-
Consecutive Hypoxia Decreases Expression of NOTCH3, HEY1, CC10, and FOXJ1 via NKX2-1 Downregulation and Intermittent Hypoxia-Reoxygenation Increases Expression of BMP4, NOTCH1, MKI67, OCT4, and MUC5AC via HIF1A Upregulation in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Sep 4;8:572276. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.572276. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33015064 Free PMC article.
-
The secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor (SLPI) in pathophysiology of non-communicable diseases: Evidence from experimental studies to clinical applications.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 17;10(2):e24550. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24550. eCollection 2024 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38312697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TGF-β1 Impairs Vitamin D-Induced and Constitutive Airway Epithelial Host Defense Mechanisms.J Innate Immun. 2020;12(1):74-89. doi: 10.1159/000497415. Epub 2019 Apr 10. J Innate Immun. 2020. PMID: 30970352 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

