T cell PKCδ kinase inactivation induces lupus-like autoimmunity in mice
- PMID: 25829232
- PMCID: PMC4464903
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clim.2015.03.017
T cell PKCδ kinase inactivation induces lupus-like autoimmunity in mice
Abstract
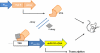
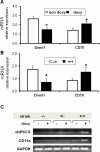
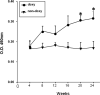
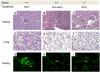
Genetic and environmental factors contribute to the onset and progression of lupus. CD4+ T cells from patients with active lupus show a decreased ERK signaling pathway, which causes changes in gene expression. The defect points to its upstream regulator, PKCδ, which exhibits a deficient activity due to oxidative stress. Our aim was to investigate the effect of a defective PKCδ in the development of lupus. We generated a double transgenic C57BL6 × SJL mouse that expresses a doxycycline-induced dominant negative PKCδ (dnPKCδ) in T cells. The transgenic mice displayed decreased T cell ERK signaling, decreased DNMT1 expression and overexpression of methylation sensitive genes involved in the exaggerated immune response in the pathogenesis of lupus. The mice developed anti-dsDNA autoantibodies and glomerulonephritis with IgG deposition. The study indicates common pathogenic mechanisms with human lupus, suggesting that environmentally-mediated T cell PKCδ inactivation plays a causative role in lupus.
Keywords: Autoimmunity; Extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK); Lupus; PKCδ; T cells; Transgenic mouse model.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
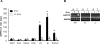


Similar articles
-
Impaired T cell protein kinase C delta activation decreases ERK pathway signaling in idiopathic and hydralazine-induced lupus.J Immunol. 2007 Oct 15;179(8):5553-63. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.8.5553. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17911642
-
Defective T-cell ERK signaling induces interferon-regulated gene expression and overexpression of methylation-sensitive genes similar to lupus patients.Genes Immun. 2008 Jun;9(4):368-78. doi: 10.1038/gene.2008.29. Genes Immun. 2008. PMID: 18523434 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase Cδ oxidation contributes to ERK inactivation in lupus T cells.Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Sep;64(9):2964-74. doi: 10.1002/art.34503. Arthritis Rheum. 2012. PMID: 22549474 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation and the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus.Transl Res. 2009 Jan;153(1):4-10. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2008.10.007. Epub 2008 Nov 14. Transl Res. 2009. PMID: 19100952 Review.
-
Key role of ERK pathway signaling in lupus.Autoimmunity. 2010 Feb;43(1):17-22. doi: 10.3109/08916930903374832. Autoimmunity. 2010. PMID: 19961364 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Oxidative Stress in Epigenetic Changes Underlying Autoimmunity.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022 Mar;36(7-9):423-440. doi: 10.1089/ars.2021.0066. Epub 2022 Jan 4. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022. PMID: 34544258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Actin reorganization at the centrosomal area and the immune synapse regulates polarized secretory traffic of multivesicular bodies in T lymphocytes.J Extracell Vesicles. 2020 Jun 19;9(1):1759926. doi: 10.1080/20013078.2020.1759926. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020. PMID: 32939232 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Phosphatase 5 Contributes to the Overexpression of Epigenetically Regulated T-Lymphocyte Genes in Patients with Lupus.Lupus (Los Angel). 2016 Dec;1(3):120. Epub 2016 Dec 30. Lupus (Los Angel). 2016. PMID: 28239687 Free PMC article.
-
Characterisation of an epigenetically altered CD4(+) CD28(+) Kir(+) T cell subset in autoimmune rheumatic diseases by multiparameter flow cytometry.Lupus Sci Med. 2016 Apr 4;3(1):e000147. doi: 10.1136/lupus-2016-000147. eCollection 2016. Lupus Sci Med. 2016. PMID: 27099767 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Reprogramming in Naive CD4+ T Cells Favoring T Cell Activation and Non-Th1 Effector T Cell Immune Response as an Early Event in Lupus Flares.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016 Sep;68(9):2200-9. doi: 10.1002/art.39720. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 27111767 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Richardson B. Effect of an inhibitor of DNA methylation on T cells. II. 5-Azacytidine induces self-reactivity in antigen-specific T4+ cells. Hum Immunol. 1986;17:456–70. - PubMed
-
- Richardson B, Scheinbart L, Strahler J, Gross L, Hanash S, Johnson M. Evidence for impaired T cell DNA methylation in systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990;33:1665–73. - PubMed
-
- Yung RL, Richardson BC. Drug-induced lupus. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1994;20:61–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

