Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, and Safety of Lisinopril in Pediatric Kidney Transplant Patients: Implications for Starting Dose Selection
- PMID: 25807932
- PMCID: PMC4536255
- DOI: 10.1002/cpt.127
Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, and Safety of Lisinopril in Pediatric Kidney Transplant Patients: Implications for Starting Dose Selection
Abstract
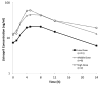
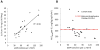
Hypertension in pediatric kidney transplant recipients contributes to long-term graft loss, yet treatment options--including angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors--are poorly characterized in this vulnerable population. We conducted a multicenter, open-label pharmacokinetic (PK) study of daily oral lisinopril in 22 children (ages 7-17 years) with stable kidney transplant function. Standard noncompartmental PK analyses were performed at steady state. Effects on blood pressure were examined in lisinopril-naïve patients (n = 13). Oral clearance declined in proportion to underlying kidney function; however, in patients with low estimated glomerular filtration rate (30-59 ml/min per 1.73m(2)), exposure (standardized to 0.1 mg/kg/day dose) was within the range reported previously in children without a kidney transplant. In lisinopril-naïve patients, 85% and 77% had a ≥ 6 mmHg reduction in systolic and diastolic blood pressure, respectively. Lisinopril was well tolerated. Our study provides initial insight on lisinopril use in children with a kidney transplant, including starting dose considerations.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01491919.
© 2015 American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Frymoyer received support from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD; 1K23HD079557 and HSSN275000002). Drs. Anand and Lewandowski receive support from Government Contract HHSN267200700051C (PI: Benjamin). Dr. Patel received support for research from NICHD contract HHSN27500007 and from industry for drug development in adults and children with kidney disease (
Figures
Similar articles
-
Placebo effect and efficacy of nebivolol in patients with hypertension not controlled with lisinopril or losartan: a phase IV, randomized, placebo-controlled trial.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2013 Apr;13(2):129-40. doi: 10.1007/s40256-013-0010-y. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23519546 Clinical Trial.
-
Sustained improvement of renal graft function for two years in hypertensive renal transplant recipients treated with nifedipine as compared to lisinopril.Transplantation. 2001 Dec 15;72(11):1787-92. doi: 10.1097/00007890-200112150-00013. Transplantation. 2001. PMID: 11740389 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of manidipine and its combination with an ACE inhibitor on insulin sensitivity and metabolic, inflammatory and prothrombotic markers in hypertensive patients with metabolic syndrome: the MARCADOR study.Clin Drug Investig. 2011;31(3):201-12. doi: 10.2165/11587590-000000000-00000. Clin Drug Investig. 2011. PMID: 21155616 Clinical Trial.
-
Lisinopril. A review of its pharmacology and clinical efficacy in the early management of acute myocardial infarction.Drugs. 1996 Oct;52(4):564-88. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199652040-00011. Drugs. 1996. PMID: 8891468 Review.
-
Lisinopril. A review of its pharmacology and clinical efficacy in elderly patients.Drugs Aging. 1997 Feb;10(2):131-66. doi: 10.2165/00002512-199710020-00006. Drugs Aging. 1997. PMID: 9061270 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in Pediatric Pharmacology, Therapeutics, and Toxicology.Adv Pediatr. 2016 Aug;63(1):227-54. doi: 10.1016/j.yapd.2016.04.015. Adv Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 27426903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of ACE Inhibitors and AT1R Antagonists with Regard to Their Effect on ACE2 Expression and Infection with SARS-CoV-2 Using a Caco-2 Cell Model.Life (Basel). 2021 Aug 10;11(8):810. doi: 10.3390/life11080810. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34440554 Free PMC article.
-
Should ACE inhibitors or calcium channel blockers be used for post-transplant hypertension?Pediatr Nephrol. 2021 Mar;36(3):539-549. doi: 10.1007/s00467-020-04485-8. Epub 2020 Feb 14. Pediatr Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 32060819
-
Dosing Recommendations for Pediatric Patients With Renal Impairment.J Clin Pharmacol. 2020 Dec;60(12):1551-1560. doi: 10.1002/jcph.1676. Epub 2020 Jun 15. J Clin Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32542790 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world evidence of lisinopril in pediatric hypertension and nephroprotective management: a 10-year cohort study.Pediatr Nephrol. 2025 Mar;40(3):797-809. doi: 10.1007/s00467-024-06531-1. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Pediatr Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39466390
References
-
- Mitsnefes MM, Khoury PR, McEnery PT. Early post-transplantation hypertension and poor long-term renal allograft survival in pediatric patients. J Pediatr. 2003;143:98–103. - PubMed
-
- Silverstein DM, LeBlanc P, Hempe JM, Ramcharan T, Boudreaux JP. Tracking of blood pressure and its impact on graft function in pediatric renal transplant recipients. J Pediatr Transplant. 2007;11:860–867. - PubMed
-
- Mitsnefes MM, Omoloja A, McEnery PT. Short-term pediatric renal transplant survival: blood pressure and allograft function. Pediatr Transplant. 2001;5:160–165. - PubMed
-
- Cross NB, Webster AC, Masson P, O’Connell PJ, Craig JC. Antihypertensives for kidney transplant recipients: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Transplantation. 2009;88:7–18. - PubMed
-
- Nielsen SE, et al. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalcin (NGAL) and kidney injury molecule 1 (KIM1) in patients with diabetic nephropathy: a cross-sectional study and the effects of lisinopril. Diabet Med. 2010;27:1144–1150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

