Stress granules regulate double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase activation through a complex containing G3BP1 and Caprin1
- PMID: 25784705
- PMCID: PMC4453520
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.02486-14
Stress granules regulate double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase activation through a complex containing G3BP1 and Caprin1
Abstract
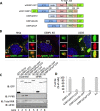
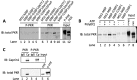
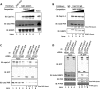
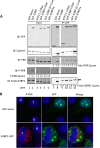
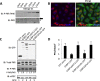
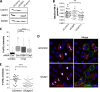
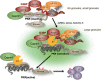
Stress granules (SGs) are dynamic cytoplasmic repositories containing translationally silenced mRNAs that assemble upon cellular stress. We recently reported that the SG nucleating protein G3BP1 promotes antiviral activity and is essential in double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR) recruitment to stress granules, thereby driving phosphorylation of the α subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF2α). Here, we delineate the mechanism for SG-dependent PKR activation. We show that G3BP1 and inactive PKR directly interact with each other, dependent on both the NTF2-like and PXXP domains of G3BP1. The G3BP1-interacting protein Caprin1 also directly interacts with PKR, regulates efficient PKR activation at the stress granule, and is also integral for the release of active PKR into the cytoplasm to engage in substrate recognition. The G3BP1-Caprin1-PKR complex represents a new mode of PKR activation and is important for antiviral activity of G3BP1 and PKR during infection with mengovirus. Our data links stress responses and their resultant SGs with innate immune activation through PKR without a requirement for foreign double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) pattern recognition.
Importance: Our previous work indicates that stress granules have antiviral activity and mediate innate immunity through functions of G3BP1; however, the mechanistic details of these functions were not resolved. We show that much of the antiviral activity of stress granules is contingent on the function of PKR in a complex with G3BP1 and Caprin1. The PKR-G3BP1-Caprin1 complex undergoes dynamic transitioning within and outside stress granules to accomplish PKR activation and translational repression. This mechanism appears to function distinctly from canonical pattern recognition of double-stranded RNA by PKR. Therefore, this mechanism bridges the stress response with innate immunity, allowing the cell to respond to many cellular stressors and amplify the pathogen pattern recognition systems of innate immunity.
Copyright © 2015 Reineke et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The stress granule protein G3BP1 recruits protein kinase R to promote multiple innate immune antiviral responses.J Virol. 2015 Mar;89(5):2575-89. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02791-14. Epub 2014 Dec 17. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25520508 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse Norovirus Infection Arrests Host Cell Translation Uncoupled from the Stress Granule-PKR-eIF2α Axis.mBio. 2019 Jun 18;10(3):e00960-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00960-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31213553 Free PMC article.
-
RNase L Amplifies Interferon Signaling by Inducing Protein Kinase R-Mediated Antiviral Stress Granules.J Virol. 2020 Jun 16;94(13):e00205-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00205-20. Print 2020 Jun 16. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32295917 Free PMC article.
-
A closer look at mammalian antiviral condensates.Biochem Soc Trans. 2024 Jun 26;52(3):1393-1404. doi: 10.1042/BST20231296. Biochem Soc Trans. 2024. PMID: 38778761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral proteins targeting host protein kinase R to evade an innate immune response: a mini review.Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2018 Apr;34(1):33-59. doi: 10.1080/02648725.2018.1467151. Epub 2018 May 2. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2018. PMID: 29716441 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of the Ubiquitin System in Stress Granule Metabolism.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 26;23(7):3624. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073624. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35408984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Organellar homeostasis and innate immune sensing.Nat Rev Immunol. 2022 Sep;22(9):535-549. doi: 10.1038/s41577-022-00682-8. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Nat Rev Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35197578 Review.
-
Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus Leader Protease Cleaves G3BP1 and G3BP2 and Inhibits Stress Granule Formation.J Virol. 2019 Jan 4;93(2):e00922-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00922-18. Print 2019 Jan 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30404792 Free PMC article.
-
TDRD3 is an antiviral restriction factor that promotes IFN signaling with G3BP1.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Jan 27;18(1):e1010249. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010249. eCollection 2022 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 35085371 Free PMC article.
-
The multi-functional reovirus σ3 protein is a virulence factor that suppresses stress granule formation and is associated with myocardial injury.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Jul 8;17(7):e1009494. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009494. eCollection 2021 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 34237110 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Solomon S, Xu Y, Wang B, David MD, Schubert P, Kennedy D, Schrader JW. 2007. Distinct structural features of Caprin-1 mediate its interaction with G3BP-1 and its induction of phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2, entry to cytoplasmic stress granules, and selective interaction with a subset of mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol 27:2324–2342. doi:10.1128/MCB.02300-06. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA125123/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HD007495/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM111700/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD007495/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI050237/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD007495/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA125123/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI050237/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056338/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA168872/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK56338/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AI50237/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA168872/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- GM111700-01/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HD007495/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
